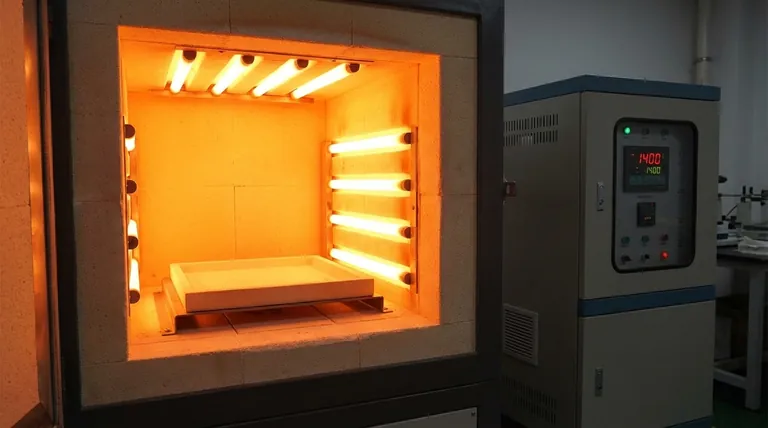
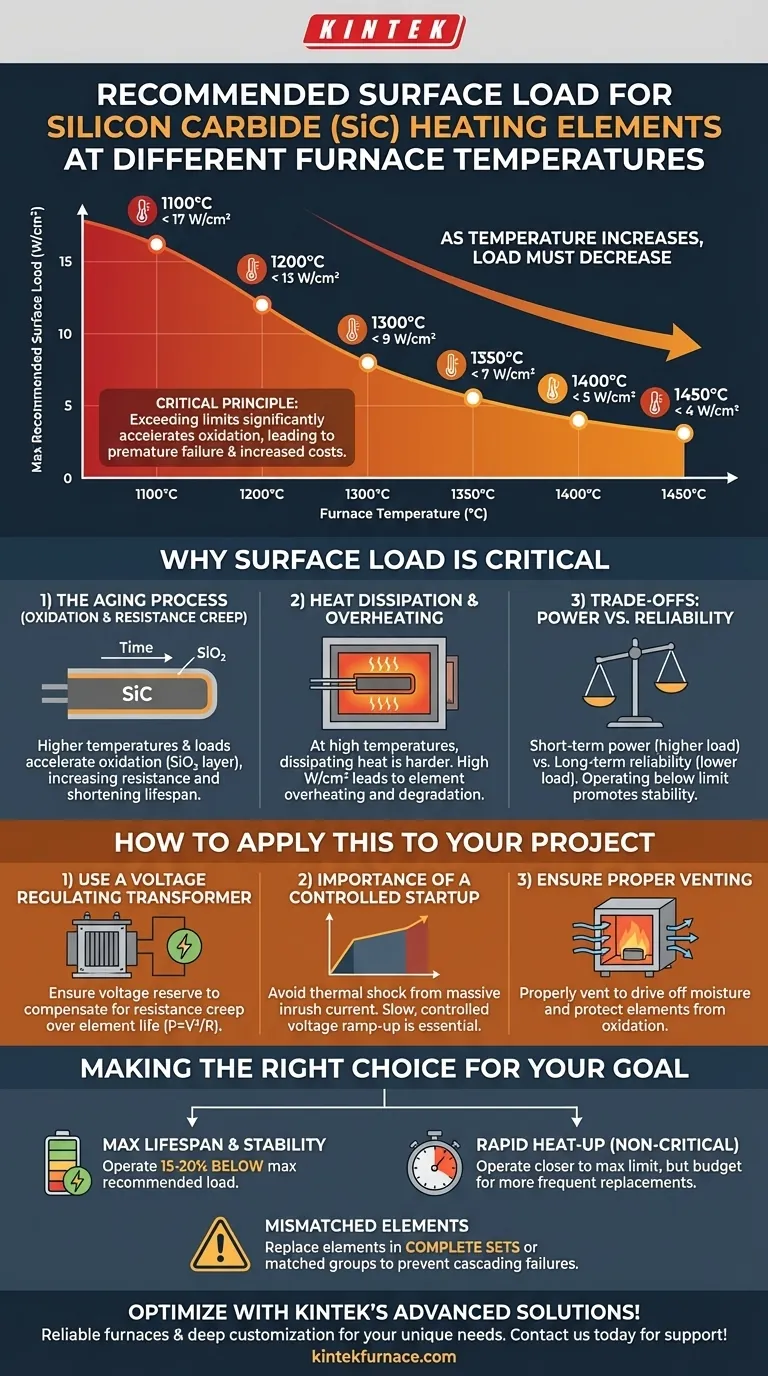
As furnace temperature increases, the recommended surface load for a silicon carbide (SiC) heating element must decrease significantly. To ensure a long operational life, you must respect these limits. For example, at 1100°C the load should be under 17 W/cm², but at 1450°C, it must be reduced to less than 4 W/cm² to prevent premature failure.
The relationship between temperature and surface load is not an arbitrary rule; it is the fundamental principle governing the lifespan of your SiC elements. Exceeding these limits significantly accelerates the oxidation and degradation of the material, leading to premature failure and increased operational costs.

Why Surface Load is Critical for Element Longevity
Understanding the "why" behind these numbers allows you to make better operational decisions. The surface load, measured in watts per square centimeter (W/cm²), is a measure of power density on the element's surface.
The Core Numbers: Load vs. Temperature
Here is a clear breakdown of the maximum recommended surface loads at various operating temperatures. Adhering to these values is the first step in maximizing element life.
- At 1100°C: < 17 W/cm²
- At 1200°C: < 13 W/cm²
- At 1300°C: < 9 W/cm²
- At 1350°C: < 7 W/cm²
- At 1400°C: < 5 W/cm²
- At 1450°C: < 4 W/cm²
The Aging Process: Oxidation and Resistance Creep
All SiC elements age through a process of slow oxidation. This oxidation forms a thin layer of silica (SiO₂) on the element's surface, which causes its electrical resistance to gradually increase over time.
Higher surface loads and higher temperatures both dramatically accelerate this oxidation process, causing the element's resistance to rise much faster and shortening its effective lifespan.
Heat Dissipation and Element Overheating
An element's job is to be hotter than the furnace chamber to transfer heat into it. At very high furnace temperatures, the temperature difference between the element and the chamber is smaller.
This makes it harder for the element to dissipate its heat. If you apply a high power load (high W/cm²) in this environment, the element's surface temperature can become drastically hotter than the furnace setpoint, leading to rapid degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operating a furnace is a balance between performance and cost. Pushing elements to their limits has direct consequences.
Short-Term Power vs. Long-Term Reliability
You can achieve faster furnace heat-up times by running a higher surface load. However, this is a direct trade-off.
Operating near the maximum recommended load will shorten element life, leading to more frequent and costly replacements. Operating well below the limit promotes stability and longevity.
The Danger of Mismatched Elements
As elements age, their resistance increases. If you replace a single failed element in a set with a brand-new one, the new element will have a much lower resistance.
When connected in series with older, high-resistance elements, the new element will draw a disproportionately high amount of power, causing it to run much hotter and fail very quickly. This creates a cycle of cascading failures.
The Importance of a Controlled Startup
A cold SiC element has a lower resistance than a hot one. Applying full voltage at startup will cause a massive inrush of current.
This current surge can create thermal shock, physically cracking or damaging the element before it even reaches operating temperature. A slow, controlled voltage ramp-up is essential.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Moving from theory to practice requires diligent control and planning.
Use a Voltage Regulating Transformer
As the elements age and their resistance increases, you will need to increase the voltage to maintain the same power output (P = V²/R).
Your power supply system, typically using SCRs or voltage-regulating transformers, must have enough "voltage reserve" to compensate for this resistance creep over the full expected life of the elements.
Ensure Proper Venting
The furnace atmosphere plays a role in element life. Moisture and certain process gases can attack the element and accelerate oxidation.
Properly venting the furnace, especially during initial heat-up to drive off moisture, is a simple but critical step to protect your heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should align with your process needs and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum element lifespan and stability: Operate at least 15-20% below the recommended maximum surface load for your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is rapid heat-up for non-critical processes: You can operate closer to the maximum limit, but you must budget for more frequent element replacement.
- If you are replacing elements in an existing furnace: Always replace elements in complete sets or, at minimum, in matched-resistance groups to prevent cascading failures.
By managing surface load effectively, you transform it from a point of failure into a tool for controlling the long-term performance and cost of your high-temperature operations.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Temperature (°C) | Max Recommended Surface Load (W/cm²) |
|---|---|
| 1100 | < 17 |
| 1200 | < 13 |
| 1300 | < 9 |
| 1350 | < 7 |
| 1400 | < 5 |
| 1450 | < 4 |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and extending equipment lifespan. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















