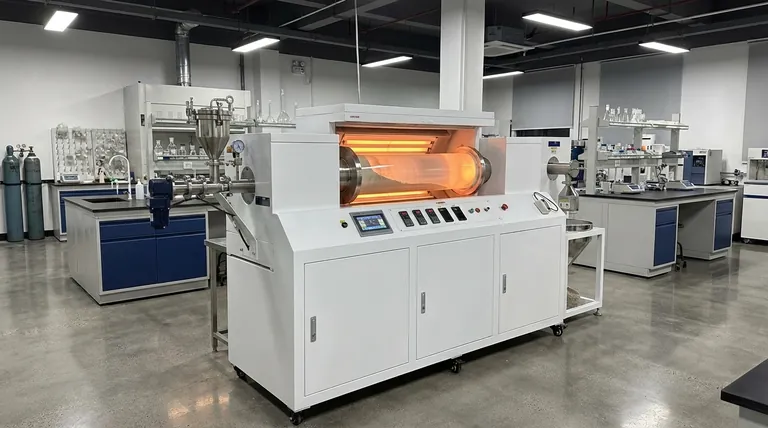
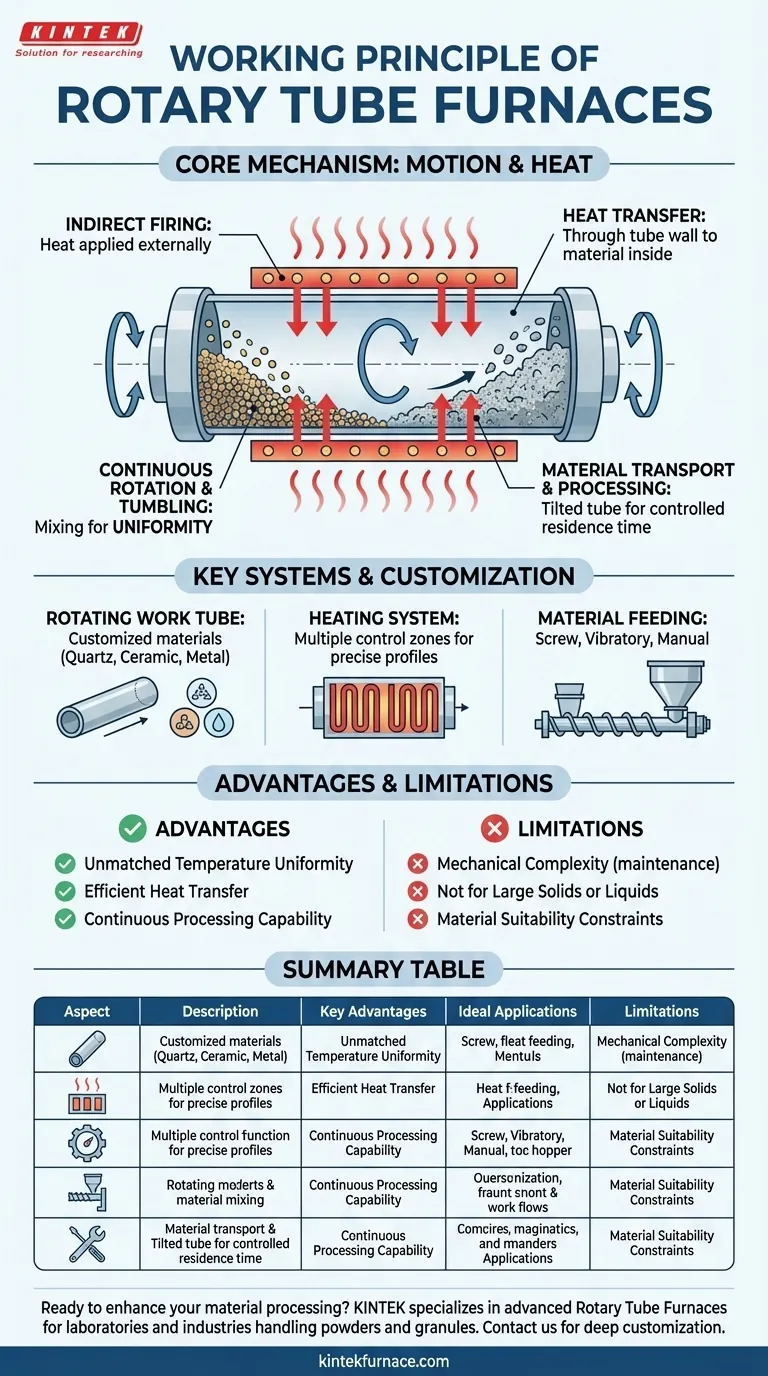
At its core, a rotary tube furnace works by tumbling loose material inside a heated, slowly rotating cylinder. This process uses indirect firing, where heat is applied to the outside of the tube and transferred to the material within. The constant motion ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the target temperature, preventing hot spots and guaranteeing consistent processing.
The fundamental challenge in heating powders or granular materials is achieving uniformity. A rotary tube furnace solves this not just with precise temperature control, but by introducing continuous mechanical motion to ensure every part of the material is treated identically.

The Core Mechanism: Combining Motion and Heat
The working principle is an elegant solution to a common thermal processing problem. It relies on the interplay between the heating method, the physical rotation, and the controlled movement of material.
Indirect Firing
A rotary tube furnace separates the heat source from the material being processed. Heating elements or gas burners heat the exterior of the work tube.
This heat then conducts through the tube wall to the material inside. This indirect method prevents contamination from combustion byproducts and allows for processing under a controlled atmosphere if needed.
Continuous Rotation and Tumbling
This is the defining feature of the furnace. The tube is mounted on rollers and driven by a motor, often with variable speed control.
As the tube rotates, the material inside is lifted up the side of the tube wall before it tumbles back down. This continuous mixing action is critical for achieving exceptional temperature uniformity throughout the bulk material.
Material Transport and Processing
For continuous operation, the furnace tube is typically installed at a slight angle. Material is fed into the higher end and slowly travels toward the lower, discharge end as the tube rotates.
The time the material spends in the furnace, known as residence time, can be precisely controlled by adjusting the rotation speed and the tilt angle, allowing for repeatable, high-quality results.
Key Systems and Customization
A functional rotary tube furnace is more than just a rotating tube. It is a complete system where each component plays a critical role in its performance and versatility.
The Rotating Work Tube
The work tube is the heart of the furnace. It can be customized in size, shape, and material (such as quartz, ceramic, or metal alloys) to suit specific temperature ranges and chemical compatibility requirements.
The Heating System
Modern furnaces often employ multiple, independent thermal control zones along the length of the tube. This allows for the creation of precise temperature profiles, enabling complex processes like drying, calcining, and reacting all within a single pass.
Material Feeding Mechanisms
How material enters the furnace is crucial for process stability. Common options include:
- Screw Conveyors: Ideal for fine powders and granules requiring a precise, controlled feed rate.
- Vibratory Hoppers: Best for materials with irregular particle sizes that need consistent, non-clogging delivery.
- Manual Loading: Suitable for small-scale lab experiments or batch processing where continuous flow is not required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its specific advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
For powders, granules, and other loose materials, no other furnace design offers better thermal uniformity. The tumbling action is a simple and effective way to eliminate temperature gradients within the product.
Advantage: Efficient Heat Transfer
The constant movement of the material maximizes its contact with the heated tube wall. This results in highly efficient and rapid heat transfer, often shortening the required processing time compared to a static furnace.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
The drive system, seals, and support rollers that enable rotation are additional points of maintenance and potential failure compared to a simple static tube or chamber furnace.
Limitation: Material Suitability
These furnaces are purpose-built for loose, free-flowing materials. They are not suitable for processing large single objects, liquids, or materials that could melt and coat the inside of the tube, impeding the tumbling action.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your material and processing goals.
- If your primary focus is research on powdered materials: The precise temperature control and reproducibility of a lab-scale rotary furnace are ideal for developing and testing new processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: The continuous processing capability and uniform output quality make it the superior choice for manufacturing materials like cement clinker or calcined alumina.
- If your primary focus is treating large, solid parts: A rotary tube furnace is the wrong tool; a box, chamber, or static tube furnace would be more appropriate.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace excels by transforming a static heating process into a dynamic one, ensuring superior uniformity for any application involving loose materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Working Principle | Tumbling of materials in a rotating, heated tube for uniform heat exposure. |
| Heating Method | Indirect firing with external heat sources to prevent contamination. |
| Key Advantages | Unmatched temperature uniformity, efficient heat transfer, and continuous processing. |
| Ideal Applications | Processing powders, granules; used in research and industrial production like calcining. |
| Limitations | Mechanical complexity, not suitable for large solids or liquids. |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precise, uniform heating? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Tube Furnaces, designed for laboratories and industries handling powders and granules. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can improve your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput



















