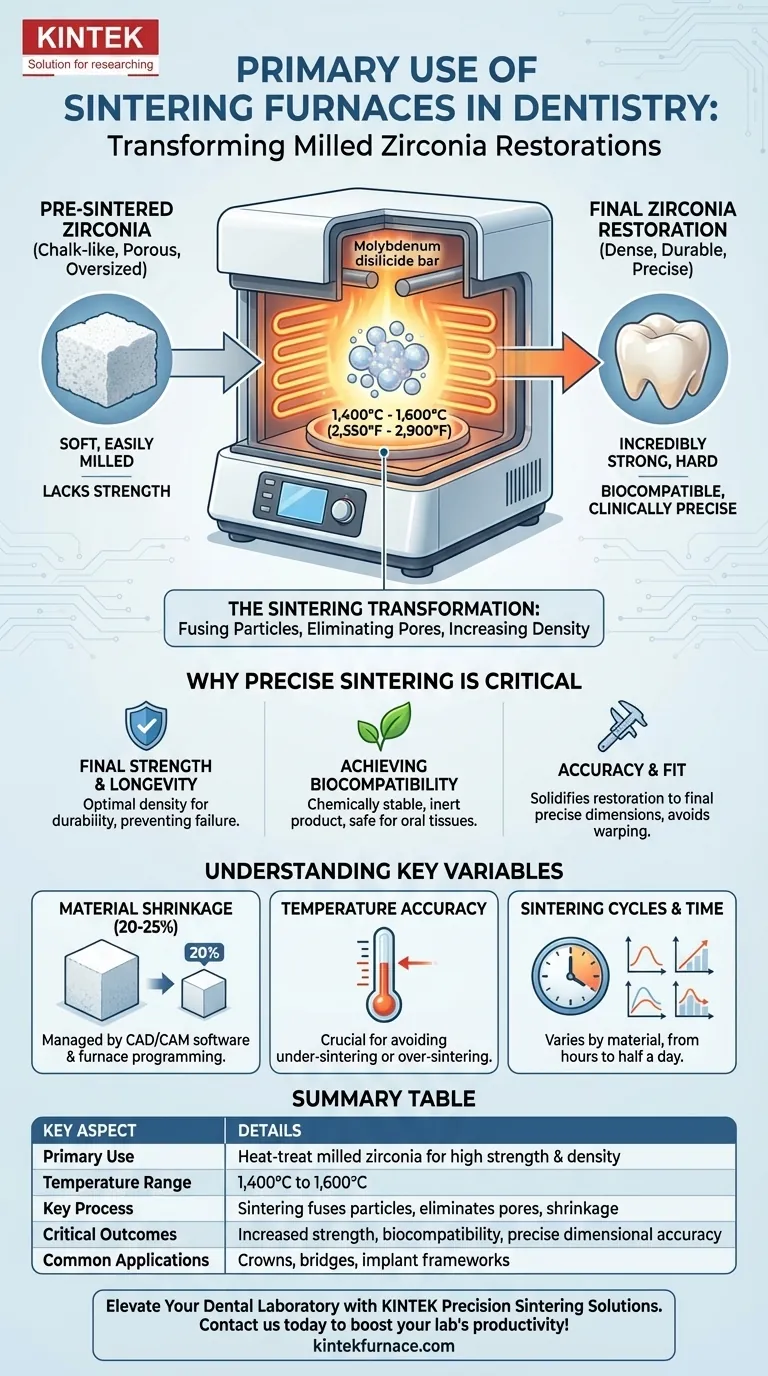
In modern dental laboratories, the primary use of a sintering furnace is to heat-treat and transform milled zirconia restorations into their final, high-strength state. This crucial step takes a soft, chalk-like pre-sintered material and, through precisely controlled high temperatures, converts it into the dense, durable ceramic used for crowns, bridges, and implant frameworks.
A sintering furnace is not merely an oven; it is a transformation device. Its core purpose is to complete the material science of zirconia, converting a fragile, oversized milling into a strong, biocompatible, and precisely dimensioned final restoration.
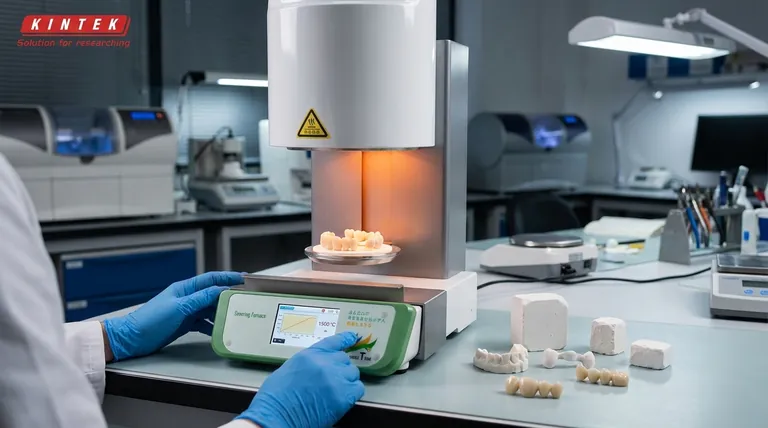

From Chalk to Ceramic: The Sintering Transformation
The journey of a zirconia restoration from a digital file to a clinical reality hinges on the sintering process. The furnace is where the material acquires the properties that make it a leading choice in restorative dentistry.
The Starting Point: Pre-Sintered Zirconia
Before entering the furnace, the dental restoration is milled from a block of partially sintered zirconia. In this "green" or "white" state, the material is soft, porous, and chalky, which allows it to be milled easily and quickly.
However, at this stage, it lacks the necessary strength for clinical use and is intentionally oversized to account for the next step.
The High-Temperature Transformation
Inside the furnace, the zirconia is subjected to extremely high temperatures, often between 1,400°C and 1,600°C (2,550°F to 2,900°F). These temperatures are typically achieved using powerful heating elements, such as molybdenum disilicide.
This intense heat causes the individual zirconia particles to fuse together, a process known as sintering.
The Outcome: Density and Strength
As the particles fuse, the pores between them are eliminated. This process dramatically increases the material's density and causes it to shrink.
The result is a final restoration that is incredibly strong, hard, and resistant to fracture, possessing the durability required to withstand the forces of chewing.
Why Precise Sintering Is Critical for Success
The quality of the sintering process directly impacts the final clinical outcome. It is the step that guarantees the structural integrity and fit of the final prosthesis.
Ensuring Final Strength and Longevity
The primary goal of sintering is to achieve the optimal density and strength of the zirconia. An incomplete or improperly controlled sintering cycle will result in a weaker restoration that is more prone to failure in the patient's mouth.
Achieving Biocompatibility
The sintering process creates a chemically stable and inert final product. This ensures the restoration is biocompatible, meaning it will not cause adverse reactions with the surrounding oral tissues.
Impact on Accuracy and Fit
The final fit of a crown or bridge is non-negotiable. The sintering process is what solidifies the restoration into its final, precise dimensions. Inconsistent heating can lead to warping or unpredictable shrinkage, compromising the fit.
Understanding the Key Variables
Achieving a perfect outcome is not automatic. It requires managing several critical variables inherent to the sintering process.
The Challenge of Material Shrinkage
Zirconia undergoes significant and predictable shrinkage during sintering, often around 20-25%. This is the most critical factor to manage.
CAD/CAM software must accurately calculate this shrinkage and design an oversized restoration for milling. The furnace must then execute the heating program flawlessly to match the shrinkage factor used in the design cálculos.
The Need for Temperature Accuracy
The furnace's ability to hit and hold precise temperatures is paramount. Deviations from the manufacturer's recommended temperature cycle can lead to a restoration that is under-sintered (weak) or over-sintered (potentially brittle or discolored).
Sintering Cycles and Time
Different types of zirconia (such as high-strength vs. high-translucency) require different sintering programs, or "cycles." These cycles dictate the heating rate, holding times, and final temperature, and can range from a few hours to over half a day.
Applying This to Your Dental Workflow
Understanding the role of a sintering furnace allows you to better control the quality and consistency of your zirconia restorations.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Prioritize a furnace with verified temperature accuracy and follow the zirconia manufacturer's sintering protocols宗教 to achieve optimal density and strength.
- If your primary focus is restoration accuracy: Ensure your CAD software's shrinkage factor is perfectly calibrated to your specific furnace and the zirconia material you are using.
- If your primary focus is workflow efficiency: Investigate modern furnaces with shorter, "speed sintering" cycles, but verify they are approved for your chosen zirconia to avoid compromising material properties.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is fundamental to transforming digital designs into durable, high-quality clinical realities.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Heat-treat milled zirconia to achieve high strength and density for dental restorations |
| Temperature Range | 1,400°C to 1,600°C (2,550°F to 2,900°F) |
| Key Process | Sintering fuses zirconia particles, eliminating pores and causing shrinkage |
| Critical Outcomes | Increased strength, biocompatibility, and precise dimensional accuracy |
| Common Applications | Crowns, bridges, and implant frameworks in dental laboratories |
Elevate Your Dental Laboratory with Precision Sintering Solutions from KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need reliable sintering for zirconia restorations or tailored systems for enhanced workflow efficiency, we deliver durable, high-performance equipment that ensures optimal material properties and clinical outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss how our sintering furnaces can transform your dental restorations and boost your lab's productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision



















