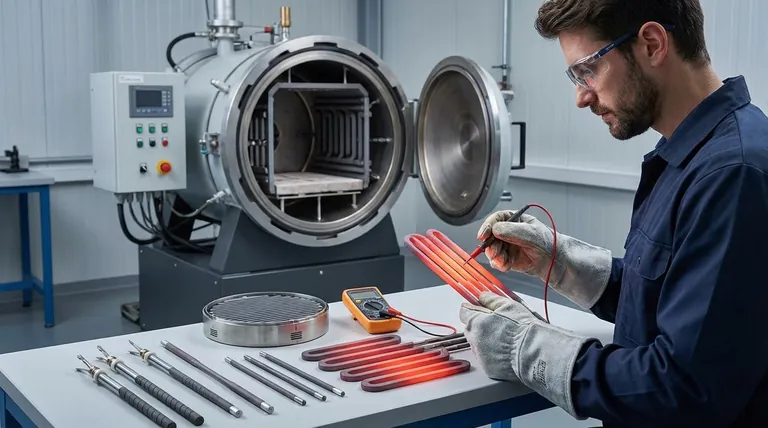
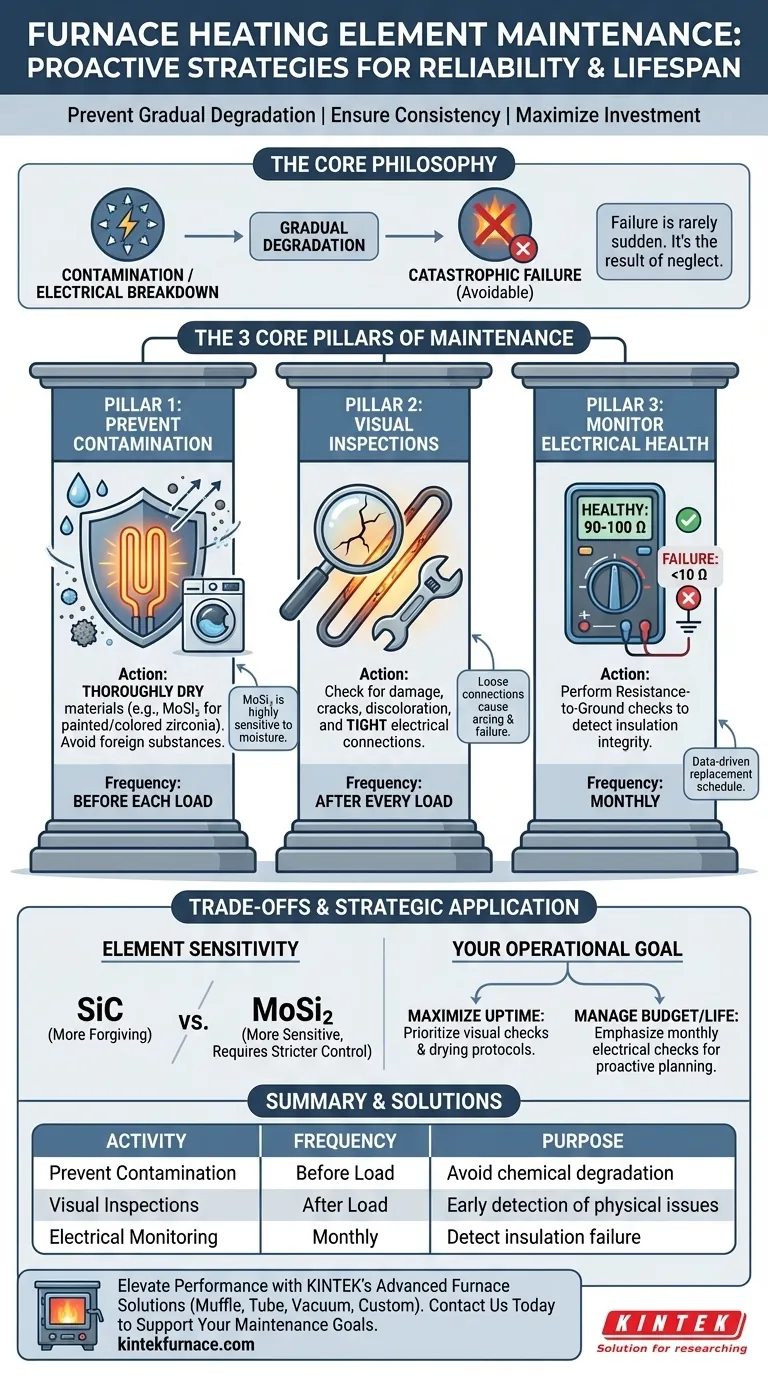
At its core, effective maintenance for furnace heating elements centers on three critical activities: preventing contamination, conducting frequent visual inspections, and monitoring the element's electrical health. These steps are not merely about cleaning; they are a proactive strategy to prevent catastrophic failure, ensure process consistency, and maximize the operational lifespan of these expensive components.
The central takeaway is that heating element failure is rarely a sudden event. It is almost always the result of gradual degradation from contamination or electrical breakdown, both of which can be identified and mitigated with a disciplined maintenance routine.

The Core Pillars of Element Maintenance
True maintenance moves beyond simple replacement. It involves creating an environment where the heating elements can perform reliably to their engineered limits. This requires a focus on prevention and early detection.
Principle 1: Prevent Contamination at the Source
Contamination is the primary cause of premature element failure. Foreign substances can chemically react with the element material at high temperatures, leading to degradation, weak spots, and eventual breakage.
MoSi₂ (molybdenum disilicide) elements are particularly sensitive to this. Technicians must ensure any materials being processed, such as colored or painted zirconia, are thoroughly dried before being placed in the furnace.
Moisture or binders can vaporize and deposit onto the elements, initiating a destructive chemical reaction. Strict adherence to oven maintenance and material preparation protocols is non-negotiable.
Principle 2: Conduct Routine Visual Inspections
Physical inspection is your first line of defense. A quick visual check can reveal developing problems long before they lead to a complete thermal shutdown.
After every single load, elements should be visually inspected for any signs of physical damage, cracking, or discoloration.
Equally important is checking that all electrical connections are tight. A loose connection can create high resistance, leading to localized overheating, arcing, and failure of both the element and its terminal.
Principle 3: Monitor Electrical Health Proactively
Visual checks can't see everything. Regular electrical testing provides a quantitative measure of an element's health and its insulation integrity.
A monthly resistance-to-ground check is a critical diagnostic tool, especially for furnaces used in demanding applications like low-pressure vacuum carburizing.
This test measures how well the element is electrically isolated from the furnace body. A healthy, well-insulated element will typically show a resistance of 90-100 ohms. A reading that drops below 10 ohms is a clear indicator of insulation failure, meaning the element is shorting to ground and requires immediate replacement.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process vs. Element Type
The references note that both SiC (silicon carbide) and MoSi₂ elements can suffer from contamination, but MoSi₂ elements are "more sensitive." This highlights a critical operational trade-off.
The Impact of Element Sensitivity
While MoSi₂ elements may offer specific performance advantages in certain temperature ranges, their heightened sensitivity to contamination demands more stringent process control.
This means that a facility using MoSi₂ elements must invest more heavily in material preparation protocols, such as pre-drying, to protect its investment. The maintenance burden is directly linked to the element's chemistry.
Choosing an Element vs. Adapting a Process
The decision is not just about which element to buy, but which maintenance and operational philosophy to adopt. A less-sensitive element like SiC might be more forgiving of minor process variations, whereas a high-performance MoSi₂ element requires a high-discipline environment to thrive.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
A structured maintenance plan transforms reactive repairs into a predictable and cost-effective operational workflow. Use the following guidelines to build your cadence.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Prioritize visual inspections after every load and strict adherence to material drying protocols to prevent the most common causes of sudden failure.
- If your primary focus is extending component life and managing budget: Emphasize monthly resistance-to-ground checks to create a data-driven replacement schedule, allowing you to order parts and plan downtime proactively.
Ultimately, disciplined maintenance shifts your relationship with your equipment from reactive to strategic, ensuring reliability is a result of your process, not a matter of chance.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Activity | Key Action | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevent Contamination | Dry materials thoroughly, avoid foreign substances | Before each load | Prevent chemical degradation and premature failure |
| Visual Inspections | Check for damage, cracks, discoloration, and tight connections | After every load | Early detection of physical issues and loose connections |
| Electrical Health Monitoring | Perform resistance-to-ground checks | Monthly | Detect insulation failure and plan proactive replacements |
Ensure your furnace heating elements operate at peak performance with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing reliability and extending component lifespan. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your maintenance goals and boost operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















