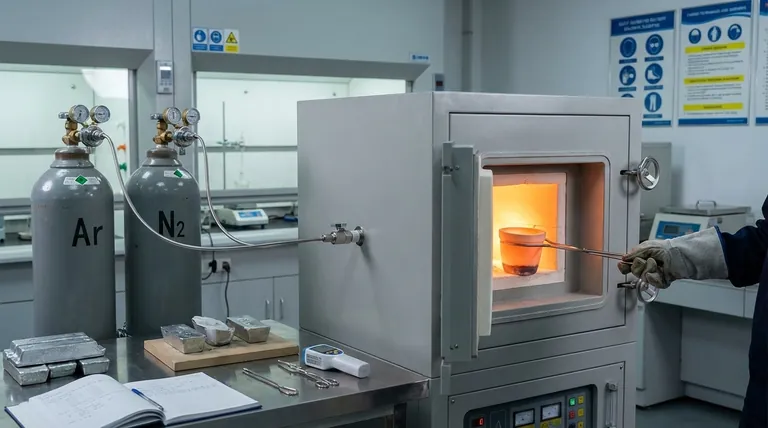
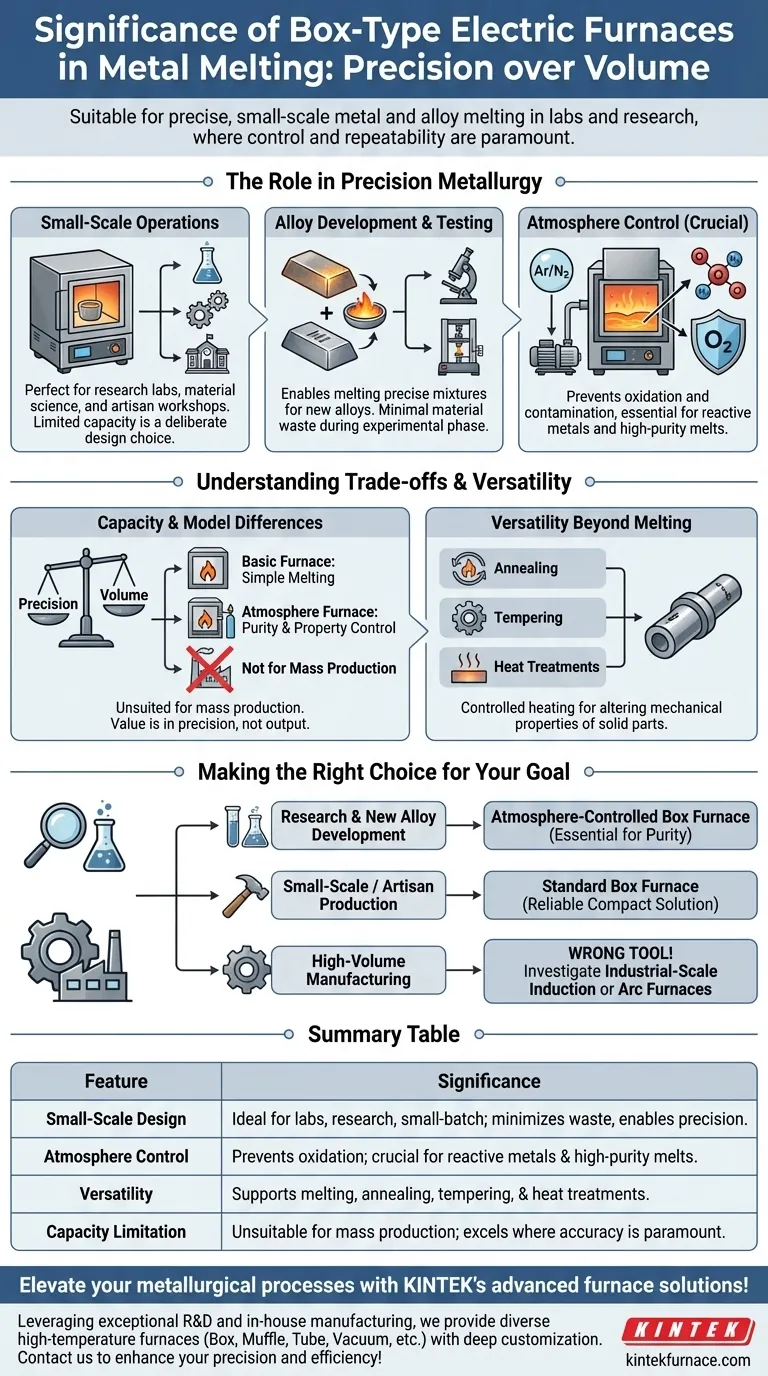
In the context of metal processing, the primary significance of a box-type electric furnace is its suitability for precise, small-scale metal and alloy melting. These furnaces are not designed for large industrial foundries but are indispensable tools in laboratory, research, and small-batch production environments where control and repeatability are paramount.
While larger furnaces handle bulk production, the true significance of the box-type furnace lies in its role as a controlled environment. It enables precise alloy development, material testing, and specialized production where accuracy is more critical than sheer volume.

The Role of Box Furnaces in Precision Metallurgy
The value of a box furnace extends beyond simply heating metal. Its design characteristics make it ideal for specific, high-stakes metallurgical tasks that are impractical or impossible with larger equipment.
Designed for Small-Scale Operations
A defining feature of these furnaces is their limited capacity. This is not a flaw but a deliberate design choice.
They are perfectly scaled for use in research labs, university materials science departments, and small-scale artisan workshops that need to melt manageable quantities of metal.
Enabling Alloy Development and Testing
Box furnaces are fundamental to materials science. They allow metallurgists to melt precise mixtures of different metals in a controlled setting.
This process creates new alloys, which can then be tested for specific properties like hardness, corrosion resistance, or conductivity. The small scale minimizes material waste during this experimental phase.
The Critical Function of Atmosphere Control
Many advanced box-type furnaces are also atmosphere furnaces. This is a key factor in their significance.
These models allow the internal chamber to be filled with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) or operated under a vacuum. This controlled atmosphere prevents oxygen from reacting with the molten metal.
By preventing oxidation and contamination, an atmosphere furnace protects the purity of the melt, which is essential when working with reactive metals or developing high-performance alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To leverage a box furnace effectively, it is crucial to understand its inherent limitations and the distinctions between different models.
Capacity is the Main Constraint
The most obvious trade-off is volume. These furnaces are fundamentally unsuited for mass production or any application requiring large castings. Their value is in precision, not output.
Not All Box Furnaces Are Equal
A basic box furnace provides heat, which is sufficient for simple melting of non-reactive metals.
However, the significant benefits of purity and property control only come with more advanced atmosphere furnace models. It is critical to distinguish between a simple heater and a controlled-environment tool.
Versatility Beyond Melting
The controlled heating capabilities of a box furnace make it useful for other thermal processes. Many are used for annealing, tempering, and other heat treatments designed to alter the mechanical properties of a solid metal part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right equipment depends entirely on your objective. A box furnace is a specialized tool, not a universal solution.
- If your primary focus is research and new alloy development: An atmosphere-controlled box furnace is essential for ensuring the purity and repeatability of your results.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or artisan production: A standard box furnace provides a reliable, compact solution for melting small batches of metal for custom parts or art.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: This is the wrong tool; you need to investigate industrial-scale induction or arc furnaces.
Ultimately, the box-type electric furnace provides a critical capability for controlled, small-volume metallurgical work, bridging the gap between theoretical research and practical application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Significance |
|---|---|
| Small-Scale Design | Ideal for labs, research, and small-batch production, minimizing waste and enabling precise operations. |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation and contamination in alloy development, crucial for reactive metals and high-purity melts. |
| Versatility | Supports not only melting but also annealing, tempering, and other heat treatments for material property control. |
| Capacity Limitation | Unsuitable for mass production but excels in applications where accuracy and repeatability are paramount. |
Elevate your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Box, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for alloy development, material testing, or small-batch production. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your precision and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in sintering? Mastering Electrolyte Tube Densification
- Why is calcination essential for NaFePO4 phase formation? Engineering High-Performance Sodium Iron Phosphate
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- Why is a box muffle furnace used for the 800°C annealing of titanium LMD samples? Optimize Your Material Performance



















