In short, vacuum annealing furnaces can process a wide range of materials, primarily those sensitive to surface reactions. This includes metals like steel, stainless steel, and titanium alloys; electronic components such as semiconductors; and special materials including rare earth metals and advanced ceramics. The common thread is the need to prevent oxidation and contamination during heat treatment.
The critical factor is not just the material itself, but its sensitivity to the atmosphere at high temperatures. Vacuum annealing is the definitive solution for materials where a pristine, oxide-free surface is essential for performance, appearance, or subsequent processing.

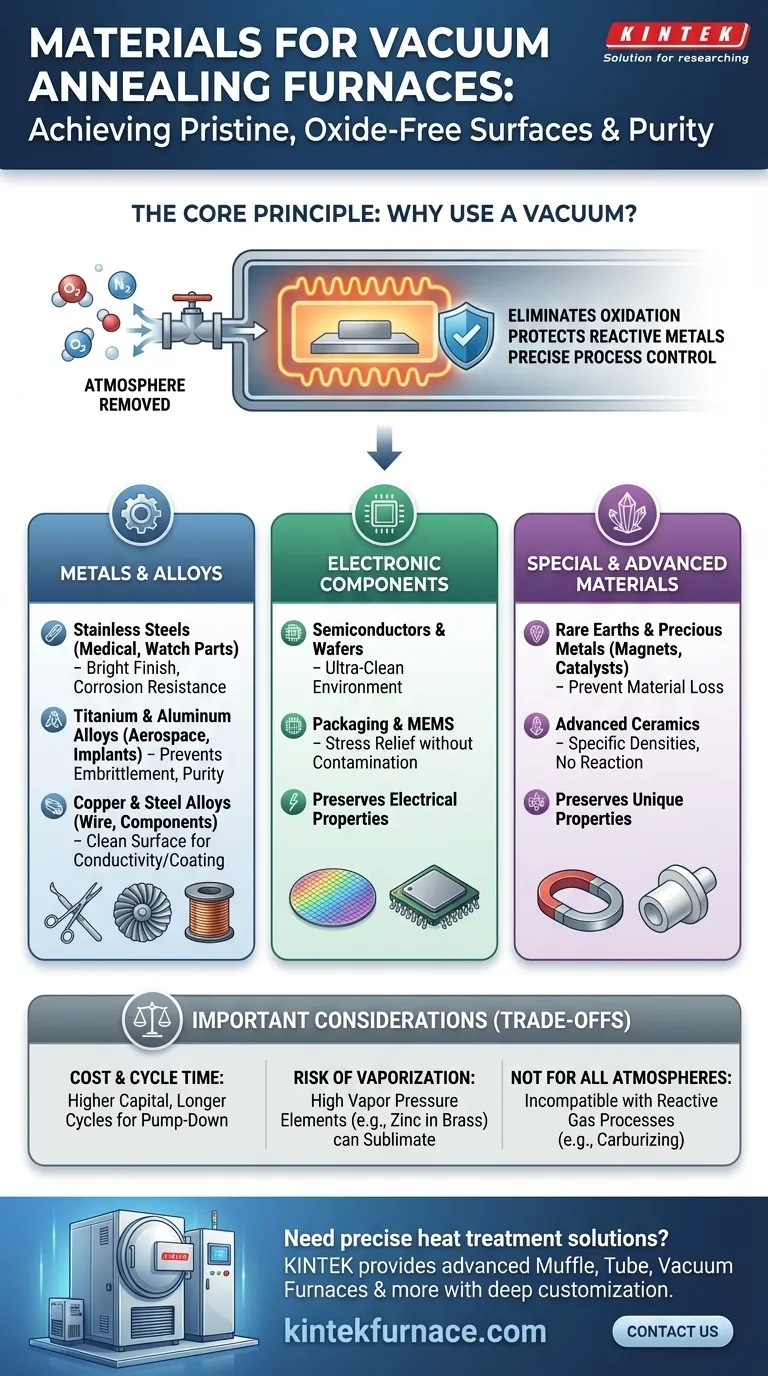
The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need to control the material's environment. By removing air and other gases, the process fundamentally prevents unwanted chemical reactions that occur in traditional atmospheric furnaces.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The primary purpose of the vacuum is to remove oxygen. At elevated annealing temperatures, oxygen aggressively reacts with most metals, forming a layer of oxide scale on the surface.
This oxidation is often undesirable, as it can alter dimensions, inhibit subsequent processes like brazing or welding, and tarnish the final appearance. Vacuum annealing produces a clean, "bright" finish that often eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning like acid pickling.
Protecting Reactive and High-Purity Metals
Some materials are exceptionally reactive. Metals like titanium, aluminum, and rare earths will readily react with not just oxygen, but also nitrogen and other trace gases at high temperatures.
For these materials, a vacuum is not just beneficial—it is essential to preserve their chemical and mechanical properties. A high-purity vacuum environment is the only way to anneal them without causing significant degradation.
Achieving Precise Process Control
Modern vacuum furnaces offer unparalleled control. The system uses a combination of mechanical and high-vacuum pumps to achieve the required pressure level, while sophisticated control systems (PID/PLC) precisely manage heating and cooling cycles.
This controlled environment ensures that processes like stress relief, recrystallization annealing, and solid solution treatment are highly repeatable and meet exact specifications.
Key Material Categories and Applications
The principles of vacuum annealing apply across several major industrial categories. Each uses the process to solve a specific material challenge.
Metals and Alloys
This is the most common application. The goal is typically to soften the metal, improve its ductility, and relieve internal stresses while maintaining a clean surface.
- Stainless Steels: Used for bright annealing of medical devices, deep-drawn parts (like sinks and plumbing fixtures), and precision watch components. The vacuum prevents surface oxidation, preserving the material's inherent corrosion resistance and aesthetic.
- Titanium and Aluminum Alloys: Critical for aerospace and medical implant applications where material purity and performance are non-negotiable. The vacuum protects these highly reactive metals from embrittlement.
- Copper and Steel Alloys: Used to anneal components after heavy cold-working. For copper, a clean surface is vital for electrical conductivity. For specialty steels, it ensures a defect-free surface for subsequent cutting or coating.
Electronic Components
The electronics industry relies on extreme purity. Even microscopic contamination can lead to device failure.
- Semiconductors and Packaging: Vacuum annealing is used to treat silicon wafers and other components in an ultra-clean environment. This removes stresses induced during manufacturing without introducing contaminants that could alter the material's electrical properties.
Special and Advanced Materials
This category includes high-value materials where preserving their unique properties is paramount.
- Rare Earths and Precious Metals: These materials are often used in high-performance magnets and catalysts. Vacuum processing is essential to prevent the loss of valuable material and protect their specific magnetic or chemical characteristics.
- Advanced Ceramics: Certain technical ceramics are processed in a vacuum to achieve specific densities and properties without reacting with atmospheric gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum annealing is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations.
Cost and Cycle Time
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and have a higher capital cost than conventional atmospheric furnaces. The process cycle can also be longer due to the time required to pump the chamber down to the target vacuum level before heating can begin.
Risk of Vaporization
Under very low pressures and high temperatures, certain elements with high vapor pressure can "boil off" or sublimate from the surface of an alloy. For example, processing brass (a copper-zinc alloy) in a hard vacuum can lead to dezincification, altering the alloy's composition. This requires careful process control and pressure management.
Not Ideal for All Atmospheres
Some heat treatment processes, like carburizing or nitriding, fundamentally require the presence of a specific reactive gas atmosphere to diffuse carbon or nitrogen into the steel's surface. These processes are, by definition, incompatible with a vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on your material's properties and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and purity: Vacuum annealing is the superior choice for reactive metals (titanium), medical-grade stainless steel, and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is simple stress relief on non-reactive steels: A more conventional and cost-effective atmospheric furnace may be sufficient for the task.
- If you are working with high-value or highly sensitive materials: The precise control and clean environment of vacuum annealing are essential to protect your material and guarantee its final performance.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select a process based on the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metals and Alloys | Stainless steel, titanium alloys, copper | Prevents oxidation, maintains surface finish, improves ductility |
| Electronic Components | Semiconductors, silicon wafers | Ensures ultra-clean environment, protects electrical properties |
| Special Materials | Rare earth metals, advanced ceramics | Preserves unique properties, prevents contamination |
Need precise heat treatment solutions for reactive metals or electronics? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental requirements are met with reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and protect your valuable materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















