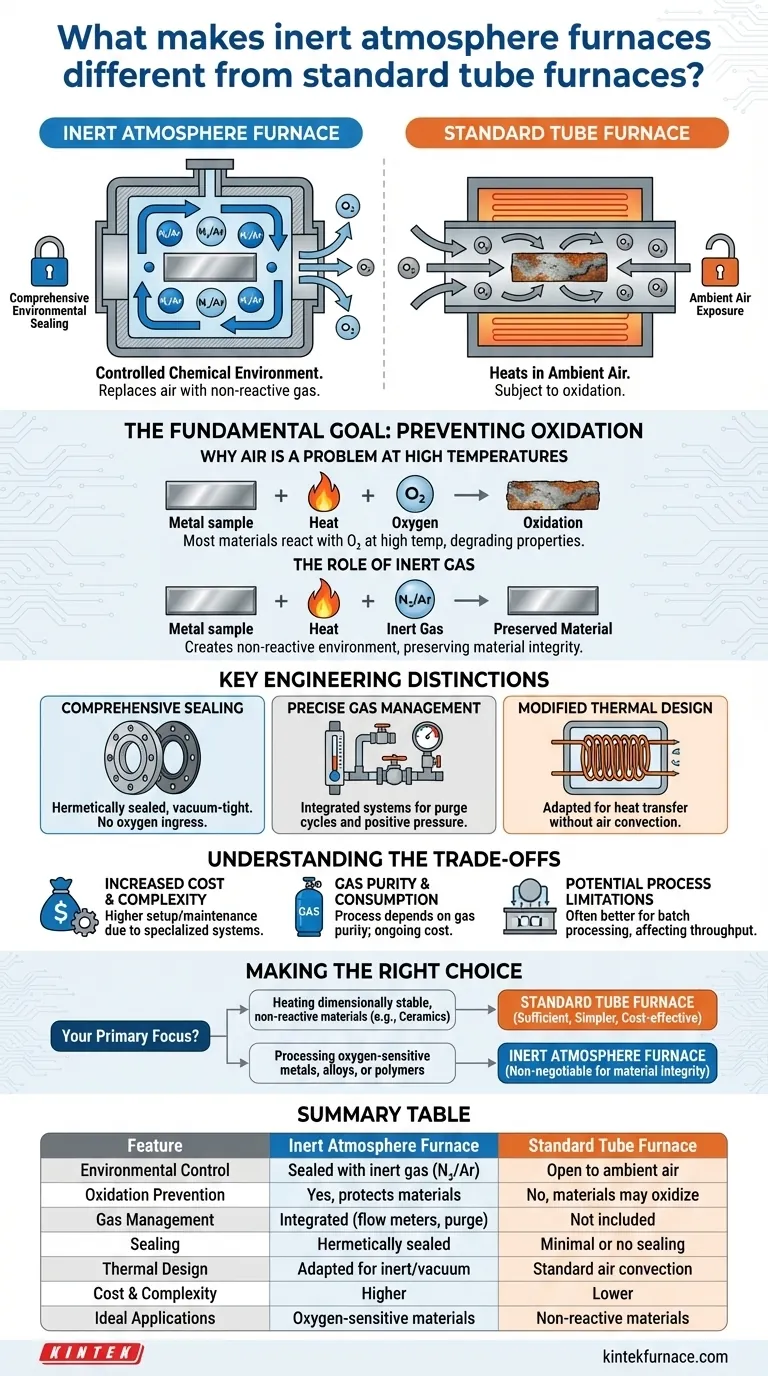
At their core, inert atmosphere furnaces are distinguished from standard tube furnaces by two critical capabilities: comprehensive environmental sealing and precise gas management systems. While a standard furnace simply heats a sample in ambient air, an inert atmosphere furnace is specifically engineered to replace that air with a non-reactive gas, protecting the material from oxidation and other chemical changes at high temperatures.
While a standard tube furnace heats a material, an inert atmosphere furnace controls the chemical environment in which it is heated. This makes it an essential tool for processing materials that would otherwise be damaged or contaminated by oxygen at high temperatures.
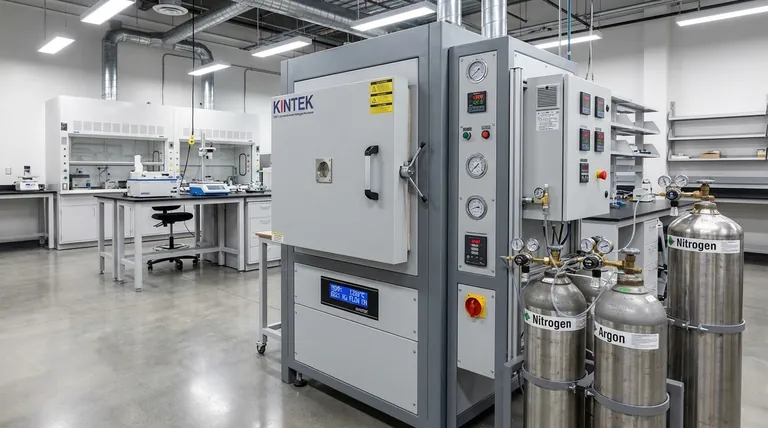

The Fundamental Goal: Preventing Oxidation
To understand the difference in hardware, you must first understand the chemical problem these furnaces solve.
Why Air is a Problem at High Temperatures
Most materials, especially metals, react with oxygen when heated. This process, known as oxidation, can degrade the material's structural, electrical, or chemical properties.
A standard tube furnace, which is open to or circulates ambient air, is unsuitable for processes where such reactions must be prevented.
The Role of Inert Gas
Inert atmosphere furnaces solve this by creating a controlled, non-reactive environment. They purge the ambient air from the heating chamber and replace it with a gas like nitrogen or argon.
These inert gases do not react with the material being processed, even at extreme temperatures, thus preserving its original composition. This is critical for applications like bonding, curing, and specific heat treatments of sensitive alloys or polymers.
Key Engineering Distinctions
The need to maintain a pure, oxygen-free environment drives several key design differences compared to standard tube furnaces.
Comprehensive Sealing Systems
The most significant difference is the furnace's ability to be hermetically sealed. An inert atmosphere furnace features vacuum-tight flanges, gaskets, and seals at all entry and exit points.
This robust sealing isolates the internal chamber from the external environment, ensuring that no oxygen leaks in during the heating process. Standard furnaces lack this level of sealing.
Precise Gas Management
Inert atmosphere furnaces include integrated gas handling systems. These typically consist of inlet and outlet ports, flow meters, valves, and pressure gauges.
This allows the operator to perform a purge cycle, where inert gas is flushed through the chamber to displace all the air before heating begins. It also enables maintaining a slight positive pressure during operation to prevent any atmospheric ingress.
Modified Thermal Design
The absence of air fundamentally changes how heat behaves. Air facilitates heat transfer through convection, which is absent in a pure inert gas or vacuum environment.
Engineers must account for this. Insulation materials may perform differently, and the design of heating elements (like induction coils) must be adapted to dissipate heat effectively without the presence of circulating air. This specialized thermal engineering is not a factor in standard furnace design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an inert atmosphere furnace introduces new operational considerations and complexities.
Increased Cost and Complexity
The specialized seals, gas delivery systems, and potential need for a vacuum pump make inert atmosphere furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than their standard counterparts. They require more rigorous setup and maintenance procedures.
Gas Purity and Consumption
The effectiveness of the process is entirely dependent on the purity of the inert gas used. Any contaminants in the gas supply can compromise the results. This also introduces an ongoing operational cost for gas consumption.
Potential Process Limitations
While standard tube furnaces can often be used in continuous processes where materials pass through, the need for sealing and purging in an inert atmosphere furnace often lends itself better to batch processing. This can affect throughput depending on the application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision between a standard and an inert atmosphere furnace is not about which is "better," but which is necessary for your specific material and process.
- If your primary focus is heating dimensionally stable, non-reactive materials (like many ceramics): A standard tube furnace is often sufficient, simpler, and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive metals, alloys, or certain polymers: An inert atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity and process repeatability: An advanced inert atmosphere furnace, often with high-vacuum capabilities, is required to create the most controlled environment possible.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace comes down to understanding the chemical stability of your material at your target processing temperature.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Inert Atmosphere Furnace | Standard Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Control | Sealed with inert gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon) | Open to ambient air |
| Oxidation Prevention | Yes, protects materials from oxygen reactions | No, materials may oxidize |
| Gas Management System | Integrated with flow meters, valves, and purge cycles | Not included |
| Sealing | Hermetically sealed with vacuum-tight components | Minimal or no sealing |
| Thermal Design | Adapted for inert gas or vacuum environments | Standard design for air convection |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher due to specialized systems | Lower and simpler |
| Ideal Applications | Oxygen-sensitive metals, alloys, polymers | Non-reactive materials like ceramics |
Need a furnace that ensures material purity and prevents oxidation? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature solutions with deep customization. Our inert atmosphere furnaces, part of a product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered with robust R&D and in-house manufacturing to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your sensitive materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















