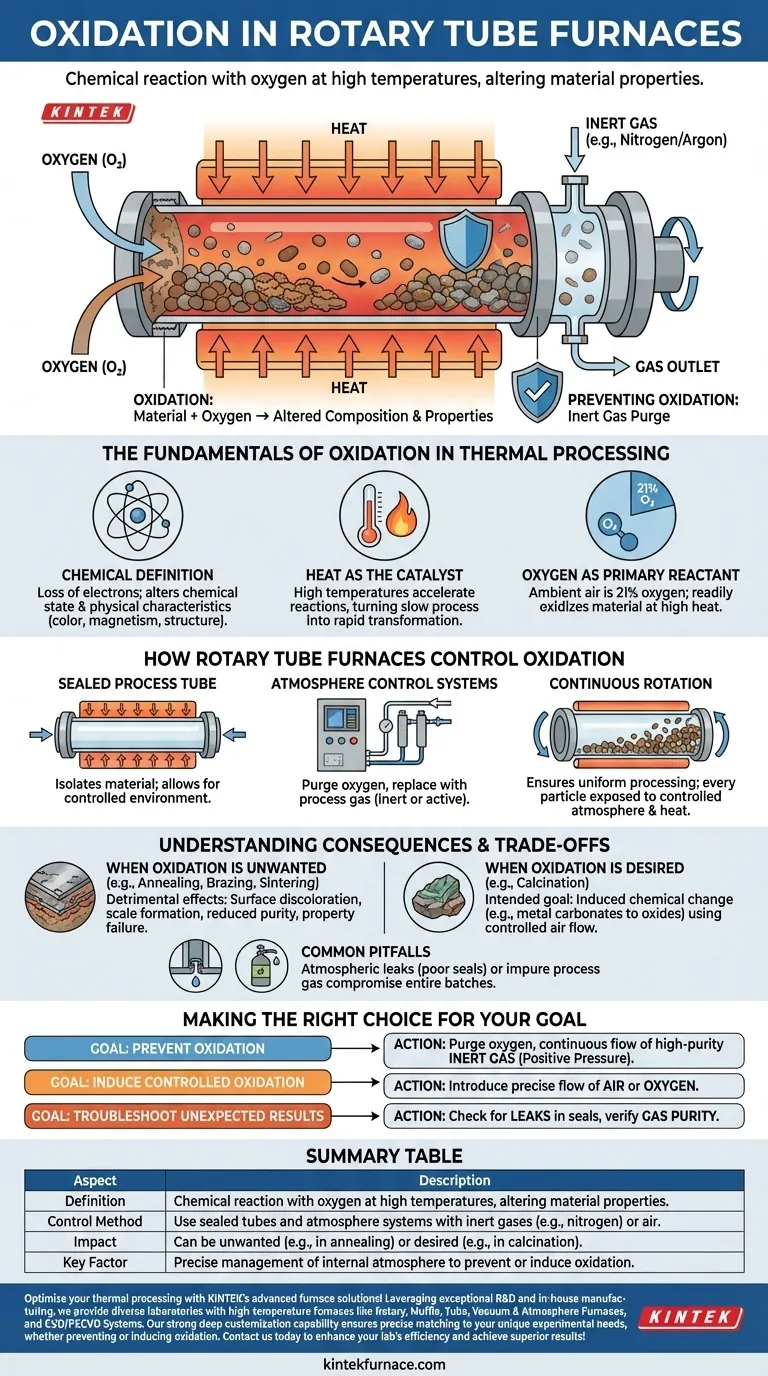
In a rotary tube furnace, oxidation is the chemical reaction where your process material reacts with oxygen, typically from the air, at high temperatures. This process fundamentally alters the material's chemical composition and physical properties, often in an undesirable way.
The presence of oxygen combined with the high heat inside a rotary tube furnace will inevitably cause oxidation. Therefore, controlling oxidation is not about eliminating heat, but about precisely managing the gaseous atmosphere within the furnace tube.
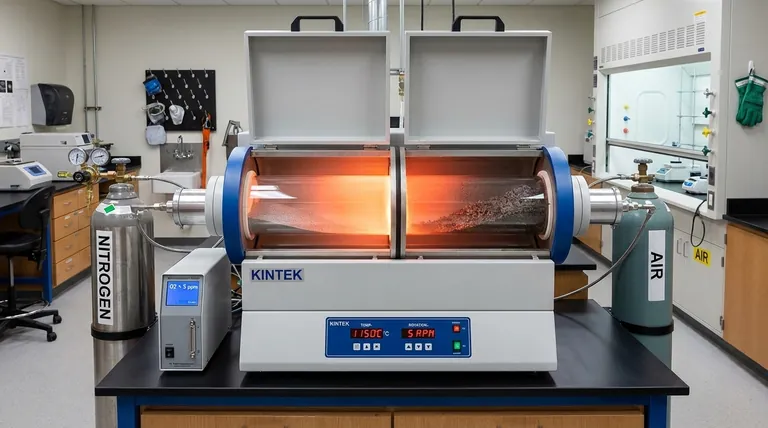

The Fundamentals of Oxidation in Thermal Processing
The Chemical Definition
At its core, oxidation is a chemical process involving the loss of electrons. When a material oxidizes, its chemical state changes, which in turn alters its physical characteristics like color, magnetism, or structural integrity.
Heat as the Catalyst
While oxidation can occur at room temperature (like rust on iron), the high heat inside a rotary tube furnace acts as a powerful catalyst. High temperatures provide the energy needed to dramatically accelerate these reactions, turning a slow process into a rapid transformation.
Oxygen as the Primary Reactant
For most applications, the term "oxidation" refers specifically to a reaction with oxygen. Since ambient air is about 21% oxygen, any uncontrolled air entering the hot furnace tube will readily oxidize the material being processed.
How Rotary Tube Furnaces Control Oxidation
The Sealed Process Tube
Rotary tube furnaces are designed with a sealed, rotating tube that contains the process material. This design is critical because it isolates the material from the outside air and the furnace's heating elements (indirect firing).
This separation allows for the creation of a tightly controlled environment inside the tube, which is the key to managing oxidation.
Atmosphere Control Systems
These furnaces are equipped with gas inlet and outlet ports. This allows operators to purge the oxygen-rich air from the tube and replace it with a specific process gas.
Commonly, an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is used to create an oxygen-free atmosphere, completely preventing oxidation during heating.
The Impact of Continuous Rotation
The rotation of the tube is essential for uniform processing. It gently tumbles the material, ensuring that every particle is exposed to the controlled atmosphere and uniform heat, preventing localized, uncontrolled reactions.
Understanding the Consequences and Trade-offs
When Oxidation is Unwanted
For many processes like annealing, brazing, or sintering metals, oxidation is detrimental. It can lead to surface discoloration, the formation of brittle oxide layers (scale), reduced product purity, and a complete failure to achieve the desired material properties.
When Oxidation is Desired
In some industrial processes, oxidation is the intended goal. Calcination, for example, often involves heating a material in the presence of air to induce a specific chemical change, such as converting metal carbonates into metal oxides. In these cases, air is intentionally fed into the furnace.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The most common failure point in preventing oxidation is an atmospheric leak. A poor seal at the furnace ends or the use of an impure process gas can introduce trace amounts of oxygen, which is often enough to compromise the entire batch at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving your desired outcome depends entirely on correctly managing the furnace's internal atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation (e.g., annealing, sintering): Your goal is to purge all oxygen and maintain a continuous flow of high-purity inert gas (like Nitrogen or Argon) to create a positive pressure.
- If your primary focus is inducing controlled oxidation (e.g., calcination): Your goal is to introduce a precise and consistent flow of air or oxygen into the furnace to drive the desired chemical reaction uniformly.
- If you are experiencing unexpected discoloration or poor results: Your first step should be to meticulously check for leaks in the system seals and verify the purity of your process gas.
Ultimately, mastering your rotary tube furnace process means mastering the atmosphere within it.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Chemical reaction with oxygen at high temperatures, altering material properties. |
| Control Method | Use sealed tubes and atmosphere systems with inert gases (e.g., nitrogen) or air. |
| Impact | Can be unwanted (e.g., in annealing) or desired (e.g., in calcination). |
| Key Factor | Precise management of internal atmosphere to prevent or induce oxidation. |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental needs, whether preventing or inducing oxidation. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















