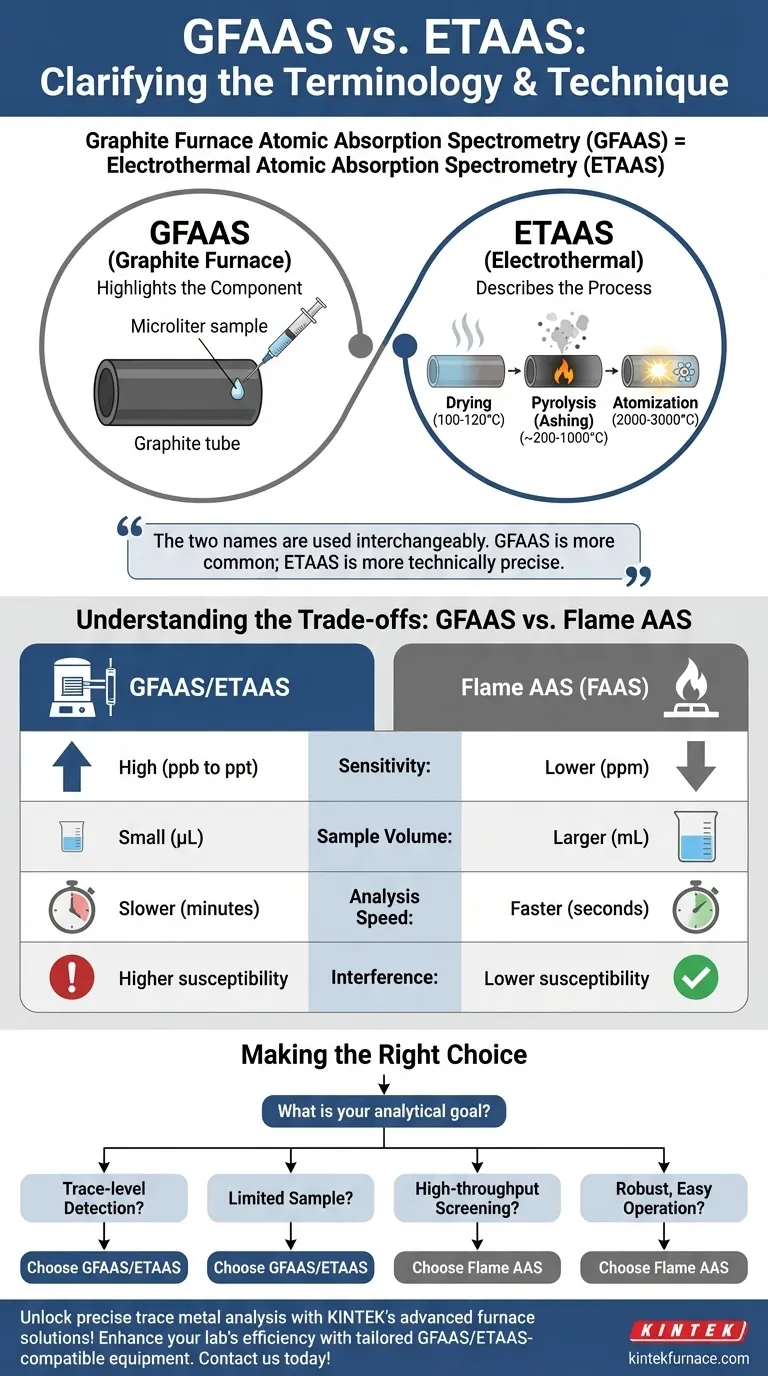
To be clear, graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS) is also known as electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ETAAS). The two names are used interchangeably in scientific literature and refer to the exact same analytical technique. The name ETAAS is often considered more technically precise as materials other than graphite can be used, but GFAAS remains more common due to its historical origin.
The core distinction is not in the technique itself, but in what each name emphasizes. "Graphite Furnace" (GFAAS) highlights the most common physical component used, while "Electrothermal" (ETAAS) describes the fundamental mechanism of atomization: using electric current to generate heat.

Why Two Names for the Same Technique?
Understanding the naming convention reveals the core principles of how this sensitive analytical method works. It is a technique designed for detecting metals and metalloids, often at extremely low concentrations.
The Role of the "Graphite Furnace" (GFAAS)
The name GFAAS focuses on the physical heart of the instrument: the graphite tube.
This small, cylindrical tube acts as the sample holder. A tiny liquid sample (microliters) is injected into it. The graphite material is chosen for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and its excellent electrical conductivity.
The "Electrothermal" Atomization Process (ETAAS)
The name ETAAS describes how the graphite tube works. The process is "electrothermal" because a high electrical current is passed directly through the graphite tube, causing it to heat up rapidly due to electrical resistance.
This heating occurs in a precisely controlled, multi-step program:
- Drying: The temperature is raised gently (around 100-120°C) to evaporate the solvent from the sample.
- Pyrolysis (Ashing): The temperature is increased further (several hundred degrees) to break down and remove the bulk of the sample matrix (organic matter, salts) without vaporizing the target analyte.
- Atomization: The furnace is heated to a very high temperature (2000-3000°C) almost instantly. This intense heat provides the energy to vaporize the remaining residue and break the chemical bonds, converting the analyte into a cloud of free, neutral atoms in the ground state.
It is this final cloud of free atoms inside the tube that is then measured by atomic absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs: GFAAS vs. Other AA Techniques
GFAAS/ETAAS is not the only method of atomic absorption. Its primary alternative is Flame AAS (FAAS). Understanding their differences highlights the specific advantages and disadvantages of the graphite furnace method.
Unmatched Sensitivity
The main advantage of GFAAS is its exceptional sensitivity. Because the atoms are trapped and concentrated within the small volume of the graphite tube for a second or two, the instrument can detect much lower concentrations.
In contrast, Flame AAS continuously aspirates a sample into a flame. The atoms pass through the light path quickly and are diluted by the flame gases, resulting in lower sensitivity. GFAAS can often detect concentrations 100 to 1,000 times lower than FAAS.
Smaller Sample Volume
GFAAS requires only a very small amount of sample, typically in the microliter (µL) range. This is a significant advantage when analyzing precious or limited samples, such as clinical fluids or unique environmental samples.
Slower Analysis Time
The primary trade-off is speed. Each GFAAS analysis requires a full heating program that can take several minutes. Flame AAS provides a nearly instantaneous reading, making it much faster for analyzing large batches of samples where ultimate sensitivity is not required.
Higher Susceptibility to Interference
The GFAAS environment is complex. The process of burning off the sample matrix during pyrolysis must be carefully optimized. If not done correctly, chemical interferences can occur during atomization, affecting the accuracy of the result. This complexity demands more skill and method development from the operator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The name you use—GFAAS or ETAAS—is a matter of convention, but choosing the technique itself depends entirely on your analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is trace-level detection: GFAAS/ETAAS is the superior choice for its ability to measure concentrations in the parts-per-billion (ppb) or even parts-per-trillion (ppt) range.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening: Flame AAS is far more efficient for analyzing many samples quickly, provided its detection limits are sufficient for your needs.
- If your sample volume is extremely limited: GFAAS/ETAAS is the only viable option, as it requires only microliters of sample.
- If you need a robust, easy-to-operate system: Flame AAS is generally less complex and more forgiving than GFAAS, requiring less intensive method development.
Ultimately, both names describe a powerful technique defined by its ability to achieve exceptional sensitivity by thermally atomizing a sample within a confined space.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | GFAAS/ETAAS | Flame AAS (FAAS) |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | High (ppb to ppt range) | Lower (ppm range) |
| Sample Volume | Small (microliters) | Larger (milliliters) |
| Analysis Speed | Slower (minutes per sample) | Faster (seconds per sample) |
| Interference | Higher susceptibility | Lower susceptibility |
| Best For | Trace-level detection, limited samples | High-throughput screening, robust operation |
Unlock precise trace metal analysis with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, whether you're analyzing environmental samples, clinical fluids, or other materials. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy with tailored GFAAS/ETAAS-compatible equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness



















