The primary role of an atmosphere control system is to act as the intelligent core of a program-controlled furnace, ensuring the gaseous environment is perfectly tailored to the material processing requirements. It functions by continuously monitoring the furnace atmosphere and automatically adjusting the gas composition, pressure, and flow rate according to a predefined program, thereby protecting the material and guiding its transformation.
An atmosphere control system transforms a furnace from a simple high-temperature oven into a precision instrument. Its purpose is to execute a programmed sequence of atmospheric changes, protecting the material from unwanted reactions while actively promoting the desired chemical and physical transformations.

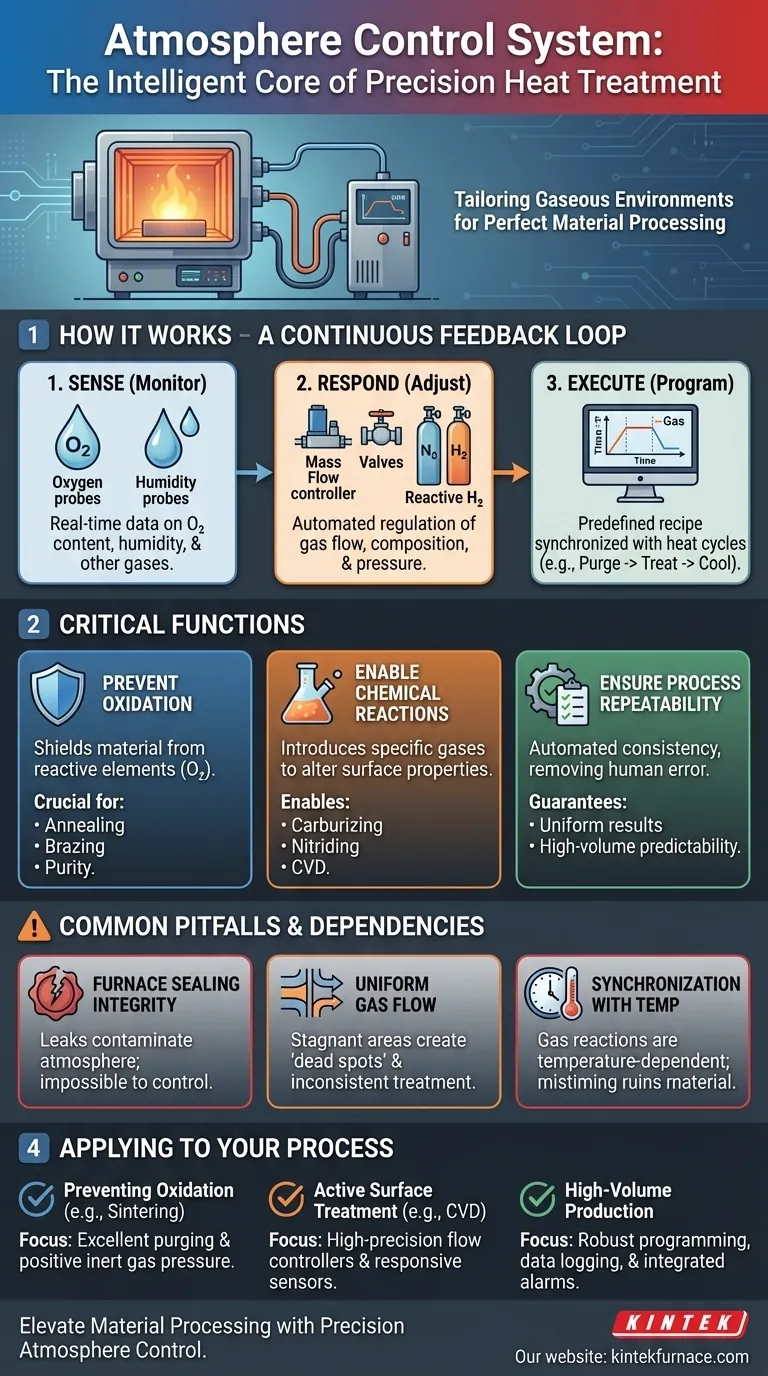
How the Atmosphere Control System Works
The system operates in a continuous feedback loop, much like a thermostat controls temperature. However, instead of just heat, it manages a complex gaseous environment to achieve specific metallurgical or chemical outcomes.
Continuous Monitoring (The Senses)
The system uses specialized sensors to get a real-time picture of the conditions inside the furnace chamber.
Key monitored parameters often include the oxygen content (measured by an oxygen probe) and humidity levels. These readings are critical because even trace amounts of oxygen or water vapor can cause unwanted oxidation at high temperatures.
Automated Adjustment (The Response)
Based on sensor feedback, the control system makes immediate, automated adjustments to maintain the programmed atmosphere.
This involves regulating a series of valves and mass flow controllers. It can increase the flow of an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to purge contaminants or introduce a precise mixture of reactive gases to initiate a specific chemical process on the material's surface.
Program Execution (The Recipe)
The "program-controlled" aspect is what enables complex, multi-stage heat treatments. The system follows a pre-set recipe that dictates how the atmosphere should change over time, in sync with the temperature profile.
For example, a process might start with a nitrogen purge, switch to a hydrogen-rich reducing atmosphere during the high-temperature hold, and finish with another inert gas purge during cooldown.
The Critical Functions of a Controlled Atmosphere
The control system isn't just a safety feature; it is an essential tool for material engineering. Its ability to precisely manage the furnace environment enables several critical functions.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the most fundamental purpose. By creating a chemically inert atmosphere, the system shields the material from reactive elements like oxygen. This is vital for processes like annealing or brazing, where maintaining material purity and a clean surface is paramount.
Enabling Specific Chemical Reactions
Beyond simply being protective, a controlled atmosphere can be reactive. The system can introduce specific gases to intentionally alter the surface of a material.
Processes like carburizing (adding carbon), nitriding (adding nitrogen), or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) rely entirely on the system's ability to deliver a precise, reactive gas mixture at a specific temperature to achieve the desired surface properties.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
In an industrial or research setting, achieving the same result every time is non-negotiable. By automating atmosphere management, the system removes human error and variability.
This ensures that every part processed under the same program experiences the exact same conditions, leading to highly consistent and predictable material properties.
Common Pitfalls and System Dependencies
An atmosphere control system cannot function in isolation. Its effectiveness is directly tied to the integrity of the entire furnace system, and overlooking these dependencies is a common source of failure.
Furnace Sealing Integrity
The most advanced control system is useless if the furnace chamber leaks. Any infiltration of outside air will contaminate the controlled atmosphere, making it impossible for the system to maintain its setpoints. Regular leak checks and proper seal maintenance are essential.
Uniform Gas Flow and Distribution
Effective control depends on the sensors getting a representative reading of the entire chamber. Poor furnace design can lead to "dead spots" where the gas is stagnant. This means the control system might report a perfect atmosphere while parts in another area are oxidizing.
Synchronization with Temperature Control
Gas reactions are highly dependent on temperature. The atmosphere control program and the temperature control program must be perfectly synchronized. Introducing a reactive gas at the wrong temperature can ruin the material or even create a safety hazard.
Applying This to Your Process
The sophistication of the control system you require is directly tied to your material processing goals.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation (e.g., bright annealing, sintering): Your system must excel at purging the chamber and maintaining a positive pressure with a pure, inert gas to prevent any air ingress.
- If your primary focus is active surface treatment (e.g., nitriding, CVD): You need a system with high-precision mass flow controllers and responsive sensors to manage complex, multi-gas reactive mixtures accurately.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for high-volume production: Your system must have robust programming, data logging for quality assurance, and integrated alarms to ensure every cycle is identical and traceable.
Ultimately, investing in the right atmosphere control system provides you with absolute authority over your material's final outcome.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Components | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Inert gases (e.g., nitrogen, argon), oxygen sensors | Protects material purity, avoids contamination |
| Enables Chemical Reactions | Reactive gases, mass flow controllers | Facilitates processes like carburizing, nitriding, CVD |
| Ensures Process Repeatability | Automated programs, data logging | Consistent results, reduced human error, traceability |
| Monitors and Adjusts Atmosphere | Sensors (oxygen, humidity), valves | Real-time feedback, precise gas composition control |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision atmosphere control? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















