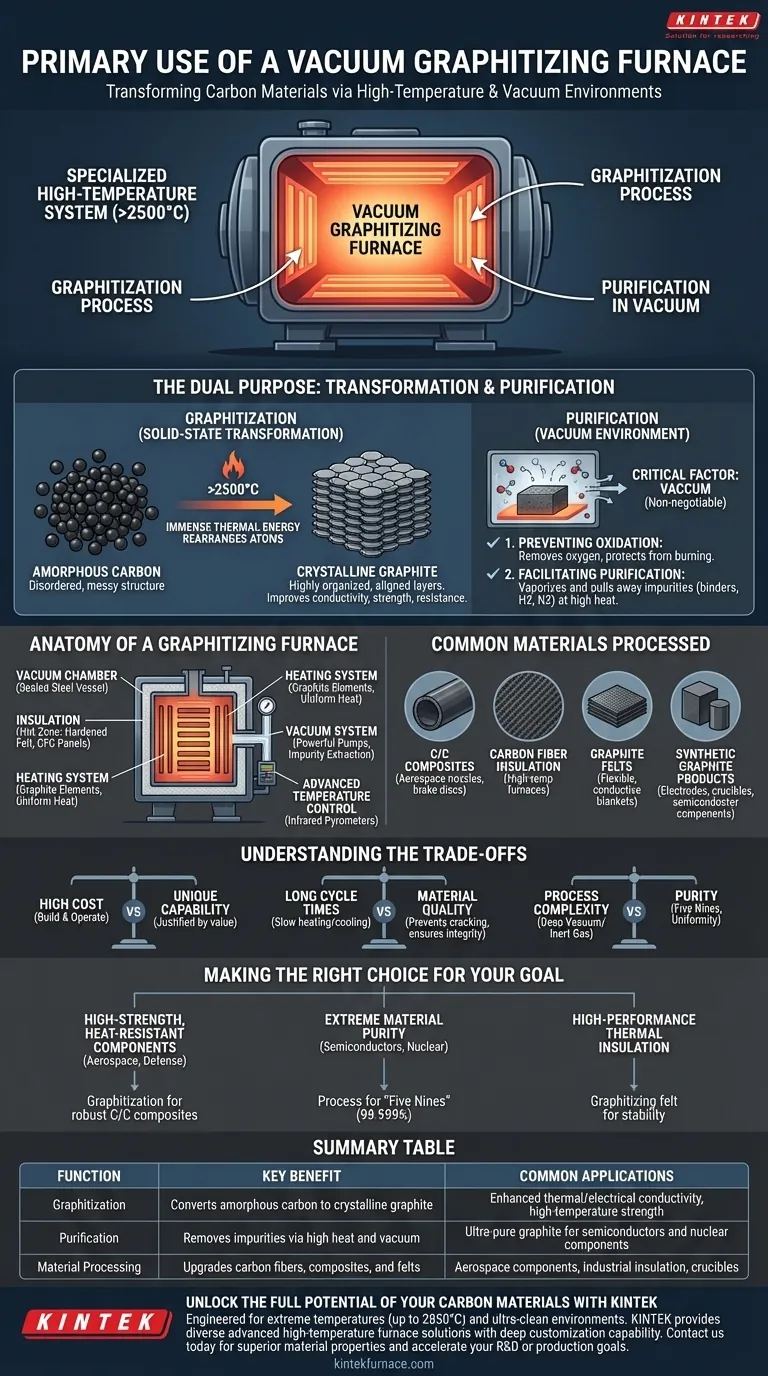
At its core, a vacuum graphitizing furnace is a specialized high-temperature system used to transform carbon-based materials into a pure, crystalline graphite structure. It achieves this by heating materials in a controlled vacuum environment to extreme temperatures, often exceeding 2500°C, which fundamentally alters their atomic arrangement and purifies them.
The primary purpose of a vacuum graphitizing furnace is not just to heat materials, but to enable the graphitization process—the conversion of amorphous carbon into ordered, crystalline graphite. The vacuum is critical to prevent the material from oxidizing (burning up) and to remove impurities at the extreme temperatures required for this transformation.

The Dual Purpose: Transformation and Purification
A vacuum graphitizing furnace serves two interconnected functions that are essential for creating high-performance carbon materials. Understanding these two roles clarifies its importance in modern manufacturing.
What is Graphitization?
Graphitization is a solid-state transformation. It uses immense thermal energy to force disordered, amorphous carbon atoms to rearrange themselves into the highly organized, layered lattice structure of crystalline graphite.
Think of it as turning a messy pile of bricks (amorphous carbon) into a strong, perfectly aligned wall (graphite). This structural change dramatically improves the material's thermal and electrical conductivity, strength at high temperatures, and resistance to chemical attack.
Why a Vacuum is Essential
Operating at temperatures up to 2850°C makes the atmosphere inside the furnace a critical factor. A vacuum environment is non-negotiable for two key reasons:
- Preventing Oxidation: In the presence of air (oxygen), carbon materials would simply ignite and burn away at these temperatures. The vacuum removes oxygen, protecting the product from complete destruction.
- Facilitating Purification: The combination of high heat and low pressure causes impurities within the material (such as residual binders, hydrogen, or nitrogen) to vaporize and be pulled away by the vacuum system, resulting in an ultra-pure final product.
Common Materials Processed
This process is vital for upgrading the properties of specific carbon-based materials for demanding applications.
Key examples include:
- Carbon-Carbon (C/C) Composites: For aerospace components like rocket nozzles and brake discs.
- Carbon Fiber Insulation: For use in other high-temperature furnaces.
- Graphite Felts: To create flexible, conductive, and heat-resistant insulation blankets.
- Synthetic Graphite Products: For electrodes, crucibles, and components used in the semiconductor industry.
Anatomy of a Graphitizing Furnace
While designs vary, the core components are engineered to withstand one of the most extreme industrial processes.
The Vacuum Chamber and Insulation
This is the sealed steel vessel where the process occurs. It is lined with a "hot zone"—a sophisticated package of graphite-based insulation, such as hardened felt and CFC panels, which contains the intense radiant heat and protects the outer chamber shell.
The Heating System
The immense temperatures are generated by large graphite heating elements. These elements use electrical resistance to generate heat. The design must ensure uniform temperature distribution across the entire workload, which is critical for consistent material properties.
The Vacuum System
A combination of powerful pumps works to first remove the air from the chamber and then to extract the gaseous impurities that are released from the material during the heating cycle.
Advanced Temperature Control
Standard thermocouples cannot survive graphitizing temperatures. Instead, these furnaces rely on infrared pyrometers aimed at the workload. These devices measure temperature from a distance by reading the thermal radiation, allowing for precise control of the heating and cooling profiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology involves significant operational considerations that represent fundamental trade-offs.
High Cost vs. Unique Capability
Vacuum graphitizing furnaces are exceptionally expensive to build and operate due to their complex systems and the extreme conditions they endure. This cost is justified only by the unique and high-value material properties that cannot be achieved through any other method.
Long Cycle Times vs. Material Quality
Heating a large mass to over 2500°C and then cooling it down is an inherently slow process, often taking several days per batch. Rushing the cycle can induce thermal stress and crack the product. The trade-off is between manufacturing throughput and final product integrity.
Process Complexity vs. Purity
While a deep vacuum is standard, some processes require backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like argon. This can help improve heat uniformity and suppress the vaporization of the graphite product itself at peak temperature, but it adds another layer of cost and control complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Specifying a graphitization process depends entirely on the performance requirements of your final material.
- If your primary focus is creating high-strength, temperature-resistant components: Graphitization is essential for producing robust C/C composites for aerospace, defense, and high-performance motorsports.
- If your primary focus is extreme material purity: This process is the only way to achieve the "five nines" (99.999%) purity required for graphite used in semiconductor manufacturing and nuclear applications.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing high-performance thermal insulation: Graphitizing carbon felt dramatically increases its thermal stability and performance for use inside other vacuum furnaces.
Ultimately, mastering the graphitization process is key to unlocking the full potential of advanced carbon and graphite materials for the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Graphitization | Converts amorphous carbon to crystalline graphite | Enhanced thermal/electrical conductivity, high-temperature strength |
| Purification | Removes impurities via high heat and vacuum | Ultra-pure graphite for semiconductors and nuclear components |
| Material Processing | Upgrades carbon fibers, composites, and felts | Aerospace components, industrial insulation, crucibles |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Carbon Materials with KINTEK
Are you developing high-performance components for aerospace, semiconductor, or advanced industrial applications? Our vacuum graphitizing furnaces are engineered to deliver the extreme temperatures (up to 2850°C) and ultra-clean environments required for precise graphitization and purification.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve superior material properties and accelerate your R&D or production goals. Reach out via our contact form for a customized solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing



















