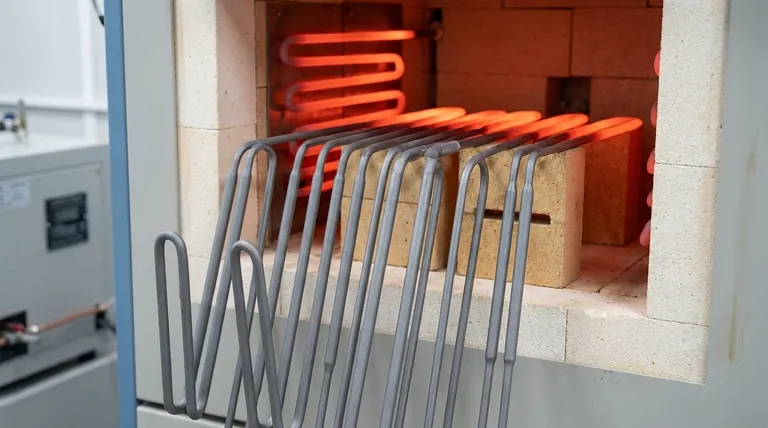
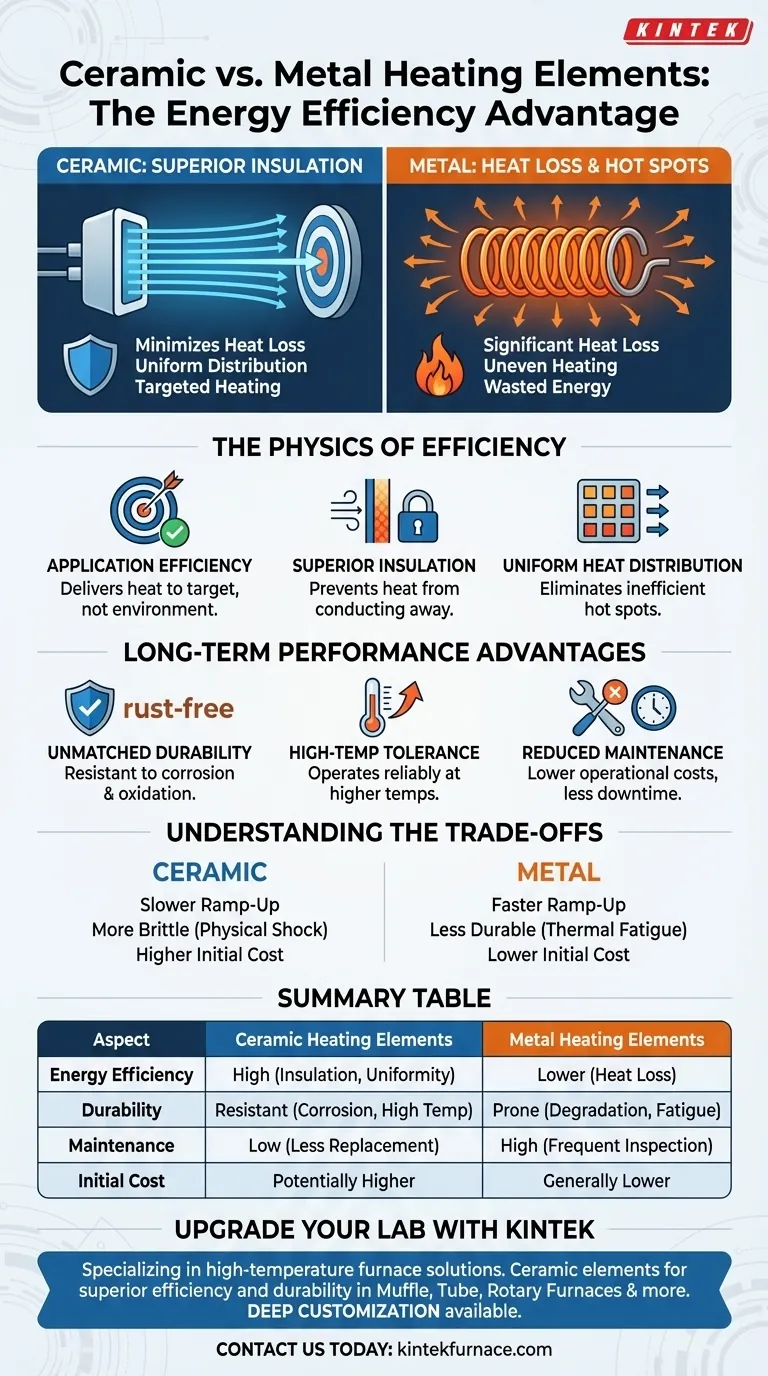
At its core, the energy efficiency of a ceramic heater stems from its material properties. Unlike metal, ceramic is a superior insulator that minimizes wasted energy by directing heat precisely where it's needed. It also distributes this heat more uniformly, preventing inefficient hot spots and ensuring the entire surface works to heat the target, not the surrounding air.
The crucial difference isn't how much electricity is converted to heat—both are nearly 100% efficient in that regard. The real-world energy savings come from how effectively the heater transfers that heat and retains it, which is where ceramic's inherent physical characteristics provide a decisive advantage.

The Physics of Efficient Heating
True heating efficiency is about minimizing waste. While a simple metal coil and an advanced ceramic element both convert electrical energy into thermal energy, how they manage and deliver that thermal energy is entirely different.
Electrical Efficiency vs. Application Efficiency
All resistive heaters, whether metal or ceramic, are nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat. This is a fundamental law of physics.
However, application efficiency is the metric that truly matters. It measures how much of that generated heat successfully reaches the intended target versus how much is lost to the environment.
The Role of Superior Insulation
Ceramic materials are excellent thermal insulators. This means they do not readily conduct heat away to unintended areas.
This property ensures that the vast majority of the generated heat is radiated or conducted toward your target. A metal element, by contrast, loses heat more easily in all directions, requiring more energy to achieve the same target temperature.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Ceramic heaters are known for providing exceptionally uniform heat across their entire surface. This eliminates "hot spots" that concentrate energy in one area while leaving others cooler.
By heating evenly, the entire element works efficiently. This reduces the total power required and improves the quality and consistency of the heating process, whether you're heating a room or a component in an industrial machine.
Ceramic's Long-Term Performance Advantages
Beyond pure energy savings, the material stability of ceramic delivers benefits in durability and consistency over the element's entire lifespan.
Unmatched Durability
Ceramic elements are highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation (rust), and chemical abrasion. This makes them ideal for use in harsh industrial environments.
Metal elements, particularly at high temperatures, oxidize and degrade. This process of thermal fatigue weakens the metal, leading to inconsistent performance and eventual failure.
High-Temperature Tolerance
Ceramics have extremely high melting points and resist deformation even when subjected to intense heat cycles.
This allows them to operate reliably at higher temperatures than many conventional metal elements, generating more heat safely without risking structural failure.
Reduced Maintenance
The inherent stability of ceramic means these heating elements require significantly less maintenance. They don't degrade or weaken in the same way as their metal counterparts.
This translates to lower operational costs and less downtime, as metal elements often require frequent inspection and replacement to prevent failure and ensure safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No engineering choice is without compromises. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to making a truly informed decision.
Thermal Inertia and Ramp-Up Time
Because ceramics are so effective at absorbing and holding heat, they can sometimes take longer to reach their target operating temperature from a cold start compared to a simple, low-mass metal coil.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
While extremely hard and durable against heat and corrosion, ceramics are more brittle than ductile metals. A significant physical impact or mechanical shock can cause a ceramic element to crack or shatter.
Initial Cost
The manufacturing processes for creating high-purity, precisely shaped ceramic components are often more complex than those for forming metal wire or strips. This can sometimes translate to a higher upfront cost for a ceramic heating element.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires balancing immediate needs with long-term performance and efficiency goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and long-term stability: Ceramic is the definitive choice, as its superior insulation and durability will deliver lower operational costs over time.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat-up for intermittent use: A simple metal element may be sufficient, but you must accept the trade-offs of higher energy loss and a shorter lifespan.
- If your application involves harsh chemical environments or sustained high temperatures: The inherent corrosion resistance and thermal stability of ceramic are essential for reliable operation.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about understanding the total cost of ownership, where ceramic's efficiency and longevity often provide the greatest long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Ceramic Heating Elements | Metal Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High due to superior insulation and uniform heat distribution | Lower due to heat loss and uneven heating |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and high temperatures | Prone to degradation and thermal fatigue |
| Maintenance | Low, with reduced need for replacement | High, requiring frequent inspections and replacements |
| Initial Cost | Potentially higher upfront | Generally lower upfront |
Upgrade Your Lab's Efficiency with KINTEK's Advanced Heating Solutions!
Struggling with energy waste and inconsistent heating in your processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our ceramic heating elements, integrated into products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, deliver superior energy efficiency, uniform heat distribution, and long-lasting durability. With our strong deep customization capability, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, reducing operational costs and downtime.
Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how our innovative heating technologies can optimize your lab's performance and save you money in the long run!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs



















