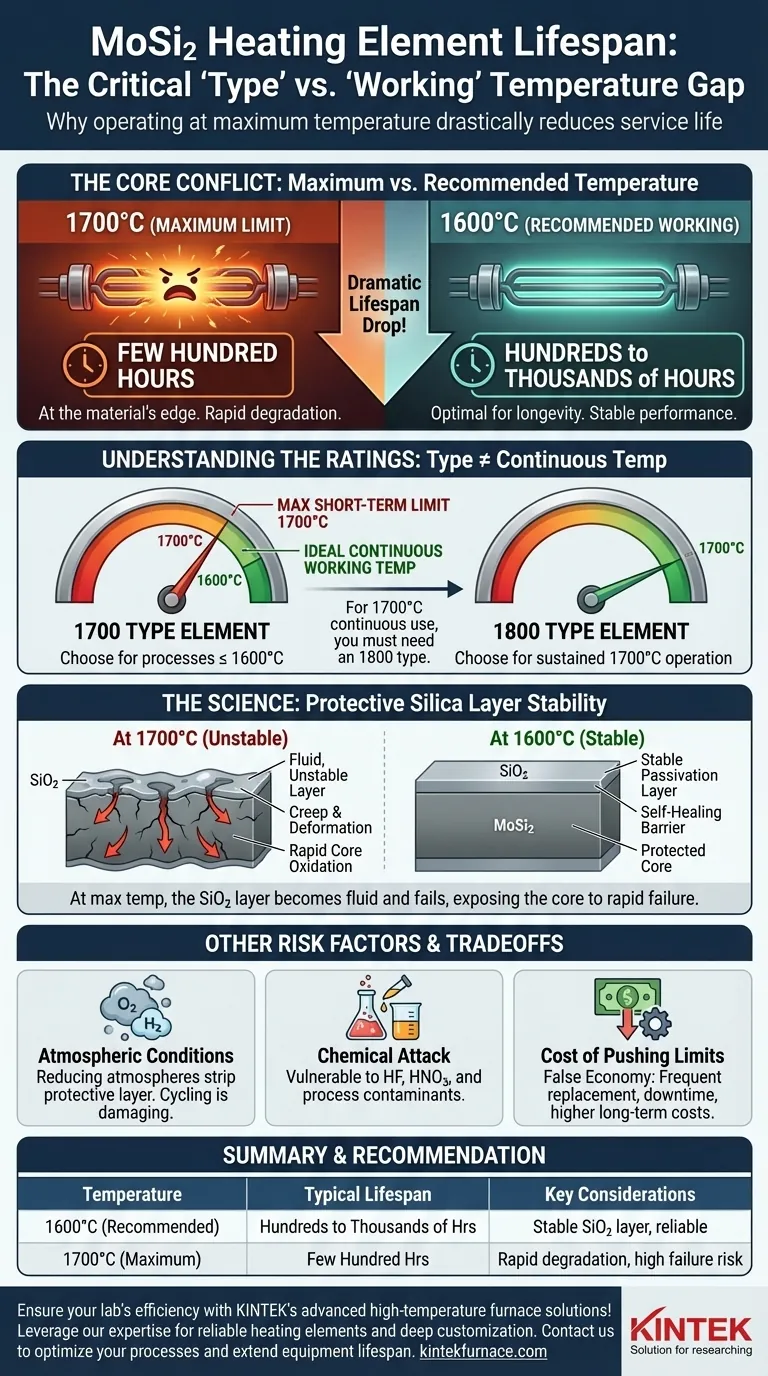
At its recommended operating temperature, a 1700-type Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating element can last for hundreds or even thousands of hours. However, when pushed to its maximum rated temperature of 1700°C, its lifespan drops dramatically to only a few hundred hours. This significant reduction highlights the critical difference between a continuous operating temperature and a maximum limit.
The crucial takeaway is that an element's "type" number (e.g., 1700) represents its maximum short-term temperature, not its ideal continuous operating temperature. For longevity and reliability, you must operate the element at its recommended "working" temperature, which is typically 100°C lower.

The Difference Between 'Type' and 'Working' Temperature
A common point of confusion is the distinction between an element's type and its practical working temperature. Understanding this is the key to managing element lifespan and furnace reliability.
### What "1700 Type" Really Means
The designation "1700 type" refers to the maximum temperature the element can withstand, typically for short periods. It does not mean it is designed for continuous, long-term operation at 1700°C.
The recommended continuous working temperature for a 1700-type element is 1600°C. Operating at this temperature balances performance with a long service life.
### The Role of the "1800 Type" Element
For applications requiring sustained operation at 1700°C, an "1800 type" element is the correct choice. Its recommended continuous working temperature is 1700°C, providing the necessary durability and thermal headroom for reliable performance at that level.
How Temperature Governs MoSi₂ Element Lifespan
The lifespan of a MoSi₂ element is directly tied to the stability of a protective surface layer. High temperatures place this layer under extreme stress, accelerating degradation and failure.
### The Protective Silica (SiO₂) Layer
At high temperatures in an oxidizing atmosphere (like air), MoSi₂ elements form a thin, glass-like layer of silica (SiO₂) on their surface. This passivation layer is self-healing and acts as a barrier, preventing the element's core from further oxidation.
This protective layer is the primary reason MoSi₂ elements have such a long service life and resistance to deformation in their intended operating range.
### Degradation at Maximum Temperature
When you push a 1700-type element to 1700°C, you are operating at the very edge of its material limits. At this temperature, the protective SiO₂ layer becomes less stable and more fluid.
This increased fluidity can lead to "creep" (slow deformation) and makes the layer more vulnerable to breakdown, exposing the core material to rapid oxidation and failure. This is why the lifespan plummets from thousands of hours at 1600°C to just a few hundred hours at 1700°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Other Risks
Operating temperature is the single biggest factor in element lifespan, but other conditions can also cause premature failure.
### The Cost of Pushing the Limit
Using a 1700-type element at 1700°C might seem like a cost-saving measure, but it leads to frequent replacement, unscheduled downtime, and potential damage to the furnace or product. The short-term savings are quickly lost to higher long-term operational costs and process instability.
### The Impact of Atmospheric Conditions
The protective SiO₂ layer relies on an oxidizing environment to form and maintain itself.
Operating in a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen or cracked ammonia) can strip away this protective layer. Cycling between reducing and oxidizing conditions is particularly damaging, as it repeatedly removes and attempts to re-form the layer, consuming the element's base material and drastically shortening its life.
### Chemical Attack and Contamination
While resistant to many substances, MoSi₂ elements are vulnerable to certain chemicals. The references note that hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid will attack the elements. Likewise, process vapors or contaminants that react with silica can degrade the protective layer and accelerate failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct element is a balance of your process requirements, budget, and desired reliability.
- If your primary focus is reliability for processes at or below 1600°C: A 1700-type element is the correct and most cost-effective choice, offering thousands of hours of stable operation.
- If your primary focus is running a furnace consistently at 1700°C: You must use an 1800-type element to ensure a reasonable service life and predictable performance.
- If you are trying to minimize initial cost for a 1700°C process: Using a 1700-type element is a false economy that will result in dramatically reduced lifespan, frequent failures, and higher long-term costs.
Ultimately, aligning the element's specified working temperature with your process needs is the most effective strategy for ensuring a long, reliable service life.
Summary Table:
| Temperature | Typical Lifespan | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1600°C (Recommended) | Hundreds to thousands of hours | Stable SiO₂ layer, reliable performance |
| 1700°C (Maximum) | Few hundred hours | Rapid degradation, high failure risk |
Ensure your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets unique experimental requirements, helping you avoid costly downtime and extend equipment lifespan. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















