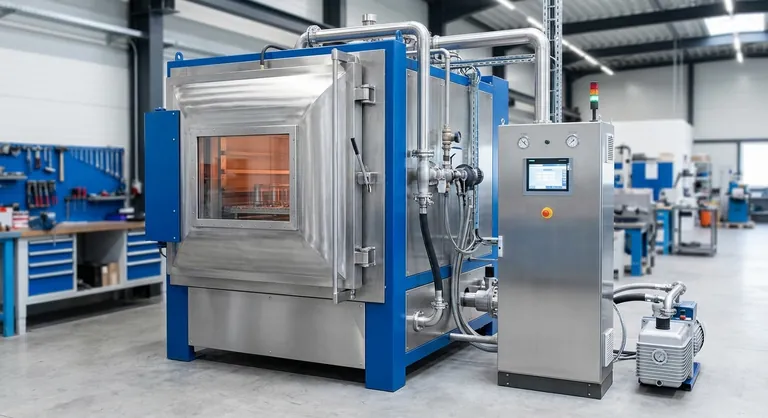
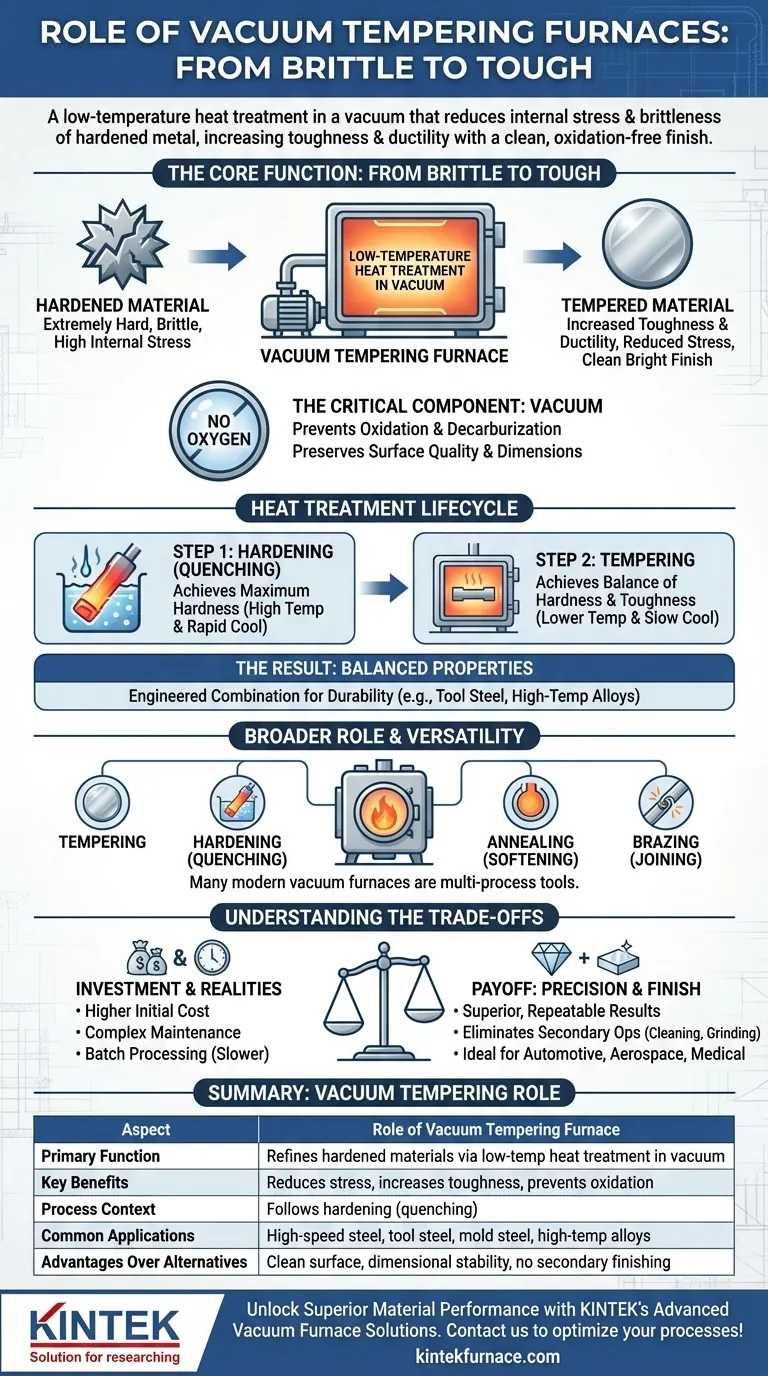
At its core, a vacuum tempering furnace refines a material that has already been hardened. Its specific role is to perform a low-temperature heat treatment in a vacuum, a process that reduces the internal stress and brittleness of a hardened metal, thereby increasing its toughness and ductility without sacrificing all of its hardness. This controlled environment prevents surface oxidation, resulting in a clean, bright part that often requires no further finishing.
The critical distinction to understand is that tempering does not make a material hard; it makes a hardened material usable. Using a vacuum for this process guarantees superior surface quality and dimensional stability, which is often impossible to achieve in a conventional atmospheric furnace.

The Core Function: From Brittle to Tough
To appreciate the role of vacuum tempering, you must first understand the state of the material before it enters the furnace. The process is not a starting point but a crucial finishing step.
The Problem with Hardened Steel
When steel or other alloys are hardened—typically through a process called quenching—their internal crystal structure is transformed to make them extremely hard and wear-resistant.
However, this process also introduces immense internal stress. The result is a material that is exceptionally hard but also very brittle, much like glass. An un-tempered hardened part could easily fracture or shatter under impact or load.
Tempering as the Solution
Tempering is a precise, lower-temperature heat treatment that follows hardening. The part is heated to a specific temperature (well below its hardening temperature), held for a set duration, and then cooled.
This process allows some of the trapped carbon atoms in the crystal structure to precipitate, relieving internal stresses. This reduces brittleness and increases toughness and ductility, making the material resilient enough for its intended application.
Why "Vacuum" is the Critical Component
Performing the tempering process in a vacuum or a controlled low-pressure inert gas environment is what sets this technology apart.
Removing oxygen from the chamber prevents oxidation and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface). This yields a clean, bright, scale-free surface finish straight out of the furnace, preserving the part's precise dimensions and material integrity.
Placing Tempering in the Heat Treatment Lifecycle
Tempering is rarely a standalone process. It is a vital step in a sequence designed to achieve a specific balance of mechanical properties.
Step 1: Hardening (Quenching)
First, the material is heated to a very high temperature and then rapidly cooled, often in the same vacuum furnace using a high-pressure gas quench. This initial step achieves the desired maximum hardness.
Step 2: Tempering
Immediately after hardening, the now-brittle part undergoes tempering. It is reheated to a much lower temperature to achieve the final desired balance of hardness and toughness. The higher the tempering temperature, the tougher but less hard the final product will be.
The Result: A Part with Balanced Properties
The final component has a carefully engineered combination of properties. For example, a tool steel part will be hard enough to hold a cutting edge but tough enough to resist chipping and fracturing during use. Common materials benefiting from this process include high-speed steel, tool steel, mold steel, and high-temperature alloys.
Understanding the Broader Role of Vacuum Furnaces
While some furnaces are dedicated to tempering, the term "vacuum furnace" often describes a highly versatile piece of equipment capable of performing many different thermal processes.
A Multi-Process Tool
Many modern vacuum furnaces are designed for a complete process chain. The same unit can perform vacuum hardening (quenching), annealing (softening), and brazing (joining parts) in addition to tempering.
Specialized Furnace Designs
It is important not to confuse a tempering furnace with other specialized vacuum furnaces. For instance, a vacuum sintering furnace has a different goal: to heat powdered materials (like metal or ceramic powders) until their particles bond to form a solid mass. While both use a vacuum, their functions—refining a solid part versus creating one from powder—are fundamentally different.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing vacuum tempering involves weighing its significant advantages against its operational realities.
The Investment Factor
Vacuum furnaces represent a higher initial capital investment and can have more complex maintenance requirements compared to simpler atmospheric furnaces.
Batch Processing Limitations
Vacuum processes are inherently batch-oriented. Loading the furnace, pumping down to a vacuum, running the cycle, and cooling takes time. This can result in lower throughput compared to continuous-belt atmospheric furnaces.
The Payoff: Unmatched Precision and Finish
The trade-off is for superior, repeatable results. The elimination of oxidation and decarburization reduces or eliminates costly and labor-intensive secondary operations like sandblasting, grinding, or acid cleaning. This precision is non-negotiable for high-performance applications in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct vacuum furnace process depends entirely on your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific balance of hardness and toughness on a finished part: Vacuum quenching followed by vacuum tempering is the definitive process.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, multi-component assemblies with clean joints: Vacuum brazing is the correct application.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, solid component from metal or ceramic powder: You require a specialized vacuum sintering furnace.
- If your primary focus is softening a material to relieve stress or improve its machinability: You should be using a vacuum annealing process.
Ultimately, understanding the specific role of each vacuum process empowers you to select the precise thermal treatment needed to achieve ideal material properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Vacuum Tempering Furnace |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Performs low-temperature heat treatment in a vacuum to refine hardened materials |
| Key Benefits | Reduces internal stress, increases toughness and ductility, prevents oxidation and decarburization |
| Process Context | Follows hardening (quenching) in the heat treatment lifecycle |
| Common Applications | Used for high-speed steel, tool steel, mold steel, and high-temperature alloys in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical |
| Advantages Over Alternatives | Provides clean, bright surface finish, dimensional stability, and eliminates need for secondary finishing operations |
Unlock Superior Material Performance with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Furnace Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, or medical industries, our vacuum tempering furnaces ensure enhanced toughness, reduced brittleness, and oxidation-free results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver reliable, high-performance outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures



















