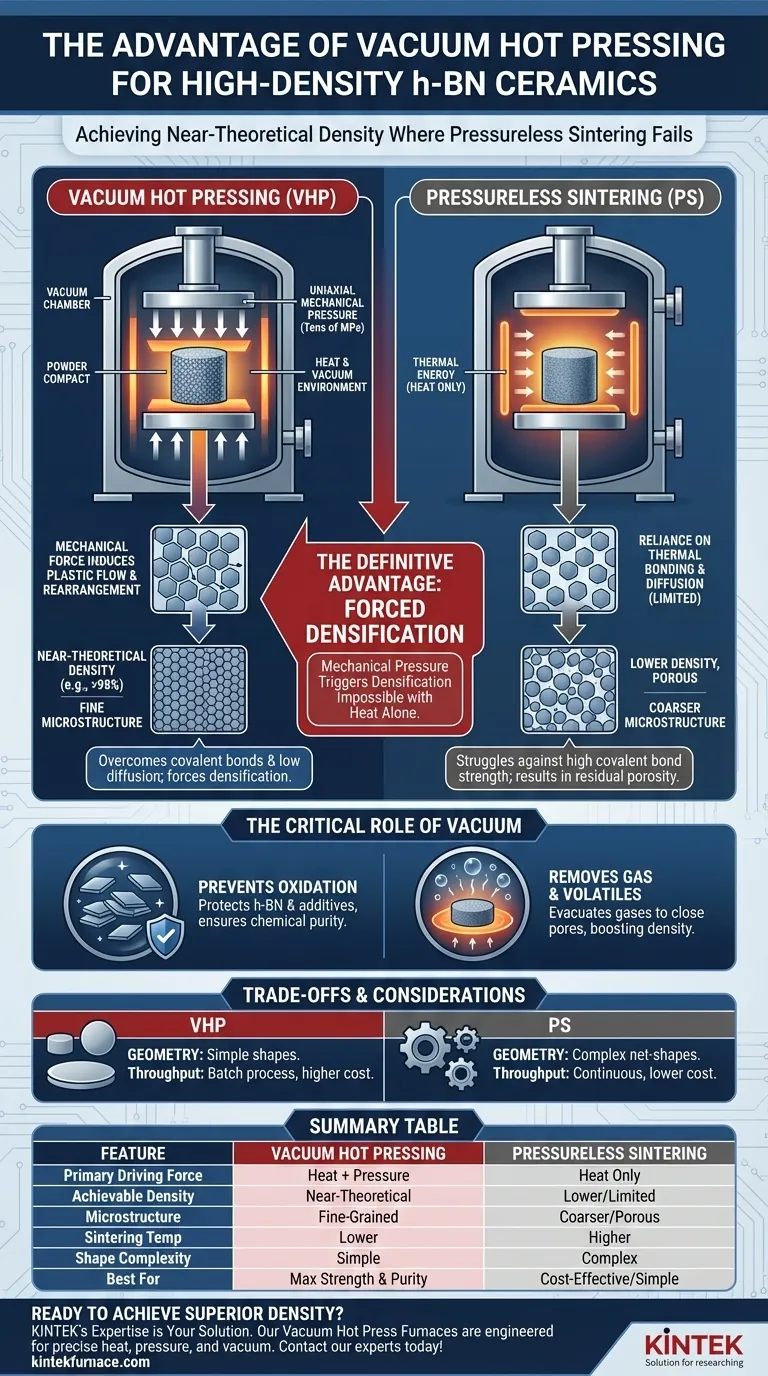
The definitive advantage of using a vacuum hot press furnace lies in its ability to force densification through mechanical pressure. Unlike pressureless sintering, which relies solely on thermal energy to bond particles, a hot press applies uniaxial force to overcome the strong covalent bonds and low self-diffusion coefficient of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). This synergy of heat and pressure triggers plastic flow and particle rearrangement, allowing you to achieve near-theoretical density that is virtually impossible with pressureless methods.
Core Takeaway h-BN is notoriously difficult to sinter due to its atomic structure and resistance to diffusion. Vacuum hot pressing resolves this by substituting thermal reliance with mechanical force, enabling high densification at lower temperatures while simultaneously stripping away impurities that inhibit bonding.

Overcoming the Kinetic Barriers of h-BN
The Challenge of Covalent Bonds
Hexagonal boron nitride consists of strong covalent bonds and possesses a plate-like microstructure. These characteristics result in a low self-diffusion coefficient, meaning atoms do not easily move to fill voids, even at extreme temperatures.
The Mechanism of Pressure-Assisted Sintering
In a pressureless environment, h-BN particles resist consolidation. A vacuum hot press overcomes this by applying uniaxial mechanical pressure (often tens of MPa) directly to the powder compact.
Forcing Plastic Flow
The applied pressure physically forces the h-BN platelets to slide past one another. This induces plastic flow and particle rearrangement, mechanically closing pores that thermal energy alone cannot eliminate.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Environment
Preventing Material Degradation
Sintering often requires temperatures where materials become reactive. The vacuum environment effectively prevents oxidation of the h-BN and any sintering additives, ensuring the chemical purity of the final ceramic.
Removing Gas to Close Pores
Raw materials often contain adsorbed gases or generate volatiles during heating. The vacuum facilitates the evacuation of these gases, which significantly reduces the formation of closed pores that would otherwise lower the density of the sintered body.
Microstructural Integrity and Performance
Achieving Lower Temperature Densification
Because mechanical pressure provides an additional driving force for sintering, high density can be achieved at significantly lower temperatures compared to pressureless methods.
Suppressing Abnormal Grain Growth
Lower sintering temperatures offer a distinct microstructural advantage: they prevent excessive grain coarsening. This allows you to preserve a finer microstructure, directly contributing to superior hardness and fracture toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Geometry Limitations
The uniaxial nature of the pressure means hot pressing is generally limited to simple shapes, such as plates, disks, or cylinders. Complex geometries often require expensive post-sintering machining or alternative methods.
Throughput and Cost
Vacuum hot pressing is inherently a batch process. While it produces superior material properties, it generally involves higher operational costs and lower throughput compared to continuous pressureless sintering techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
While vacuum hot pressing offers superior material properties, your choice depends on the specific constraints of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: Choose vacuum hot pressing, as the pressure-assisted mechanism is the only reliable way to overcome the covalent nature of h-BN.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and interface quality: Choose vacuum hot pressing, as the vacuum environment removes volatiles and prevents oxidation that weakens grain boundaries.
- If your primary focus is complex net-shape manufacturing: Acknowledge that vacuum hot pressing will require significant diamond machining after sintering to achieve intricate features.
Ultimately, for h-BN ceramics, vacuum hot pressing is not just an optimization—it is often the only viable path to achieving structural-grade density.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Hot Pressing | Pressureless Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driving Force | Heat + Mechanical Pressure | Heat Only |
| Achievable Density for h-BN | Near-Theoretical | Lower, Limited |
| Typical Microstructure | Fine-Grained, Dense | Coarser, More Porous |
| Sintering Temperature | Lower | Higher |
| Shape Complexity | Simple (e.g., disks) | Complex Net-Shapes Possible |
| Best For | Maximum Strength & Purity | Cost-Effective, Simple Shapes |
Ready to achieve superior density and performance in your advanced ceramics?
If your goal is to overcome the sintering challenges of difficult materials like h-BN, KINTEK's expertise is your solution. Our vacuum hot press furnaces are engineered to provide the precise combination of heat, pressure, and vacuum environment necessary to force densification and achieve near-theoretical density with superior microstructural integrity.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum hot press furnace can be tailored to your specific R&D or production requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What role do high-power heating plates play in vacuum contact drying furnaces? Unlock Rapid Thermal Diffusion
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?



















