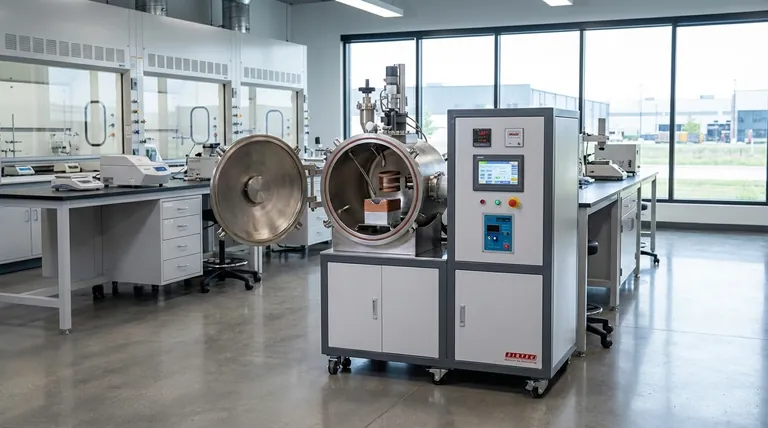
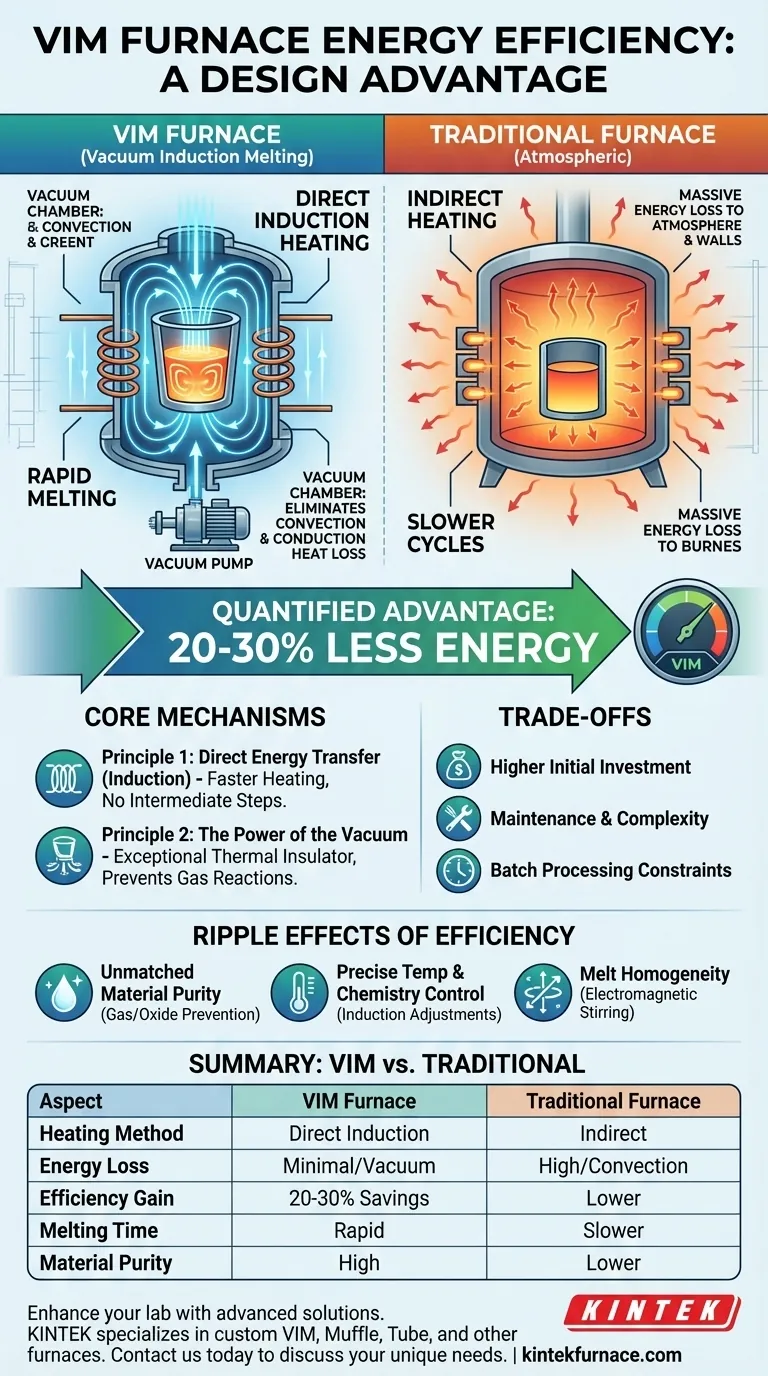
The energy efficiency of a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace stems from two core design principles working in tandem. First, induction heating generates heat directly within the metal charge itself, avoiding the massive energy losses inherent in heating a material from an external source. Second, the vacuum environment acts as a superior insulator, drastically reducing heat loss to the surrounding atmosphere.
The decision to use a VIM furnace is not just about saving energy; it's about investing in a fundamentally more precise and controlled melting process. Its efficiency is a direct consequence of a design that prioritizes heating the material itself, not the environment around it.

The Core Mechanisms of VIM Efficiency
To understand the VIM advantage, we must look at how it manipulates both energy and atmosphere. The efficiency isn't from a single component but from the synergy of the entire system.
Principle 1: Direct Energy Transfer via Induction
Traditional furnaces are inefficient because they operate indirectly. They heat elements or burn fuel to heat the furnace chamber, which then slowly radiates heat to the material. A significant portion of this energy is lost heating the furnace walls and the surrounding air.
Induction heating is fundamentally different. An alternating current is passed through a coil, creating a powerful magnetic field. This field induces strong electrical currents—known as eddy currents—directly within the conductive metal. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
This method eliminates the intermediate transfer steps, channeling energy almost entirely into the melt. This is why VIM systems boast extremely fast melting times, often just a few minutes, compared to much longer cycles in conventional furnaces.
Principle 2: The Power of the Vacuum
The vacuum in a VIM furnace serves two critical energy-saving functions.
First, it is an exceptional thermal insulator. By removing most of the air molecules from the chamber, it virtually eliminates heat loss through convection and conduction. The heat generated within the melt stays in the melt.
Second, the vacuum prevents unwanted gas interactions. In a conventional furnace, energy is wasted on chemical reactions between the hot metal and atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. In a VIM furnace, this is prevented, ensuring energy is used for melting, not for creating oxides.
Quantifying the Advantage
When compared to traditional atmospheric furnaces, a VIM furnace can be significantly more efficient.
Studies and operational data consistently show that VIM systems typically require 20-30% less energy for the same melting task. This is a direct result of improved heat transfer efficiency and dramatically reduced heat losses.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, VIM technology is not the universal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
VIM systems are more complex than their atmospheric counterparts. The need for robust vacuum chambers, high-power induction coils, and sophisticated control systems results in a significantly higher upfront capital cost.
Maintenance and Operational Complexity
The components that deliver VIM's efficiency—especially the vacuum pumps, seals, and power supplies—require specialized knowledge and a rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure reliable operation.
Batch Processing Constraints
By its nature, VIM is a batch process. While ideal for producing high-quality, discrete amounts of material, it may not be as suitable for continuous, high-throughput industrial operations where other types of furnaces might excel.
Beyond Energy: The Ripple Effects of Efficiency
The design principles that make VIM furnaces energy-efficient also produce several other critical benefits for high-performance applications.
Unmatched Material Purity
The vacuum environment is the single greatest advantage for quality. It prevents the formation of oxides and removes dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen from the melt, resulting in an exceptionally clean and pure final product.
Precise Temperature and Chemistry Control
Induction allows for nearly instantaneous power adjustments, giving operators extremely tight control over the temperature profile of the melt. Furthermore, the electromagnetic field gently stirs the molten bath, ensuring excellent melt homogeneity and a consistent final alloy chemistry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your end goal. The efficiency of a VIM system must be weighed against its cost and complexity in the context of your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: The 20-30% energy reduction of a VIM furnace can lead to substantial savings that offset the higher initial investment over the equipment's lifecycle.
- If your primary focus is material purity and performance: The VIM process is non-negotiable for producing the clean, gas-free, and precisely alloyed metals required for aerospace, medical, and other critical applications.
- If your primary focus is process speed and flexibility for specialized batches: The rapid melting times and precise control inherent to induction make VIM an ideal choice for research, development, and the production of specialty alloys.
Ultimately, choosing a VIM furnace is an investment in process control, purity, and precision, where energy efficiency is a welcome and significant benefit.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | VIM Furnace | Traditional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct induction heating in metal | Indirect heating via external sources |
| Energy Loss | Minimal due to vacuum insulation | High from convection and conduction |
| Efficiency Gain | 20-30% energy savings | Lower efficiency |
| Melting Time | Rapid (minutes) | Slower (longer cycles) |
| Material Purity | High, with gas and oxide prevention | Lower, prone to impurities |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with advanced high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in custom VIM furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we deliver tailored solutions for diverse laboratories, ensuring precise temperature control, energy savings, and superior material purity. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can meet your unique experimental needs and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















