In short, the future outlook is exceptionally strong. Three-zone tube furnaces are transitioning from specialized equipment to strategic infrastructure for any organization serious about materials innovation. Their adoption is set to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for precise, repeatable, and flexible thermal processing required to develop the next generation of advanced materials.
The core reason for their growing importance is simple: creating tomorrow's materials requires a level of thermal control that older, single-zone furnaces cannot provide. The ability to program distinct, stable temperature profiles across three zones is the key to unlocking new material properties and enabling breakthroughs in energy, electronics, and medicine.

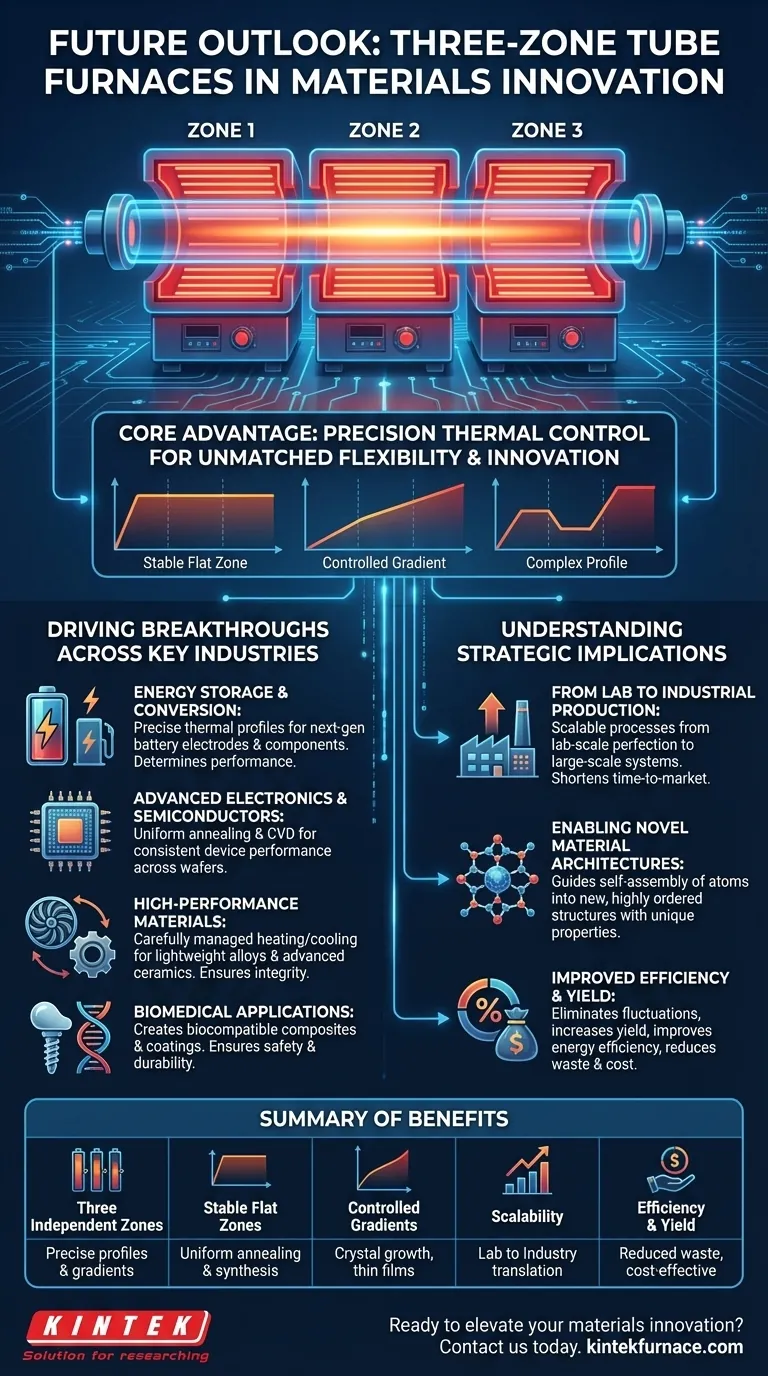
The Core Advantage: Precision Thermal Control
The fundamental value of a three-zone furnace lies in its ability to manipulate the thermal environment with unparalleled precision. This is not an incremental improvement; it is a capability that opens entirely new avenues for research and production.
Three Zones for Unmatched Flexibility
Unlike a single-zone furnace that maintains one uniform temperature, a three-zone furnace has three independent heating elements. Each zone can be programmed with its own distinct temperature profile.
This allows researchers to create a stable, extended flat zone of uniform temperature in the center, which is critical for processes like annealing semiconductor wafers. Alternatively, it allows for a stepped temperature profile for complex synthesis reactions.
Creating Precise Temperature Gradients
The independent zones can be used to establish a controlled temperature gradient—a gradual increase or decrease in temperature—along the length of the tube.
This capability is vital for processes like crystal growth, thin film deposition, and nanoparticle synthesis, where the rate of temperature change directly influences the material's final structure, phase, and properties.
Simulating Complex Thermal Environments
By programming the three zones, operators can accurately simulate complex thermal conditions found in industrial processes or extreme applications. This de-risks development and allows for rapid optimization of material synthesis without expensive, full-scale production runs.
Driving Breakthroughs Across Key Industries
The precise control offered by three-zone furnaces is not a theoretical benefit. It is a direct enabler of innovation in the most demanding and fastest-growing technology sectors.
Energy Storage and Conversion
These furnaces are crucial for fabricating next-generation battery electrodes and fuel cell components. The exact thermal profile during synthesis and sintering determines the material's porosity, crystalline structure, and electrochemical performance.
Advanced Electronics and Semiconductors
In electronics, perfection is the standard. Three-zone furnaces are used for the annealing of semiconductor wafers and the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of thin films. Precise temperature uniformity ensures consistent device performance across the entire wafer.
High-Performance Materials
The creation of lightweight, high-strength alloys and the sintering of advanced ceramics depend on carefully managed heating and cooling cycles. Even minor deviations can introduce stress or impurities, compromising the final product's integrity.
Biomedical Applications
Three-zone furnaces are used to create biocompatible composites and coatings for medical implants and devices. The ability to control the thermal process ensures the resulting material is safe, durable, and performs its intended biological function without adverse reactions.
Understanding the Strategic Implications
Investing in a three-zone furnace is more than a simple equipment purchase; it's a strategic decision that positions an organization for future success.
From Lab-Scale Research to Industrial Production
The principles of multi-zone heating are scalable. Processes and material recipes perfected in a lab-scale three-zone furnace can be more reliably translated to larger, industrial thermal processing systems, shortening the time from discovery to market.
Enabling Novel Material Architectures
This technology allows scientists to create materials that were previously impossible. By carefully controlling temperature gradients and profiles, they can guide the self-assembly of atoms and molecules into new, highly ordered structures with unique properties.
Improved Efficiency and Yield
Precision means less waste. By eliminating temperature fluctuations, these furnaces increase the yield of usable material from each run. This improves energy efficiency and reduces the consumption of expensive precursor materials, directly impacting the bottom line.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting this technology requires aligning its capabilities with your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: The key takeaway is the furnace's ability to create novel thermal environments to explore new material phases and structures.
- If your primary focus is process development: The key takeaway is the power to simulate and optimize complex industrial thermal profiles at a smaller, more manageable scale.
- If your primary focus is high-yield production: The key takeaway is the unmatched process control that ensures batch-to-batch consistency and minimizes defects in sensitive materials.
Ultimately, mastering the thermal environment is a prerequisite for leading in materials science, and the three-zone tube furnace is the definitive tool for achieving that mastery.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Three independent heating zones | Enables precise temperature profiles and gradients for flexible processing |
| Stable, extended flat zones | Critical for uniform annealing and synthesis in applications like semiconductor wafers |
| Controlled temperature gradients | Facilitates crystal growth, thin film deposition, and nanoparticle synthesis |
| Scalability from lab to industry | Shortens time from research to production with reliable process translation |
| Improved efficiency and yield | Reduces waste and material consumption, enhancing cost-effectiveness |
Ready to elevate your materials innovation with precision thermal control? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in energy storage, electronics, or biomedical research, our three-zone tube furnaces can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















