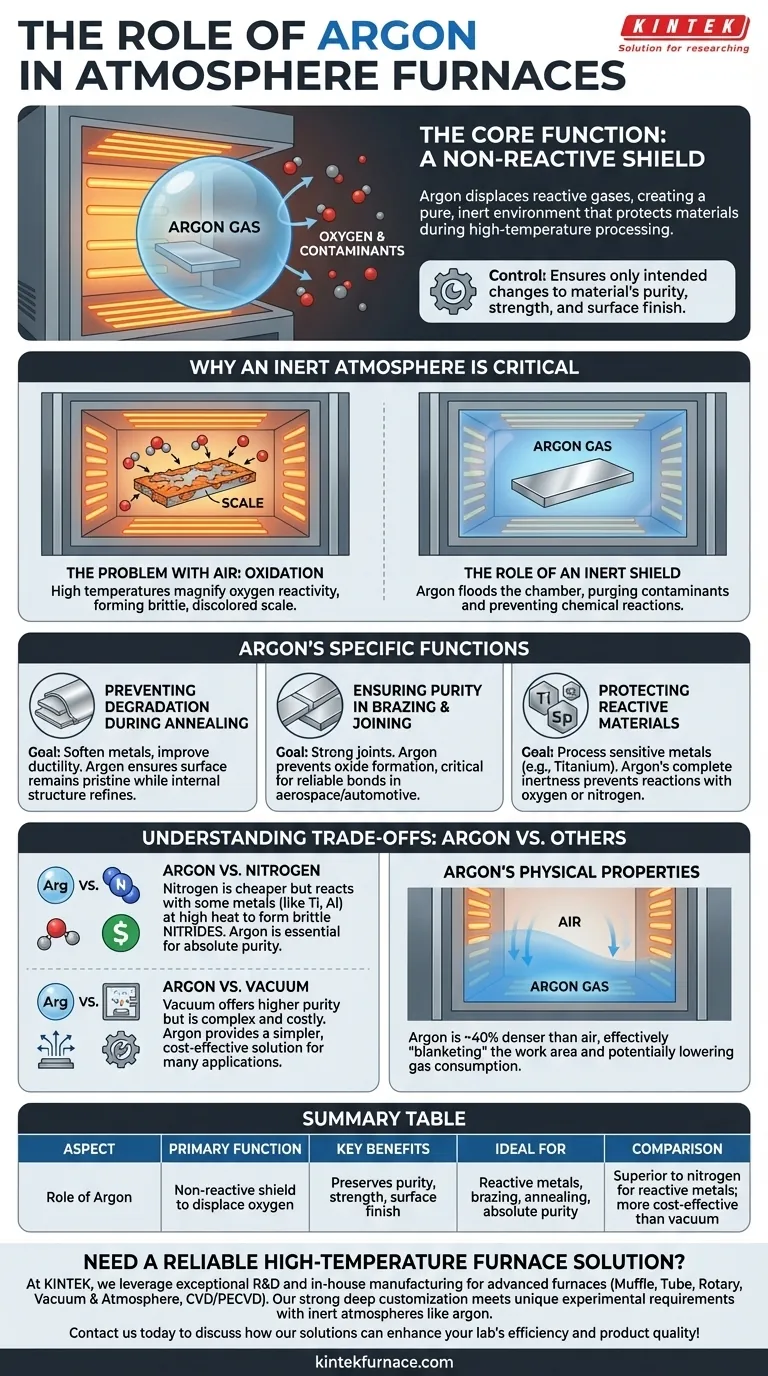
In an atmosphere furnace, argon's primary role is to serve as a completely non-reactive shield. It is pumped into the furnace chamber to displace oxygen and other active gases, creating a pure, inert environment that protects materials from unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation during high-temperature processing.
At its core, using argon is about control. By removing reactive gases from the furnace environment, you ensure that the only changes happening to the material are the ones you intend, preserving its purity, strength, and surface finish.

Why an Inert Atmosphere is Critical
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is only mildly reactive. However, when you heat materials to hundreds or thousands of degrees in a furnace, this reactivity is magnified enormously.
The Problem with Air: Oxidation and Contamination
Heating metals in the presence of oxygen causes oxidation—the same chemical process that causes rust, but happening far more rapidly.
This results in the formation of a brittle, discolored scale on the material's surface. This scale can ruin the part's dimensions, compromise its surface finish, and create impurities that weaken the final product.
The Role of an Inert Shield
An inert gas is one that does not readily participate in chemical reactions. Argon is a noble gas, making it exceptionally stable and non-reactive, even at extreme temperatures.
By flooding the furnace chamber with argon, you physically push out, or purge, the oxygen, water vapor, and other contaminants. This leaves the part surrounded by a protective bubble, ensuring the heat treatment process happens in a pure environment.
Argon's Specific Functions in Heat Treatment
Different processes leverage argon's inert properties to achieve specific outcomes. It is not merely about preventing rust; it is about guaranteeing the intended metallurgical result.
Preventing Degradation During Annealing
Annealing is a process used to soften metals, relieve internal stresses, and improve ductility. The goal is to change the material's internal crystal structure, not its surface chemistry.
If done in air, the surface would oxidize, becoming hard and brittle—the exact opposite of the desired outcome. Argon ensures the surface remains pristine while the internal structure is refined.
Ensuring Purity in Brazing and Joining
Brazing involves joining two pieces of metal using a molten filler material. The success of the joint depends on the filler metal wetting and bonding cleanly to the parent materials.
Oxygen interferes with this process, creating oxides that prevent a strong, continuous bond from forming. Using an argon atmosphere ensures a clean, powerful, and reliable joint, which is critical in aerospace and automotive applications.
Protecting Reactive Materials
Some materials, like titanium and certain specialty stainless steels, are highly reactive at elevated temperatures. They can react not only with oxygen but also with other gases, like nitrogen. Argon's complete inertness makes it the only safe choice for processing these sensitive and expensive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Argon vs. Other Atmospheres
While argon is highly effective, it is not the only option for creating a controlled atmosphere. The right choice depends on the material, the process, and the budget.
Argon vs. Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the most common alternative to argon and is also largely inert. Its primary advantage is that it is significantly less expensive.
However, at very high temperatures, nitrogen can react with certain metals (like titanium, aluminum, and some steels) to form nitrides. These can make the material brittle. Argon does not have this limitation, making it the superior choice for highly reactive metals or when absolute purity is non-negotiable.
Argon vs. Vacuum
A vacuum furnace achieves a pure environment by removing almost all gases, rather than replacing them. A vacuum can provide an even higher level of purity than argon can.
The trade-off is complexity and cost. Vacuum furnaces and their associated pumping systems are more expensive and require more maintenance than a standard atmosphere furnace running on argon. Argon provides a simpler, more cost-effective solution for a vast range of applications.
Argon's Physical Properties
Argon is about 40% denser than air. This is an advantage in some furnace designs, as it can effectively "blanket" the work area, settling at the bottom of the chamber and displacing lighter gases more easily. This can sometimes lead to lower gas consumption compared to a lighter inert gas.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the correct atmosphere is a balance of technical requirements and economic realities. Your decision should be guided by the material you are working with and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for common steels: Nitrogen is often a sufficient and more economical choice for processes like neutral hardening.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity for reactive metals (e.g., titanium, zirconium): Argon is the necessary choice to prevent the formation of brittle nitrides or oxides.
- If your primary focus is flawless brazing or medical-grade components: Argon's superior inertness provides the highest reliability and prevents joint failures or surface contamination.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is fundamental to controlling the properties of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Argon |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Serves as a non-reactive shield to displace oxygen and prevent oxidation |
| Key Benefits | Preserves material purity, strength, and surface finish during high-temperature processing |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals (e.g., titanium), brazing, annealing, and applications requiring absolute purity |
| Comparison | Superior to nitrogen for reactive metals; more cost-effective than vacuum for many uses |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you achieve superior results with inert atmospheres like argon. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing



















