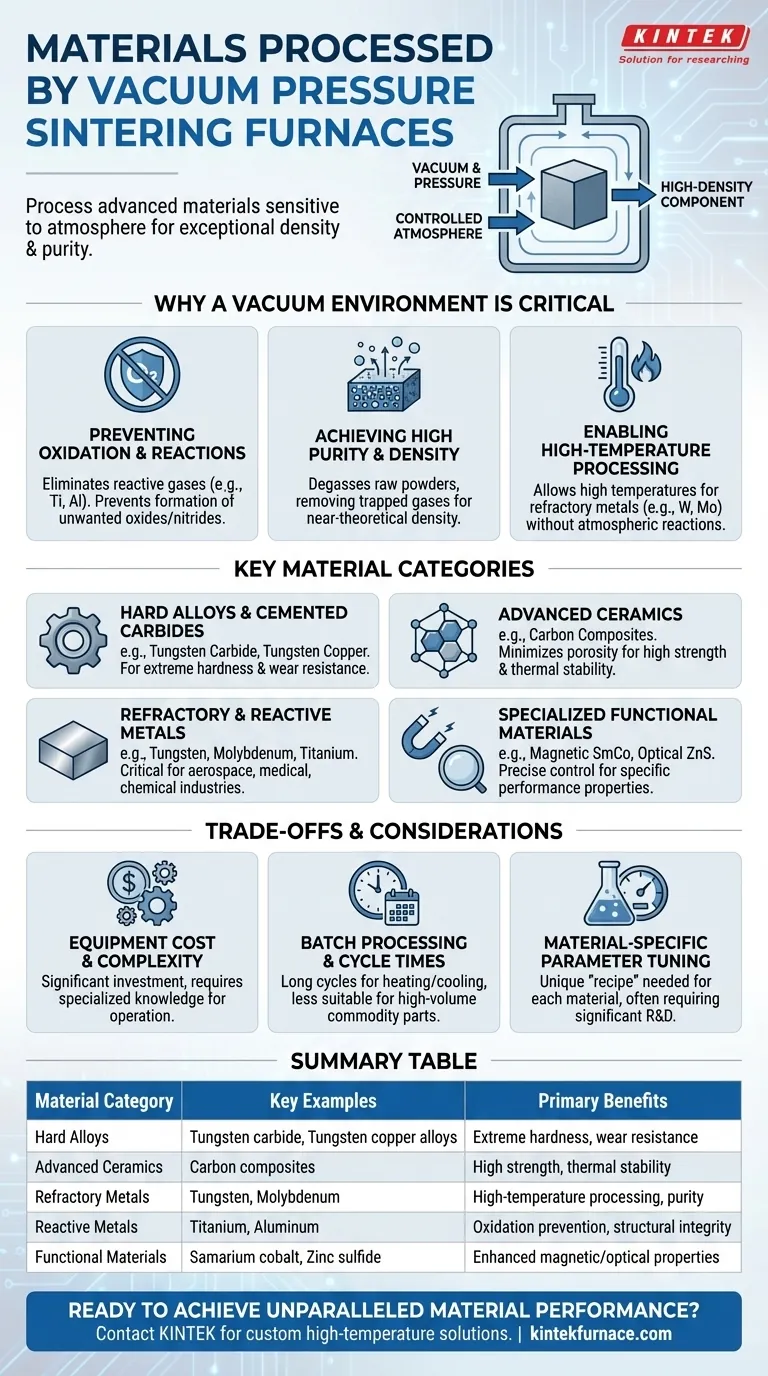
At its core, a vacuum pressure sintering furnace can process a wide range of advanced materials that are either sensitive to atmospheric gases or require exceptional density and purity. This includes categories like hard alloys, advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and certain magnetic and optical materials.
The fundamental advantage of this technology isn't just the materials it can process, but the properties it can achieve. By precisely controlling the atmosphere and applying pressure, these furnaces create highly dense, pure, and strong components that are impossible to produce with conventional sintering methods.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
The defining feature of this process is the removal of atmospheric gases. This seemingly simple step has profound implications for the final material properties.
Preventing Oxidation and Reactions
Many advanced materials, particularly metals like titanium (Ti) and aluminum (Al), are highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen, especially at the high temperatures required for sintering.
A vacuum environment eliminates these reactive gases, preventing the formation of unwanted oxides or nitrides that would degrade the material's structural integrity and performance.
Achieving High Purity and Density
The vacuum helps to degas the raw material powders, pulling out trapped or adsorbed gases. This outgassing is crucial for preventing contamination and internal porosity.
By removing these gases before applying pressure, the process can achieve near-theoretical density, resulting in components with superior strength and durability.
Enabling High-Temperature Processing
Refractory metals like tungsten (W) and molybdenum (Mo) have extremely high melting points.
Sintering them in a vacuum allows for the necessary high temperatures without the risk of atmospheric reactions, which is essential for creating high-purity parts from these challenging metals.
A Breakdown of Key Material Categories
While the principles are universal, the applications are diverse. These furnaces are tailored to create specific high-performance materials across several industries.
Hard Alloys and Cemented Carbides
These furnaces are extensively used for materials like tungsten carbide and tungsten copper alloys.
The combination of vacuum and pressure ensures the complete densification required for the extreme hardness and wear resistance needed in cutting tools, dies, and armor.
Advanced and High-Strength Ceramics
Technical ceramics, including carbon composite materials, benefit greatly from this process.
Vacuum pressure sintering minimizes porosity and grain growth, leading to ceramic components with exceptional strength and thermal stability for aerospace and industrial applications.
Refractory and Reactive Metals
This technology is the gold standard for processing metals that cannot tolerate air at high temperatures.
This includes refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, as well as reactive metals such as titanium, which are critical for aerospace, medical, and chemical processing industries.
Specialized Functional Materials
The precise control offered by these furnaces is ideal for materials with specific functional properties.
This includes magnetic materials like samarium cobalt (SmCo) and aluminum nickel cobalt (AlNiCo), as well as infrared optical materials like zinc sulfide (ZnS) and zinc selenide (ZnSe), where purity and density directly impact performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum pressure sintering is a specialized process with important considerations. It is not a universal solution for all manufacturing needs.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum pressure furnaces are significant capital investments. They are complex systems requiring specialized knowledge for operation, maintenance, and safety protocol adherence.
Batch Processing and Cycle Times
Unlike some continuous manufacturing processes, sintering is a batch process. Cycle times can be long due to the need to achieve a high vacuum, heat up, apply pressure, and cool down, making it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost commodity parts.
Material-Specific Parameter Tuning
This is not a "set it and forget it" technology. Each material requires a unique and precisely developed "recipe" of temperature, pressure, vacuum level, and time to achieve the desired properties. Significant R&D may be required to optimize the process for a new material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum pressure sintering should be driven by the non-negotiable requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation: This process is essential for achieving high performance in reactive materials like titanium, aluminum, and certain specialty alloys.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: This method is unparalleled for creating high-performance ceramics and hardmetals that are nearly free of porosity.
- If your primary focus is exceptional purity: The clean vacuum environment is critical for producing materials used in demanding electronic, optical, or medical applications.
Ultimately, vacuum pressure sintering is the key to unlocking the full potential of today's most advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Alloys | Tungsten carbide, Tungsten copper alloys | Extreme hardness, wear resistance |
| Advanced Ceramics | Carbon composites | High strength, thermal stability |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | High-temperature processing, purity |
| Reactive Metals | Titanium, Aluminum | Oxidation prevention, structural integrity |
| Functional Materials | Samarium cobalt, Zinc sulfide | Enhanced magnetic/optical properties |
Ready to achieve unparalleled material performance? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum pressure sintering furnaces can enhance your material processing and deliver superior results for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability



















