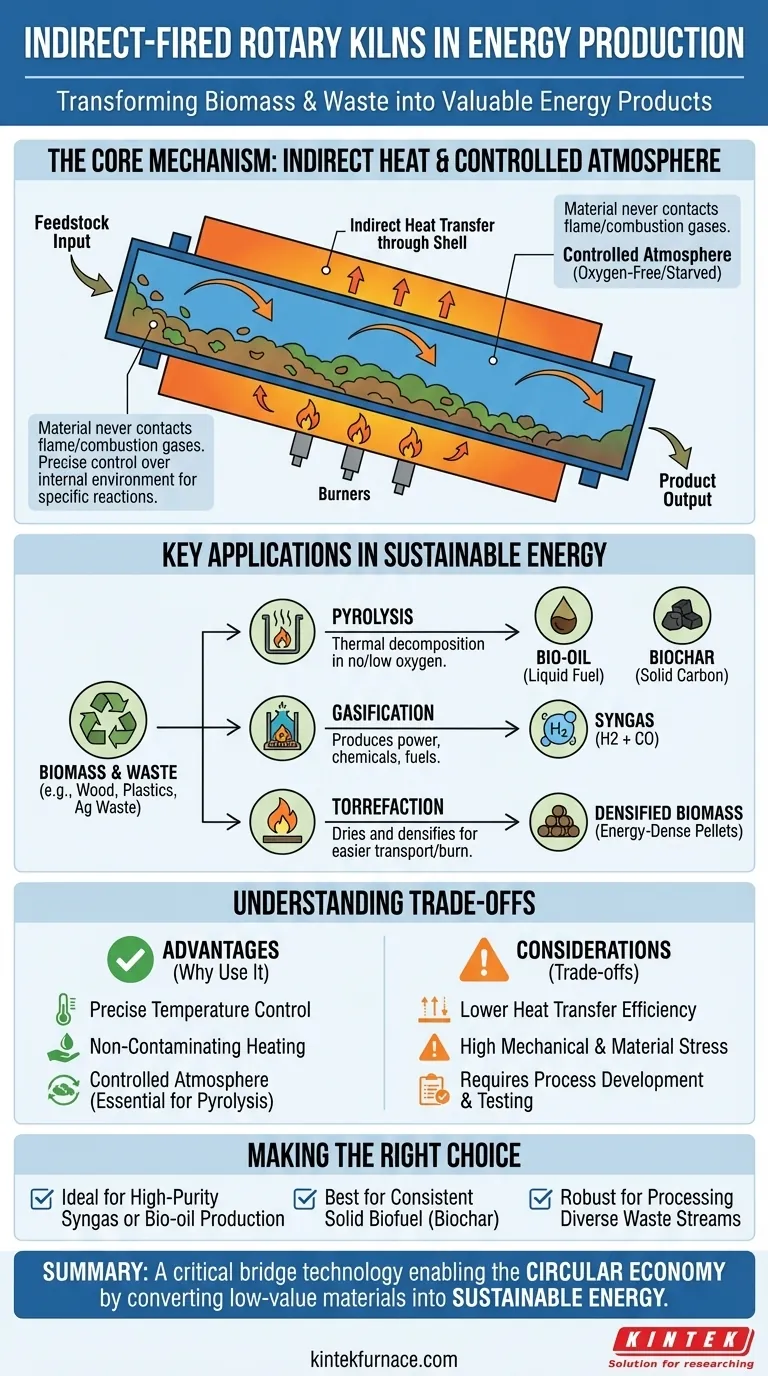
In energy production, the primary role of an indirect-fired rotary kiln is to convert biomass and waste materials into valuable energy products through advanced thermal processes. These kilns are specialized reactors used for pyrolysis, gasification, and torrefaction, creating outputs like syngas, bio-oil, and energy-dense biochar in a highly controlled environment.
The crucial advantage of an indirect-fired kiln is its design: the material being processed never directly contacts the flame or combustion gases used for heating. This separation allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere, which is essential for driving specific chemical reactions needed to create high-quality fuels from biomass and waste.
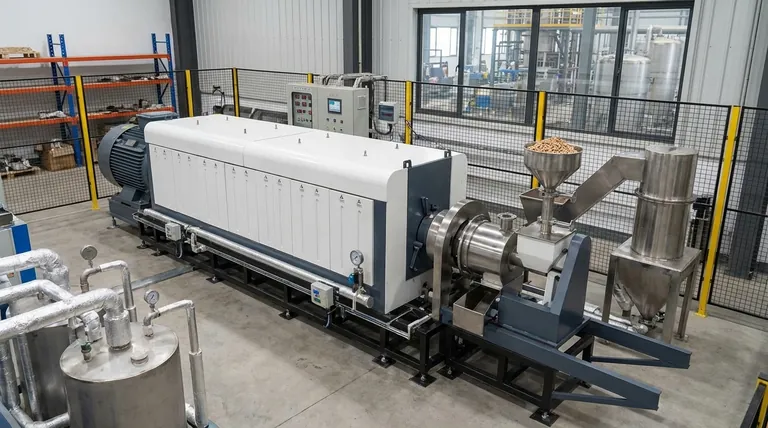

The Core Mechanism: How Indirect Firing Works
A rotary kiln is fundamentally a large, rotating cylinder inclined at a slight angle. Material fed into the higher end tumbles its way down to the lower end as the kiln turns, ensuring all of it is mixed and exposed to heat evenly.
The "Indirect" Difference
Unlike direct-fired kilns where a flame heats the material directly, an indirect-fired kiln is housed inside an external furnace or jacket. The burners heat the outside of the rotating kiln shell, and that heat is then transferred through the shell wall to the material tumbling inside.
Enabling Controlled Atmospheres
This separation is the key to its function in energy production. Because no combustion gases enter the kiln, operators have absolute control over the internal environment. It can be made oxygen-free (inert) or oxygen-starved, which is a mandatory condition for processes like pyrolysis.
Key Applications in Sustainable Energy
The unique capabilities of indirect-fired kilns make them indispensable for specific waste-to-energy and biomass conversion technologies.
Pyrolysis and Gasification
These processes involve heating organic materials (like wood chips, agricultural waste, or plastics) in a low- or no-oxygen environment. This thermal decomposition breaks the material down into valuable products.
- Pyrolysis produces bio-oil (a liquid fuel) and biochar (a solid carbon product).
- Gasification produces syngas (synthesis gas), a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide that can be used to generate power or be converted into other chemicals and fuels.
An indirect kiln is ideal because it can maintain the necessary oxygen-starved atmosphere while providing the high temperatures needed for the reaction.
Biochar and Torrefaction
Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich solid created via pyrolysis that can be used as a soil amendment or as a solid fuel. Torrefaction is a milder thermal process that dries and densifies biomass, creating an energy-dense, coal-like pellet that is easier to transport and burn. Both require precise temperature control to optimize product quality, a key strength of the indirect kiln.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, indirect-fired kilns are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for successful implementation.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
Because heat must conduct through the thick metal shell of the kiln, the overall heat transfer can be less efficient and slower compared to direct-fired systems. This can limit the maximum processing capacity or require a larger, more expensive furnace design.
Mechanical and Material Stress
The kiln shell is subjected to extreme conditions: high temperatures on the outside from the furnace and constant abrasive tumbling of material on the inside. This puts significant stress on the material of construction, typically a high-alloy steel, which requires careful design and maintenance to prevent failure.
The Need for Process Development
As noted by industry experts, these systems are not "plug-and-play." Optimizing the kiln for a specific feedstock—whether it's municipal solid waste, wood chips, or biosolids—requires thorough testing and process development to determine the ideal temperature, rotation speed, and residence time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating an indirect-fired rotary kiln, match its capabilities to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity syngas or bio-oil: The non-contaminating, controlled atmosphere of an indirect kiln is non-negotiable for enabling effective pyrolysis or gasification.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid biofuel like biochar: The precise temperature management and uniform heating of an indirect kiln will deliver a consistent, high-quality product.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or sensitive waste streams: The kiln's flexibility and separation of process gas from flue gas make it a robust choice for converting difficult materials into valuable resources.
Ultimately, the indirect-fired rotary kiln serves as a critical bridge technology, enabling the circular economy by transforming low-value materials into sustainable energy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Converts biomass and waste into energy products via thermal processes like pyrolysis and gasification. |
| Key Processes | Pyrolysis (produces bio-oil and biochar), Gasification (produces syngas), Torrefaction (densifies biomass). |
| Advantages | Controlled atmosphere (oxygen-free), precise temperature management, non-contaminating heating. |
| Limitations | Lower heat transfer efficiency, high mechanical stress, requires process development for specific feedstocks. |
| Ideal For | Producing high-purity syngas, consistent biochar, and processing diverse waste streams sustainably. |
Ready to transform your biomass and waste into clean energy? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for energy production. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our solutions precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your energy conversion processes and drive sustainability in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the key components and parameters of a rotary kiln? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing
- How does a rotary furnace compare to a fixed-bed furnace for powder? Optimize Uniformity in Large-Scale Production
- Why is an industrial-grade rotary reactor necessary in the oil sludge pyrolysis process? Maximize Yield & Efficiency
- What technical requirements are placed on heating equipment for fast pyrolysis? Master High-Yield Bio-Oil Production
- What are the advantages of a rotary kiln for bio-reductants? Achieve Industrial-Scale Uniformity and Scalability



















