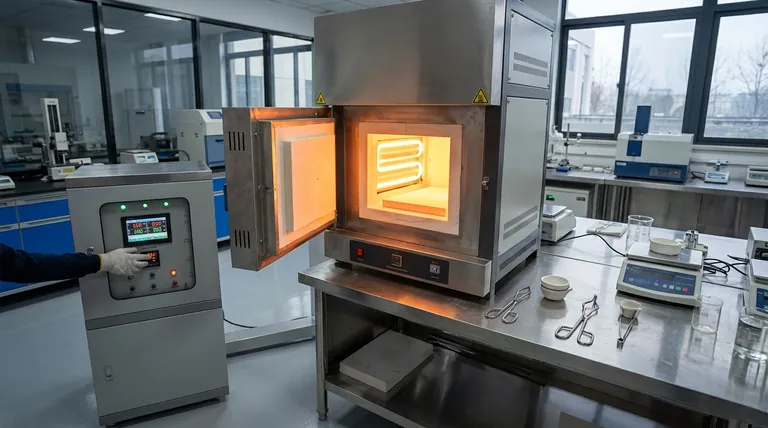
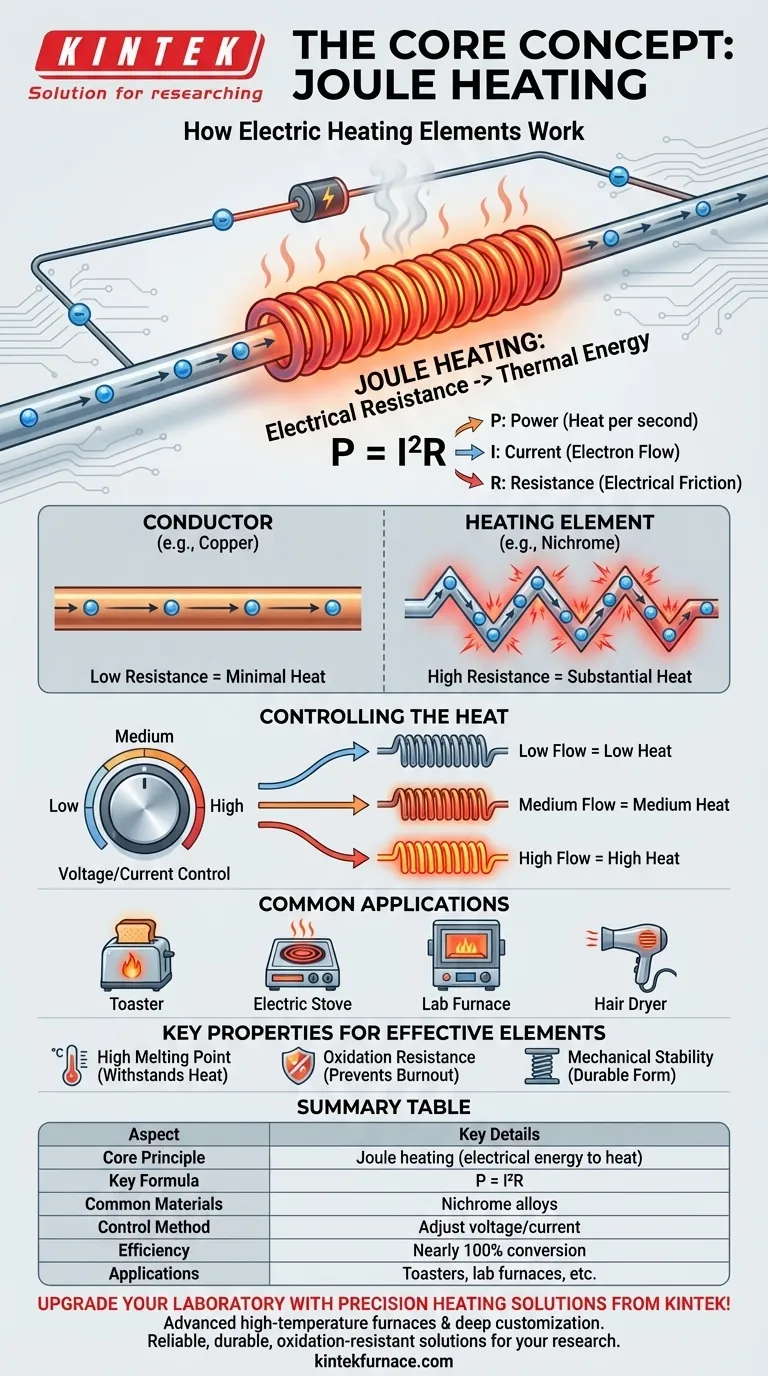
At their core, all electric heating elements operate on a single principle: Joule heating. This phenomenon occurs when a material's natural electrical resistance impedes the flow of electric current, causing the electrical energy to be converted directly into thermal energy, or heat. The element is specifically designed to maximize this effect in a controlled way.
The central purpose of a heating element is not merely to conduct electricity, but to intentionally resist it. By selecting materials with high electrical resistance, engineers can predictably transform electrical energy into a precise and usable amount of heat.

The Physics of Controlled Heat
To understand how a simple wire can perfectly toast bread or heat a room, we must first look at the underlying physics. The entire process hinges on the deliberate exploitation of electrical resistance.
What is Electrical Resistance?
Electrical resistance is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it opposes the flow of an electric current. Think of it as a form of electrical friction.
In a highly conductive material like copper, electrons flow easily with very little opposition. In a resistive material, electrons must expend significant energy to move through the atomic structure.
The Principle of Joule Heating
This expended energy is not lost; it is converted directly into heat. This is known as Joule heating or ohmic heating.
The amount of heat generated is defined by the formula P = I²R, where 'P' is the power (heat per second), 'I' is the current, and 'R' is the resistance. This equation shows that heat increases exponentially with current and linearly with resistance.
The Critical Role of the Material
Heating elements are made from specialized alloys, like nichrome (nickel-chromium), not common conductors like copper.
These materials are chosen because they possess very high electrical resistance. This high 'R' value ensures they generate substantial heat even with a standard household current.
From Principle to Practical Application
The genius of the heating element is its ability to make thermal energy as controllable as electrical energy.
How Heat is Controlled
By adjusting the voltage and current ('I') flowing into the element, we can precisely control the heat output according to the P = I²R formula. This is how your electric stove offers low, medium, and high settings.
Turning the dial simply changes the amount of electricity allowed to flow through the resistive element, giving you instant and predictable control over the temperature.
Common Examples in Your Home
This principle is at work all around you. The glowing wires in a toaster, the hot coils on an electric stove, the element inside a water heater, and the component that warms the air in a hair dryer are all examples of Joule heating in action.
Each of these devices contains a material specifically chosen to resist electricity and, in doing so, produce the heat required for its task.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Properties
Creating an effective heating element involves more than just finding a material with high resistance. Several other properties are critical for safety, efficiency, and a long operational life.
High Melting Point
The most obvious requirement is that the element must withstand its own operating temperature without melting or deforming. Heating element alloys are designed to remain solid and stable at extremely high temperatures.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen in the air and rapidly degrade—a process called oxidation. A good heating element material, like nichrome, forms a stable, protective outer layer of oxide that prevents it from quickly burning out.
Mechanical Stability
The material must also be durable enough to be formed into practical shapes, like coils or ribbons, and resist sagging or breaking after thousands of heat-up and cool-down cycles.
Making Sense of This Principle
Understanding Joule heating provides a new lens through which to view the technology that powers our modern lives.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an appliance: A failed heating element almost always means the resistive wire has physically broken, creating an open circuit and stopping the flow of current.
- If your primary focus is on energy efficiency: All the electricity consumed by a purely resistive heating element is converted into heat; it is nearly 100% efficient at this energy conversion.
- If your primary focus is simply understanding technology: The next time you see the orange glow of a heating coil, recognize it as the elegant and intentional conversion of electrical energy into controlled heat.
This simple principle of electrical resistance is a cornerstone of modern convenience, safely delivering the power of fire with the precision of an electric switch.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Joule heating converts electrical energy to heat via electrical resistance. |
| Key Formula | P = I²R (Power = Current² × Resistance) |
| Common Materials | Nichrome alloys for high resistance and durability. |
| Control Method | Adjust voltage/current to regulate heat output precisely. |
| Efficiency | Nearly 100% energy conversion in resistive elements. |
| Applications | Toasters, stoves, lab furnaces, and hair dryers. |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with Precision Heating Solutions from KINTEK!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need reliable heating elements for energy-efficient processes or tailored systems for complex applications, we deliver durable, oxidation-resistant, and mechanically stable solutions that enhance your lab's performance and safety.
Ready to harness the power of controlled heat in your experiments? Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can support your research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















