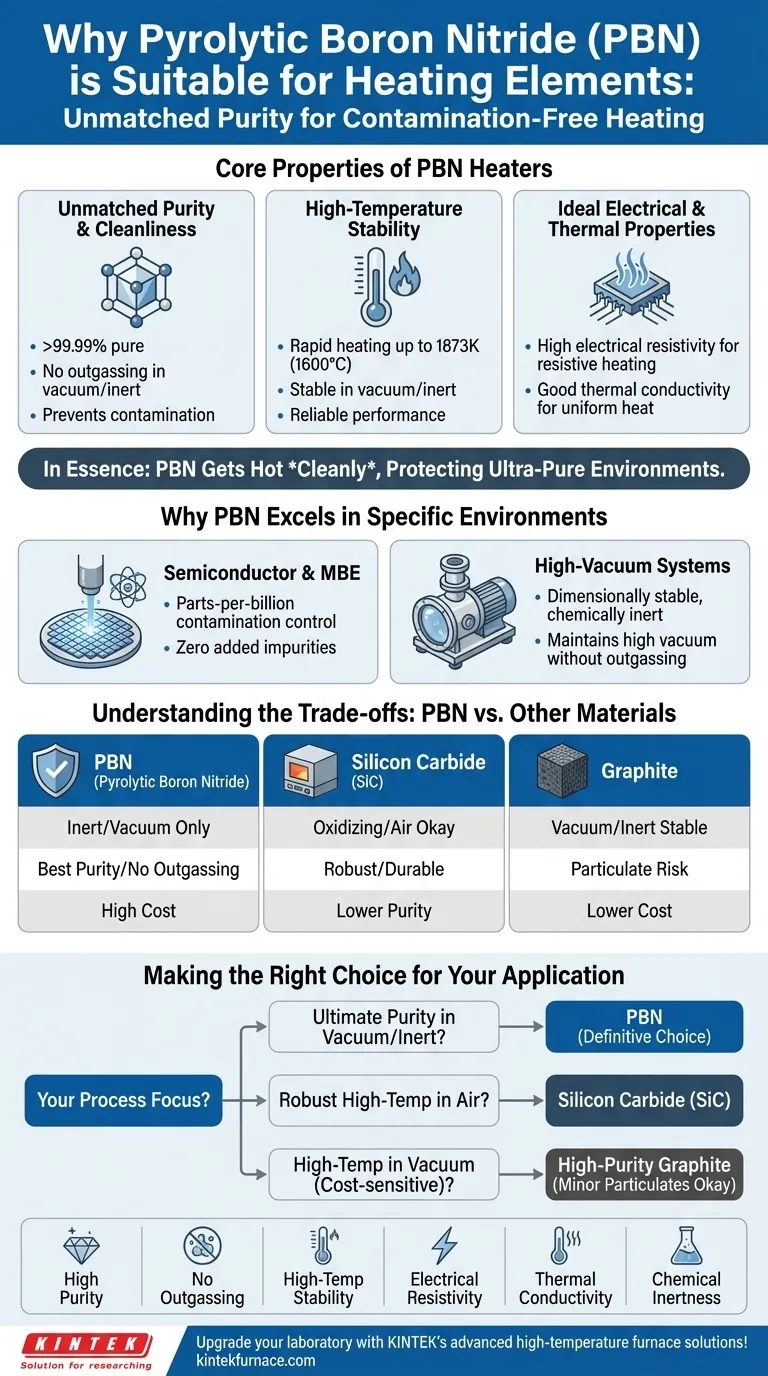
In essence, Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) is suitable for heating elements due to its unique combination of extreme chemical purity, high-temperature stability in controlled atmospheres, and its signature property of not releasing any gases when heated. This makes it an essential material for applications where preventing any form of contamination is the highest priority.
While many materials can get hot, PBN is unique because it gets hot cleanly. Its value is not just in its thermal performance, but in its ability to protect the ultra-pure environments required for advanced manufacturing, such as in the semiconductor industry.
The Core Properties of PBN Heaters
The suitability of PBN for specialized heating elements comes down to a few key characteristics that set it apart from more common industrial materials.
Unmatched Purity and Cleanliness
PBN is manufactured to an exceptional purity level, often exceeding 99.99%.
Unlike other materials, it does not "outgas"—release trapped gases or vaporized molecules—when heated to extreme temperatures. This ensures the absolute integrity of the process chamber, preventing contamination that could ruin sensitive components like semiconductor wafers.
High-Temperature Stability
PBN can be rapidly and repeatedly heated to very high temperatures, up to 1873K (approximately 1600°C), without degrading.
Crucially, it maintains this stability in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres. This is a perfect match for the controlled environments where high-purity processes take place.
Ideal Electrical and Thermal Properties
As a ceramic, PBN has high electrical resistivity, which is a fundamental requirement for a resistive heating element to generate heat from an electric current.
It also possesses good thermal conductivity, allowing it to distribute this generated heat efficiently and uniformly across its surface, preventing damaging hot spots.
Why PBN Excels in Specific Environments
PBN is not a general-purpose heating material. It is a specialist solution for environments where standard materials would fail or cause unacceptable contamination.
Semiconductor and MBE Applications
In processes like Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) or semiconductor wafer processing, even parts-per-billion contamination can cause device failure.
PBN heaters guarantee that the only thing introduced into the chamber is controlled heat, with zero added chemical impurities from the heater itself.
High-Vacuum Systems
In a high-vacuum system, any material that outgasses works directly against the vacuum pumps and contaminates the environment.
Because PBN is dimensionally stable and chemically inert at temperature and under vacuum, it is one of the few materials that can serve as a heating source without compromising the vacuum level.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PBN vs. Other Materials
Choosing a heating element involves weighing performance against environmental conditions and cost. PBN is an elite material, and its trade-offs reflect this.
The Critical Limitation: Oxidizing Atmospheres
PBN's stability is limited to inert (non-reactive) gas or vacuum environments. It will readily oxidize and break down if operated at high temperatures in open air, making it completely unsuitable for such applications.
PBN vs. Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is a robust industrial workhorse known for its excellent durability and ability to operate in air. It is the go-to choice for furnaces and kilns. However, it is not as pure as PBN and is not used where ultimate cleanliness is the goal.
PBN vs. Graphite
Graphite also has excellent high-temperature stability in vacuum. However, it can be a source of particulate (carbon dust) contamination and is generally less pure than PBN. PBN is chosen when even the smallest amount of carbon contamination is unacceptable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of heating material must be aligned with the primary constraints of your process environment.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and process integrity in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: PBN is the definitive and often non-negotiable choice.
- If your primary focus is robust, high-temperature heating in an open-air or oxidizing atmosphere: Silicon Carbide (SiC) is the technically superior and more durable option.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance in a vacuum at a lower cost: High-purity graphite is a viable alternative, provided minor particulate contamination is tolerable.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material is about understanding that the environment dictates the requirements for the heater, not the other way around.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage |
|---|---|
| High Purity (>99.99%) | Prevents contamination in sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing |
| No Outgassing | Maintains integrity in vacuum and inert atmospheres without releasing gases |
| High-Temperature Stability (up to 1873K) | Reliable performance in controlled environments with rapid heating cycles |
| High Electrical Resistivity | Enables efficient resistive heating for uniform heat distribution |
| Good Thermal Conductivity | Reduces hot spots and ensures even heating across the element |
| Chemical Inertness | Ideal for high-vacuum systems and processes requiring ultra-clean conditions |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored heating elements, including PBN-based options, to ensure contamination-free performance in vacuum and inert atmospheres. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Don't let contamination compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability


















