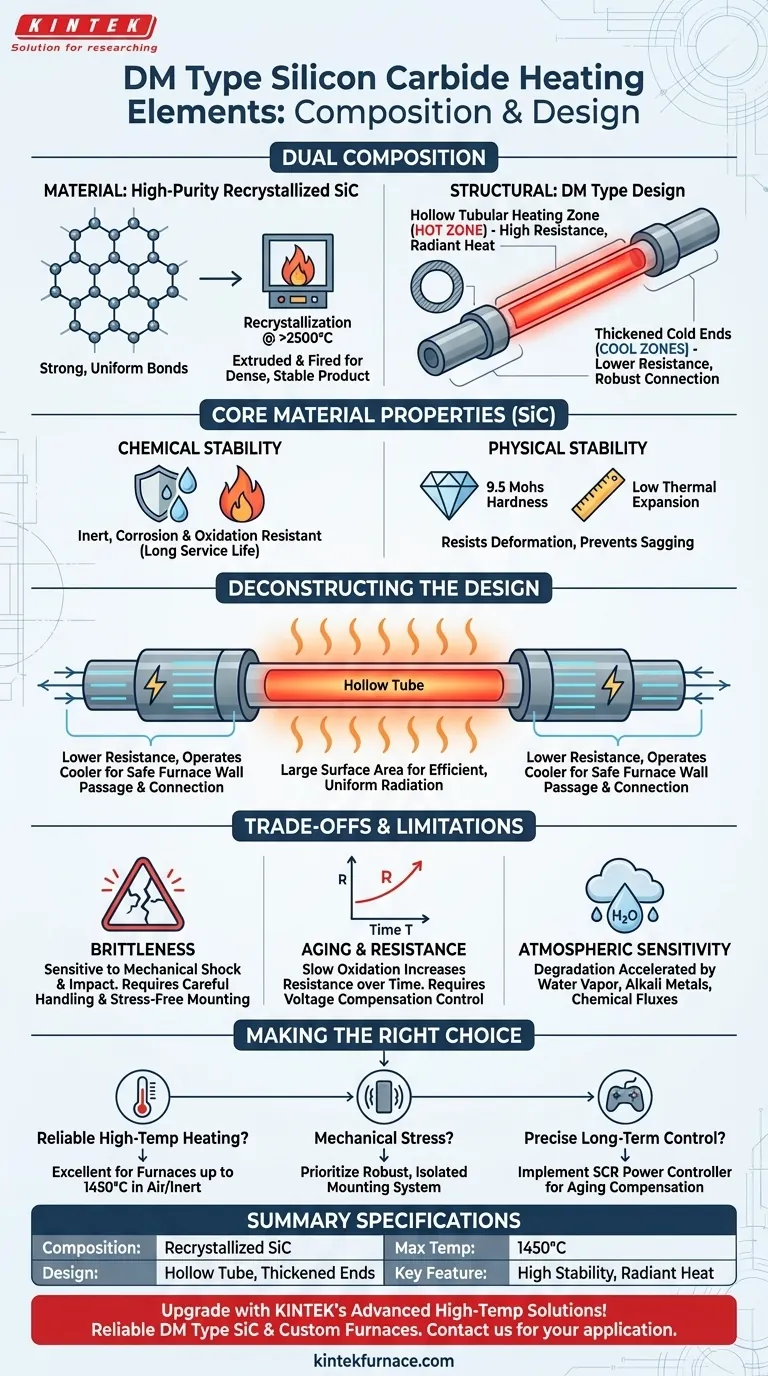
At its core, a DM Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating element has a dual composition. Materially, it is made from high-purity, recrystallized silicon carbide, a robust ceramic compound. Structurally, the "DM Type" designation refers to its specific shape: a hollow tube that serves as the main heating section, connected to integrated, thickened "cold ends" for electrical termination.
The true value of a DM Type element lies in how its material science (the inherent stability of silicon carbide) combines with its physical design (the tubular shape and thickened ends) to deliver reliable, high-temperature performance in demanding industrial environments.

The Core Material: Understanding Silicon Carbide (SiC)
To understand the element's performance, you must first understand its foundational material. Silicon carbide is not just a simple conductor; it is an advanced ceramic engineered for extreme conditions.
How It Is Made
These elements are formed from high-density silicon carbide. The material is extruded into rods or tubes and then fired in a process called re-crystallization at temperatures exceeding 2500°C (4530°F).
This intense process creates strong, uniform bonds between the SiC grains, resulting in a physically dense and highly stable final product.
Key Chemical Properties
The primary advantage of SiC is its chemical stability. It is largely inert and exhibits exceptional resistance to both corrosion and oxidation, even at high temperatures.
This allows the elements to operate for long periods in air or other process atmospheres without rapid degradation, contributing to a long service life.
Key Physical Properties
Silicon carbide is extremely hard (9.5 on the Mohs scale) and resists deformation even under intense heat. Its low thermal expansion means it maintains its shape and integrity during rapid temperature changes.
This combination of hardness and thermal stability prevents sagging or warping, a common failure point in lesser metallic elements.
Deconstructing the "DM Type" Design
The "DM Type" name refers to the element's specific physical construction. This design is not arbitrary; each part serves a critical function.
The Hollow Tubular Heating Zone
The main body of the element is a hollow tube. This is the "hot zone" where electrical resistance is highest, generating the radiant heat for the furnace.
A tubular shape provides a large surface area, which allows for efficient and uniform heat radiation into the furnace chamber.
The Thickened Cold Ends
The ends of the element are manufactured to be significantly thicker than the central heating tube. This increased cross-sectional area intentionally lowers their electrical resistance.
Because they have lower resistance, these "cold ends" operate at a much cooler temperature. This allows them to pass through the furnace walls and serve as robust connection points for the electrical supply without overheating or damaging the furnace insulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the trade-offs of silicon carbide is essential for proper application and avoiding premature failure.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is hard but very brittle. The elements cannot withstand significant mechanical shock, vibration, or impact.
Careful handling during installation and ensuring a secure, stress-free mounting are critical to prevent fracture.
Natural Aging and Resistance
Over its operational life, a SiC element will experience slow oxidation. This process gradually increases its electrical resistance.
Control systems must be able to compensate for this change by delivering higher voltage over time to maintain the desired power output and temperature.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
While highly resistant, SiC's lifespan can be reduced by certain atmospheres. The presence of heavy water vapor, alkali metals, or certain chemical fluxes can accelerate degradation compared to operation in clean, dry air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to select and use SiC elements effectively. Match the element's known characteristics to your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is reliable high-temperature heating: SiC elements are an excellent choice for consistent operation in furnaces up to 1450°C in air or inert atmospheres.
- If your environment involves mechanical stress or vibration: You must prioritize a robust mounting system that isolates the brittle element from any potential shock or impact.
- If your goal is precise and stable long-term temperature control: Implement a power controller (typically an SCR) that can automatically adjust voltage to compensate for the element's natural aging and resistance increase.
By aligning the unique properties of the material with the demands of your process, you can ensure optimal performance and a long service life.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity, recrystallized silicon carbide (SiC) |
| Structural Design | Hollow tubular heating zone with thickened cold ends |
| Key Properties | High temperature resistance (up to 1450°C), corrosion and oxidation resistance, low thermal expansion |
| Common Applications | Industrial furnaces for high-temperature processes in air or inert atmospheres |
| Limitations | Brittleness (sensitive to mechanical shock), resistance increases with aging, sensitive to certain atmospheres |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating elements like DM Type SiC, along with Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















