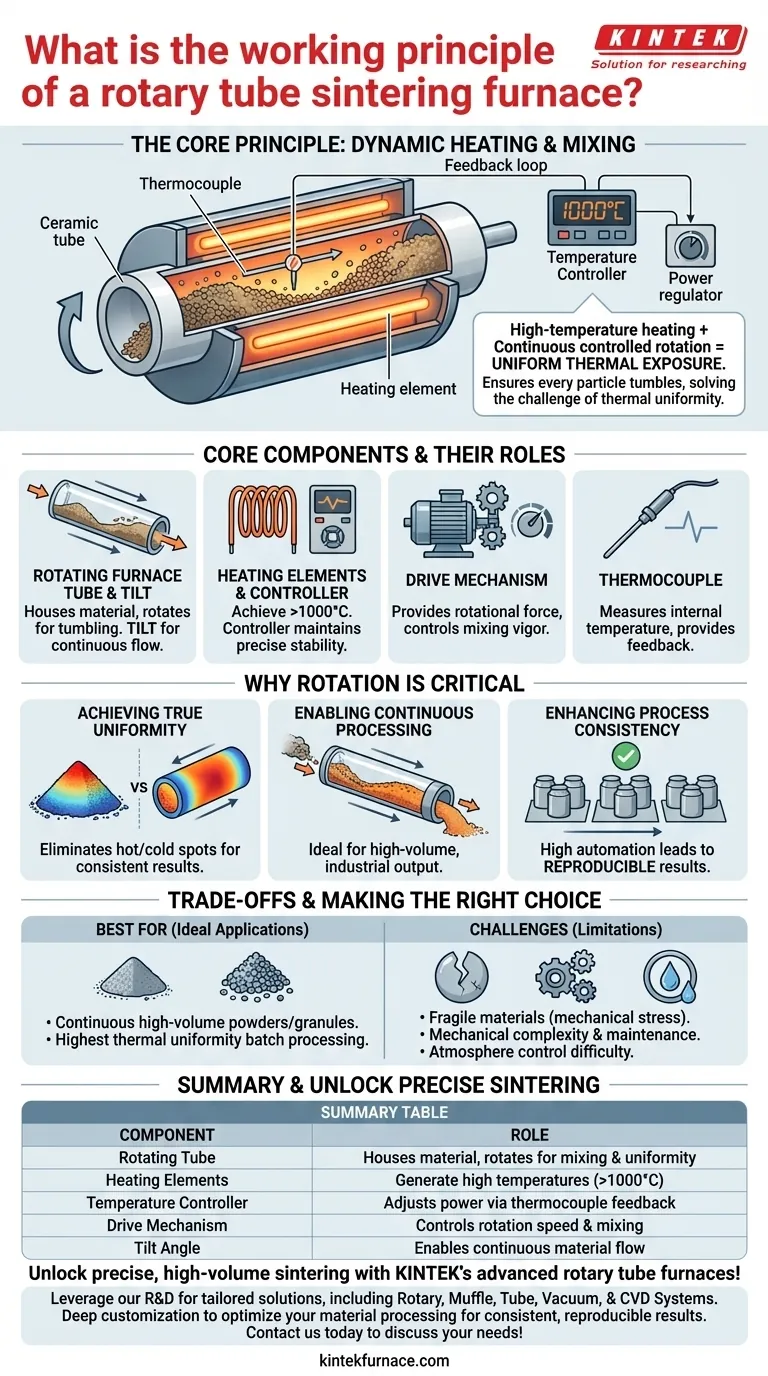
At its core, a rotary tube sintering furnace operates by combining high-temperature heating with continuous, controlled rotation of a central tube. This dual-action mechanism forces the material inside to tumble and mix constantly, ensuring every particle is exposed to a uniform temperature profile throughout the processing cycle. The entire system is governed by a precise feedback loop where thermocouples measure the temperature, a controller compares it to a set program, and the power to the heating elements is adjusted accordingly.
The fundamental challenge in high-temperature material processing is achieving perfect thermal uniformity. A rotary tube furnace solves this by replacing static heating with dynamic mixing, ensuring consistent, repeatable results that are difficult to achieve in stationary furnaces, especially for powders and granular materials.
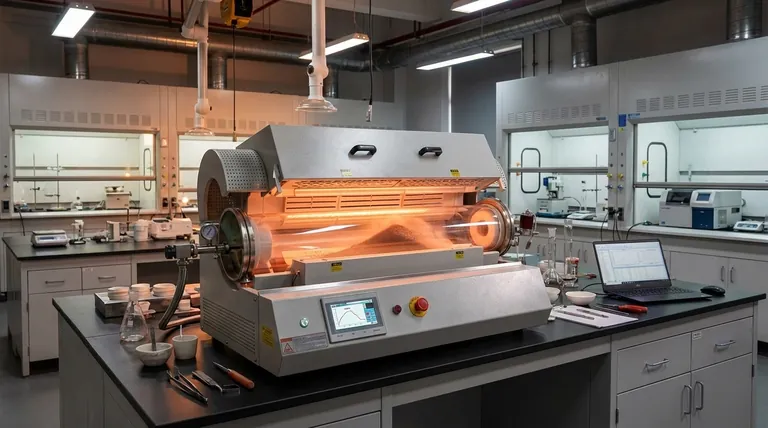

The Core Components and Their Roles
To understand the working principle, we must first look at the integrated system of components that make it function. Each part plays a critical role in achieving the final outcome.
The Rotating Furnace Tube
The central element is a cylindrical tube, typically made of quartz, ceramic, or a metal alloy, which houses the material being processed. This tube is mounted on a mechanism that allows it to rotate around its longitudinal axis.
Many models also feature an adjustable tilt angle. This slight incline uses gravity to facilitate the movement of material from the entry point to the exit point, enabling a continuous workflow.
The Heating and Control System
Surrounding the furnace tube are high-power heating elements. Their job is to bring the chamber to the required sintering temperature, which can often exceed 1000°C.
A thermocouple acts as a sensor, constantly measuring the internal temperature and converting it into an electrical signal. This signal is sent to a temperature controller, which is the brain of the operation. The controller compares the actual temperature to the user-defined program and adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements to maintain precise thermal stability.
The Drive Mechanism
An independent electric motor provides the rotational force. The speed of this rotation is a critical process parameter that can be controlled precisely. Adjusting the rotation speed influences how vigorously the material tumbles, affecting heat transfer rates and mixing efficiency.
Why Rotation is the Critical Advantage
The rotation is not an auxiliary feature; it is the defining principle that provides the furnace with its unique capabilities and solves common processing challenges.
Achieving True Thermal Uniformity
In a static furnace, material at the bottom and center of a pile heats more slowly than the material on the surface. This creates temperature gradients that lead to inconsistent results.
The rotary furnace eliminates this problem. The continuous tumbling action ensures that no single particle remains in one position for long, averaging out any potential hot or cold spots and guaranteeing exceptionally uniform heating.
Enabling Continuous Processing
The combination of rotation and tilt transforms the furnace from a single-batch device into a continuous production tool. Raw material can be fed into the higher end of the tube, and the processed material is discharged at the lower end. This is ideal for industrial-scale operations requiring a steady, consistent output.
Enhancing Process Consistency
With intelligent control over temperature, time, and rotation speed, every parameter can be meticulously managed and recorded. This high degree of automation ensures that each batch is processed under identical conditions, leading to highly reproducible results and improved quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary tube design is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Material Compatibility
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can be detrimental to certain materials. Delicate, brittle, or large single-piece samples may be damaged by the mechanical stress of rotation. This method is best suited for powders, granules, and other free-flowing solids.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and seals, introduces mechanical complexity not found in a static furnace. These moving parts require regular maintenance and represent potential points of failure over the lifetime of the equipment.
Atmosphere Control Challenges
While many rotary furnaces support controlled atmospheres (e.g., inert gas), maintaining a perfect seal on a rotating tube is inherently more complex than on a stationary one. For applications requiring ultra-high purity or extremely sensitive atmospheres, this can be a significant consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Ultimately, the decision to use a rotary tube furnace depends entirely on your specific material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-volume production of powders or granules: The flow-through capability and uniform heating of a rotary furnace make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible thermal uniformity for batch processing: The active mixing in a rotary furnace provides consistency that is very difficult to match in a static system.
- If your primary focus is processing fragile structures, single large components, or materials sensitive to mechanical stress: A static box or tube furnace is the more appropriate and safer option.
By understanding its core principle of dynamic heating, you can effectively determine if this technology is the right tool to achieve your processing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Working Principle |
|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Houses material and rotates for tumbling and mixing, ensuring uniform exposure to heat |
| Heating Elements | Generate high temperatures (often >1000°C) for sintering processes |
| Temperature Controller | Adjusts power based on thermocouple feedback to maintain precise thermal stability |
| Drive Mechanism | Controls rotation speed for optimal mixing and heat transfer efficiency |
| Tilt Angle | Uses gravity to enable continuous material flow from entry to exit points |
Unlock precise, high-volume sintering with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your material processing for consistent, reproducible results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















