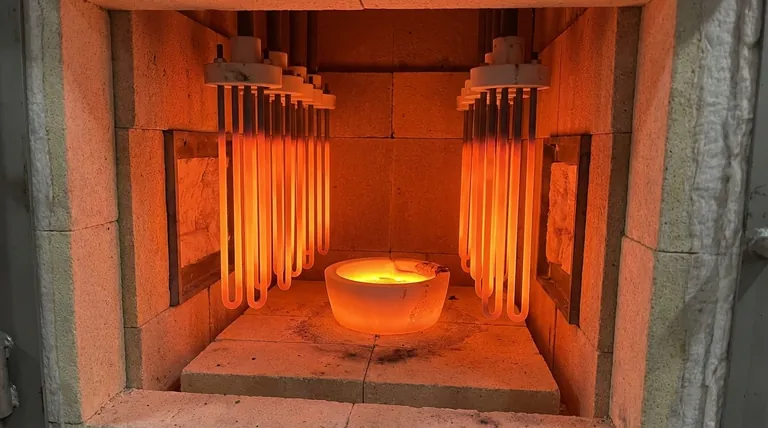
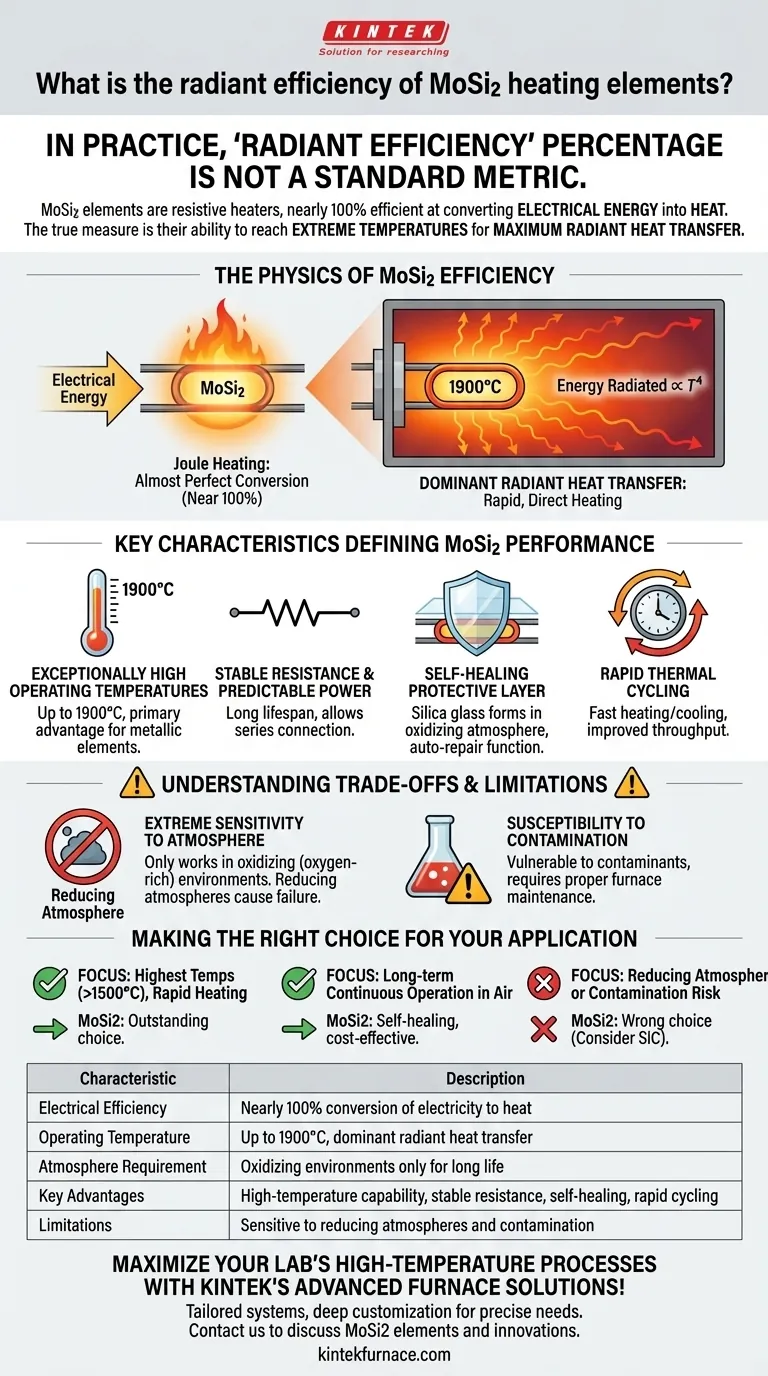
In practice, a specific "radiant efficiency" percentage is not a standard industry metric for Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements. These elements are fundamentally resistive heaters, meaning they are nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat. The true measure of their effectiveness lies in their unparalleled ability to reach extremely high temperatures, which maximizes the transfer of that heat via radiation.
The efficiency of a MoSi2 element isn't defined by a single percentage, but by its core capability: reaching extreme temperatures (up to 1700°C) where radiant heat transfer becomes exceptionally dominant and effective. Your focus should be on matching its unique properties to your specific furnace environment.
The Physics of MoSi2 Efficiency
The term "efficiency" can be misleading. For a heating element, the critical question is not if electricity becomes heat, but how effectively that heat is delivered for a specific purpose at a desired temperature.
From Electricity to Heat
A MoSi2 element is a resistor. According to the principles of Joule heating, virtually all electrical energy passing through it is converted directly into thermal energy. In this sense, its conversion efficiency is almost perfect.
The Power of High Temperature
The real story of MoSi2's efficiency is in radiant heat transfer. The amount of energy an object radiates is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature (T⁴).
Because MoSi2 elements can operate at surface temperatures up to 1900°C, they become incredibly powerful radiators. This allows for rapid, direct heating of materials inside a furnace, making the entire process faster and more energy-efficient.
Key Characteristics Defining MoSi2 Performance
The practical advantages of MoSi2 elements stem from a unique combination of material properties that make them ideal for high-temperature applications.
Exceptionally High Operating Temperatures
MoSi2 elements are designed for furnace temperatures between 1600°C and 1700°C, among the highest available for metallic heating elements. This capability is their primary advantage.
Stable Resistance and Predictable Power
These elements maintain a stable electrical resistance over their long lifespan. This stability allows for predictable power consumption and performance, and critically, it means new elements can be connected in series with older ones without issue.
The Self-Healing Protective Layer
In an oxygen-rich atmosphere, MoSi2 develops a protective outer layer of silica glass. This layer prevents internal oxidation of the element, giving it an auto-repair function and contributing to its remarkably long life expectancy in continuous operation.
Rapid Thermal Cycling
The material can withstand fast heating and cooling cycles without degradation. This feature is crucial for processes that require frequent temperature changes, improving throughput and reducing energy waste during idle periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No heating element is perfect for every situation. The high performance of MoSi2 comes with specific operational requirements that are critical to understand.
Extreme Sensitivity to Atmosphere
The protective silica layer that gives MoSi2 its long life only forms in an oxidizing (oxygen-rich) environment. Using these elements in a reducing atmosphere will strip this layer away, leading to rapid failure.
Susceptibility to Contamination
The elements are vulnerable to contamination. For example, failing to properly dry painted or colored zirconia before firing can release compounds that attack the element, significantly shortening its life. Proper furnace maintenance is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching its strengths and weaknesses to your specific operational goals and environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible process temperatures (>1500°C) with rapid heating: MoSi2 is an outstanding choice due to its superior temperature capability and radiant output.
- If your primary focus is long-term, continuous operation in an air or oxygen-rich atmosphere: The self-healing properties of MoSi2 provide exceptional lifespan and reliability, making it a cost-effective solution.
- If your process involves a reducing atmosphere or a risk of chemical contamination: MoSi2 is likely the wrong choice; its lifespan will be severely compromised, and an alternative like Silicon Carbide (SiC) may be more suitable.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of a MoSi2 element is realized when it is deployed in the high-temperature, oxidizing environment for which it was designed.

Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Efficiency | Nearly 100% conversion of electricity to heat |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1900°C, enabling dominant radiant heat transfer |
| Atmosphere Requirement | Oxidizing environments only for long life |
| Key Advantages | High-temperature capability, stable resistance, self-healing, rapid cycling |
| Limitations | Sensitive to reducing atmospheres and contamination |
Maximize your lab's high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you require rapid thermal cycling, stable performance, or operation in oxidizing atmospheres. Contact us today to discuss how our MoSi2 heating elements and other innovations can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















