At its core, a box-type resistance furnace is constructed from three primary categories of materials. The outer structure is built from welded angle steel and steel plates for rigidity, the internal chamber is lined with refractory materials like ceramic fiber to contain heat, and critical components in the hot zone may use high-temperature alloy steels to withstand thermal stress.
The selection of materials for a furnace is not about finding a single best substance, but about engineering a layered system. Each material is chosen for its specific role in managing either structural load at low temperatures or extreme heat in the core, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
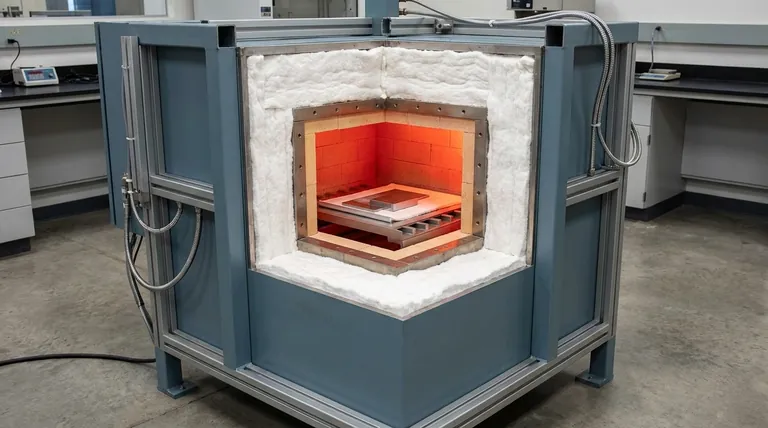

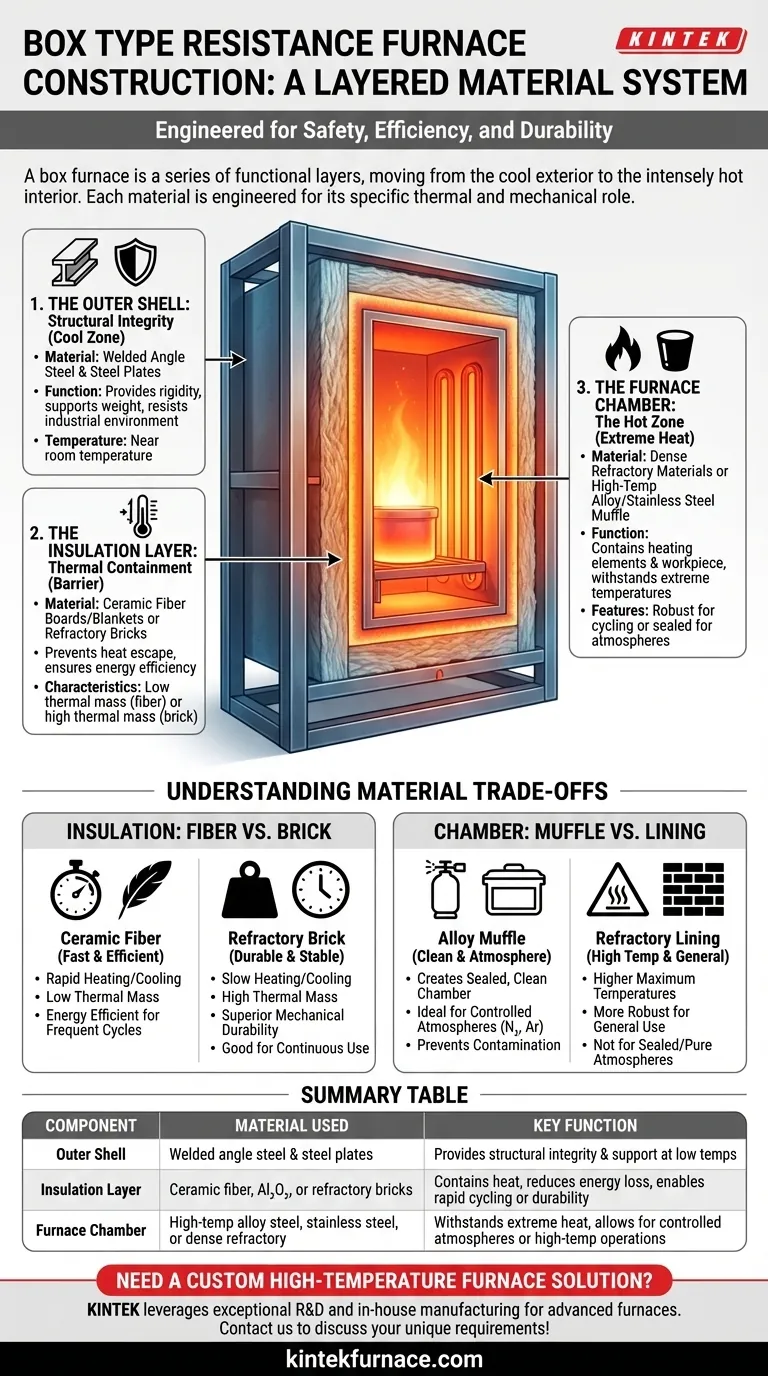
The Furnace Structure: A Layered System
A box furnace is best understood as a series of functional layers, moving from the cool exterior to the intensely hot interior. Each layer uses a material specifically chosen for the unique thermal and mechanical demands of its position.
This design philosophy separates the task of providing physical strength from the task of containing extreme heat, allowing for a more efficient, durable, and safe design.
Core Components and Their Materials
To grasp the furnace's construction, we must examine each layer's specific material and purpose.
The Outer Shell: Structural Integrity
The furnace's external frame and casing provide its foundational strength. This "skeleton" is responsible for supporting the weight of all internal components and resisting the rigors of an industrial environment.
The materials used are angle steel and high-quality steel plate. These are welded together to form a rigid, durable box structure. Standard steel is used here because it is strong, cost-effective, and easy to fabricate. Since this outer shell is protected by internal insulation, it operates at or near room temperature and does not require high-temperature resistance.
The Insulation Layer: Thermal Containment
The insulation is arguably the most critical component for performance and efficiency. It is a thick layer sandwiched between the outer shell and the inner furnace chamber. Its sole purpose is to prevent heat from escaping.
Common materials include aluminum oxide or ceramic fiber boards and blankets. These materials have excellent thermal insulation properties but low thermal mass. Refractory bricks may also be used. This layer ensures that the intense heat generated inside stays inside, keeping the outer shell cool to the touch and drastically reducing energy consumption.
The Furnace Chamber: The Hot Zone
The furnace chamber, also known as the hearth or muffle, is the innermost layer that contains the heating elements and the workpiece. It directly faces the extreme temperatures of the furnace's operation.
Materials for this hot face must be exceptionally robust. They often consist of dense refractory materials or, in some designs, a sealed liner or "muffle" made of high-temperature alloy steel or stainless steel. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand constant thermal cycling up to very high temperatures without degrading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between different insulation and chamber materials is not arbitrary; it represents a critical trade-off between performance characteristics.
Insulation: Fiber vs. Brick
A furnace built with ceramic fiber insulation has a low thermal mass. This allows it to heat up and cool down very quickly, making it more energy-efficient for processes that require frequent cycles.
Conversely, a furnace lined with refractory firebricks has a high thermal mass. It heats and cools slowly but offers superior mechanical durability and is better suited for continuous, long-duration operation at stable temperatures.
Chamber Material: Alloy Muffle vs. Refractory Lining
A high-temperature alloy muffle creates a clean, sealed inner chamber. This is essential for heat-treating in controlled atmospheres (like nitrogen or argon) or when preventing any contamination from insulation dust is paramount.
A refractory-lined chamber (where elements are embedded in the insulation) can often reach higher maximum temperatures and is typically more robust for general-purpose work. However, it is not suitable for creating a sealed, pure atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these material layers allows you to select a furnace that is precisely matched to your operational needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and energy efficiency: Prioritize a furnace built with lightweight ceramic fiber insulation for its fast heat-up and cool-down times.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability for heavy loads or continuous use: A furnace with a dense refractory brick lining is the more robust and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or controlled atmospheres: You must select a furnace equipped with a sealed high-temperature alloy steel muffle.
By looking beyond the surface and understanding the function of each material, you can ensure the furnace you choose is perfectly engineered for its intended task.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Used | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Welded angle steel and steel plates | Provides structural integrity and support at low temperatures |
| Insulation Layer | Ceramic fiber, aluminum oxide, or refractory bricks | Contains heat, reduces energy loss, and enables rapid cycling or durability |
| Furnace Chamber | High-temperature alloy steel, stainless steel, or dense refractory materials | Withstands extreme heat, allows for controlled atmospheres or high-temperature operations |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements for efficiency, durability, and purity. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















