Effective maintenance of a multi-zone tube furnace hinges on a consistent schedule of inspection and cleaning. The most critical practices involve regularly checking the power supply, heating elements, and any air or gas circuits for signs of wear or malfunction. Keeping the equipment clean and tidy is also essential for preventing contamination and ensuring proper performance, while any significant issues should be addressed by a qualified professional.
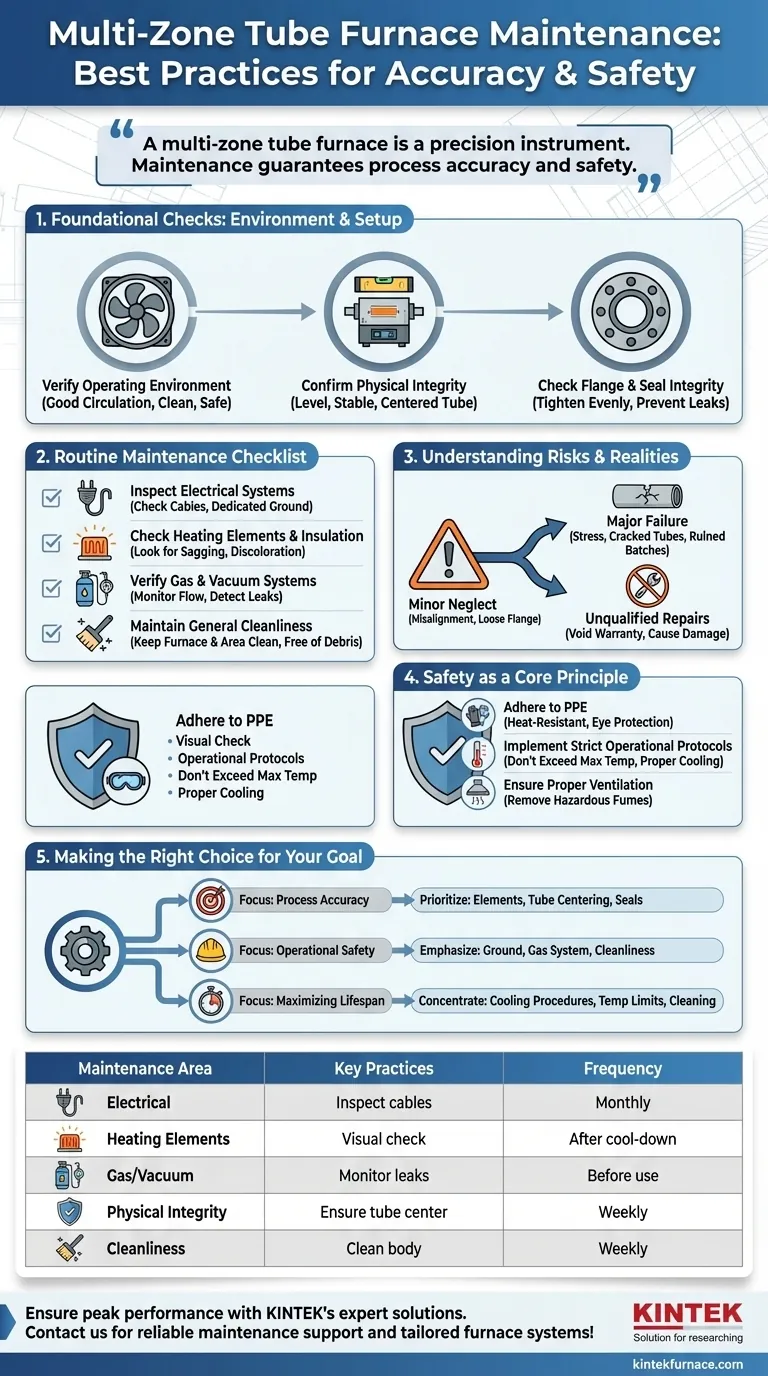
A multi-zone tube furnace is a precision instrument where maintenance is not just about preventing failure, but about guaranteeing process accuracy and safety. Moving beyond a simple cleaning checklist to a holistic system of checks is the key to protecting your investment and your results.

Foundational Checks: The Environment and Setup
Before focusing on the furnace itself, you must ensure its operating environment is stable and safe. These foundational elements are the first line of defense against premature wear and catastrophic failure.
Verify the Operating Environment
The furnace should be placed in a location with good air circulation to aid in cooling and dissipate heat. The area must be free of excessive dust, vibration, and any flammable or explosive materials that could create a hazard at high temperatures.
Confirm Physical Integrity
Ensure the furnace is level and stable. The process tube must be installed symmetrically, centered within the furnace body so it does not touch the heating elements. Uneven placement can lead to thermal stress, causing the tube to crack.
Check Flange and Seal Integrity
The end flanges create the seal for atmosphere control. Regularly confirm that the screws are tightened evenly to prevent leaks or skewing. A compromised seal can ruin an experiment and, depending on the gases used, create a significant safety risk.
The Routine Maintenance Checklist
This systematic checklist forms the core of your recurring maintenance plan. It should be performed regularly, with the frequency depending on the furnace's usage.
Inspect Electrical Systems
Visually inspect all power cables for fraying or damage. Most importantly, verify that the furnace has an effective and dedicated ground connection. This is a critical safety measure to prevent electric shock.
Check Heating Elements and Insulation
When the furnace is cool, visually inspect the heating elements for any signs of sagging, discoloration, or degradation. Damaged elements are a primary cause of temperature inaccuracy and failure, which is especially critical in a multi-zone system that relies on precise gradients.
Verify Gas and Vacuum Systems
If you are using process gases, constantly monitor the flow meters and connections for any potential leaks. The integrity of your gas delivery system is paramount for both process control and lab safety.
Maintain General Cleanliness
Keep the furnace body and surrounding area clean. Dust and debris can block ventilation, act as insulators that trap heat, or even contaminate your process if they enter the furnace tube.
Understanding the Risks and Realities
Objective maintenance requires understanding the potential consequences of neglect and the limits of in-house repairs.
The Risk of Unqualified Repairs
A multi-zone tube furnace, especially a complex model like one used for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), is a sophisticated piece of equipment. For any issue beyond basic cleaning or a loose connection, it is essential to contact the manufacturer or a certified technician. Attempting complex repairs without proper knowledge can cause more damage and void your warranty.
How Minor Neglect Leads to Major Failure
A slightly misaligned tube, a loose flange, or a single degrading heating element may seem like small issues. However, these problems create stress on the entire system, eventually leading to cracked tubes, complete element failure, or ruined experimental batches. Consistent maintenance catches these issues while they are still minor.
The Impact on Process Accuracy
The primary purpose of a multi-zone furnace is to create a precise thermal profile. Poor maintenance directly compromises this function. Degraded elements, poor seals, or incorrect tube placement will make it impossible to achieve a repeatable and accurate temperature gradient, rendering your results unreliable.
Safety as a Core Maintenance Principle
Safety protocols are not separate from maintenance; they are an integral part of it. The high temperatures and controlled atmospheres of these furnaces demand strict adherence to safety rules.
Adhere to Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Always wear heat-resistant gloves and proper eye protection when operating the furnace or handling items that have been removed from it.
Implement Strict Operational Protocols
Never operate the furnace above its maximum rated temperature. Follow the manufacturer's specified procedures for heating and, just as importantly, for cooling. Allowing the furnace to cool naturally prevents thermal shock that can damage the tube and elements.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is non-negotiable, especially when working with process gases. It removes hazardous fumes and ensures a safe breathing environment for all personnel in the lab.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align with your primary objective for using the furnace.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and accuracy: Prioritize routine inspection of the heating elements, process tube centering, and the integrity of the flange seals.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and lab compliance: Emphasize verification of the electrical ground, regular checks of the gas delivery system, and maintaining a clean, hazard-free operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Concentrate on following proper cooling procedures, never exceeding the rated temperature, and performing consistent cleaning.
Ultimately, diligent maintenance is an investment in the safety, accuracy, and longevity of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Area | Key Practices | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Systems | Inspect cables, check ground connection | Monthly |
| Heating Elements | Visual check for sagging, discoloration | After each cool-down |
| Gas/Vacuum Systems | Monitor for leaks, verify flow meters | Before each use |
| Physical Integrity | Ensure tube is centered, flanges sealed | Weekly |
| Cleanliness | Clean furnace body and area | Weekly |
Ensure your multi-zone tube furnace operates at peak performance with KINTEK's expert solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today for reliable maintenance support and tailored furnace systems that guarantee safety, accuracy, and longevity in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations



















