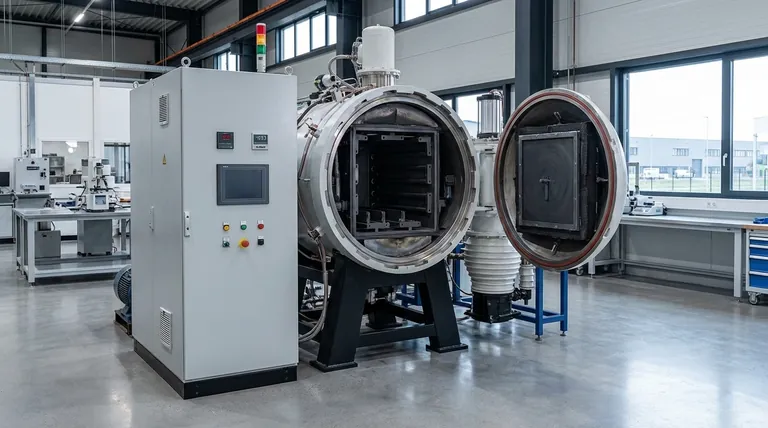
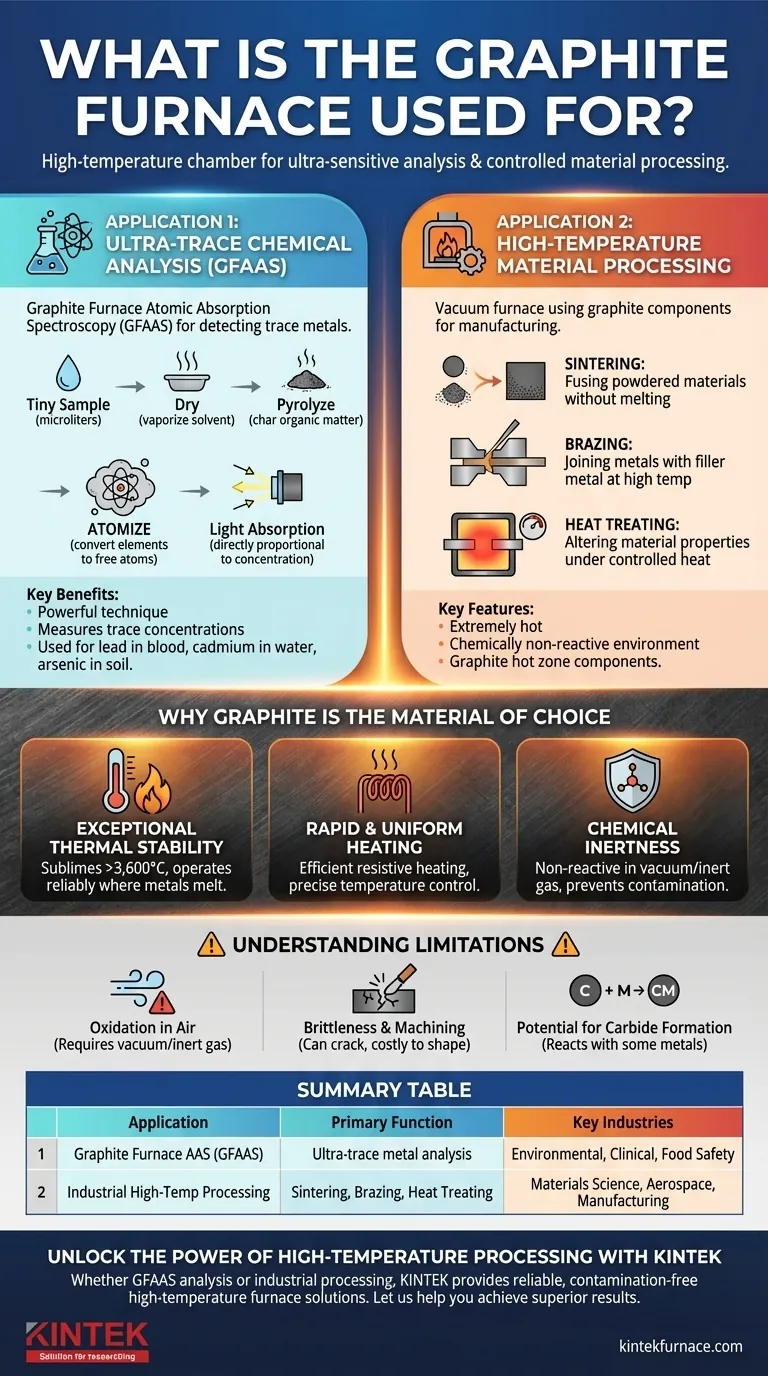
At its core, a graphite furnace is a high-temperature chamber used for two distinct but related purposes: performing ultra-sensitive chemical analysis and processing materials under controlled conditions. In analytical chemistry, it is the central component of a technique called Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) for detecting trace metals. In industrial settings, vacuum furnaces use graphite components for high-temperature processes like heat treating, brazing, and sintering materials.
The term "graphite furnace" can be confusing because it refers to both a specific analytical instrument and a general class of industrial furnaces. The common thread is the use of graphite for its unparalleled ability to withstand extreme heat while remaining chemically stable.

The Two Primary Applications
The function of a graphite furnace is best understood by separating its two main uses: one in the laboratory for measurement, and one in manufacturing for material transformation.
Application 1: Ultra-Trace Chemical Analysis (GFAAS)
A graphite furnace is the namesake component in Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS). This is a powerful analytical technique.
The furnace's role is to take a tiny liquid sample (microliters) and heat it in a series of precise steps. This process dries, pyrolyzes (chars), and finally atomizes the sample, converting the elements of interest into a cloud of free atoms inside a graphite tube.
Light from a specific lamp is then passed through this atomic vapor. The atoms absorb the light, and the amount of absorption is directly proportional to the element's concentration.
GFAAS is the method of choice for measuring trace and ultra-trace concentrations of metals in complex samples, such as lead in blood, cadmium in water, or arsenic in soil.
Application 2: High-Temperature Material Processing
In industrial and materials science contexts, the term often refers to a vacuum furnace that uses graphite components. Graphite is used for heating elements, insulation, and the fixtures that hold parts (trays, racks, baskets).
These furnaces leverage graphite's properties to create an extremely hot, chemically non-reactive environment. This is essential for processes like:
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials together with heat (but without melting) to create a solid object.
- Brazing: Joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal at high temperatures.
- Heat Treating: Altering the physical and chemical properties of a material through controlled heating and cooling, often in a vacuum to prevent oxidation.
In this context, the entire furnace isn't made of graphite, but its critical internal "hot zone" components are.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
Graphite is not used by accident. Its unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes it ideal for these demanding high-temperature applications.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes (turns directly from a solid to a gas) at an incredibly high temperature, over 3,600°C (6,500°F). This allows it to operate reliably at temperatures that would melt most metals.
Rapid & Uniform Heating
Graphite has excellent electrical conductivity and resistance, making it a highly efficient resistive heating element. An electric current passed through it generates intense, uniform heat very quickly. This allows for precise temperature control, which is critical for both analytical accuracy and material processing.
Chemical Inertness
In a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon), graphite is extremely non-reactive. It will not contaminate the sample in an GFAAS analysis or react with the materials being processed in an industrial furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, graphite is not a perfect material. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Oxidation in Air
Graphite's most significant weakness is its reaction with oxygen at high temperatures. It will literally burn away, converting to CO and CO2 gas. This is why graphite furnaces must be operated in a vacuum or flooded with an inert gas to protect the graphite components from destruction.
Brittleness and Machining
Unlike metals, graphite is brittle and can crack or fracture if subjected to mechanical shock. Machining graphite into the complex shapes required for heating elements and fixtures is a specialized process that can be more costly than working with conventional metals.
Potential for Carbide Formation
At very high temperatures, the carbon in graphite can react with certain metals (like titanium or tungsten) to form metal carbides. While sometimes this is a desired outcome (in carbide manufacturing), it can be an unwanted source of contamination or material alteration in other applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding which "graphite furnace" you are dealing with is a matter of context. Your application will define the furnace's specific role.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis of trace elements: You are working with a Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (GFAAS), where the furnace's job is precise and rapid sample atomization.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing: You are using a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace with graphite components to leverage its thermal stability for tasks like sintering, brazing, or heat treating.
Ultimately, graphite is the enabling material for achieving extreme temperatures in a controlled, non-contaminating environment.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite Furnace AAS (GFAAS) | Ultra-trace metal analysis | Environmental, Clinical, Food Safety |
| Industrial High-Temp Processing | Sintering, Brazing, Heat Treating | Materials Science, Aerospace, Manufacturing |
Unlock the Power of High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Whether your work requires the precise trace analysis capabilities of a GFAAS system or the robust material transformation of an industrial high-temperature furnace, the core challenge is achieving reliable, contamination-free results at extreme heat. KINTEK specializes in solving this challenge.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your analytical precision or manufacturing efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability



















