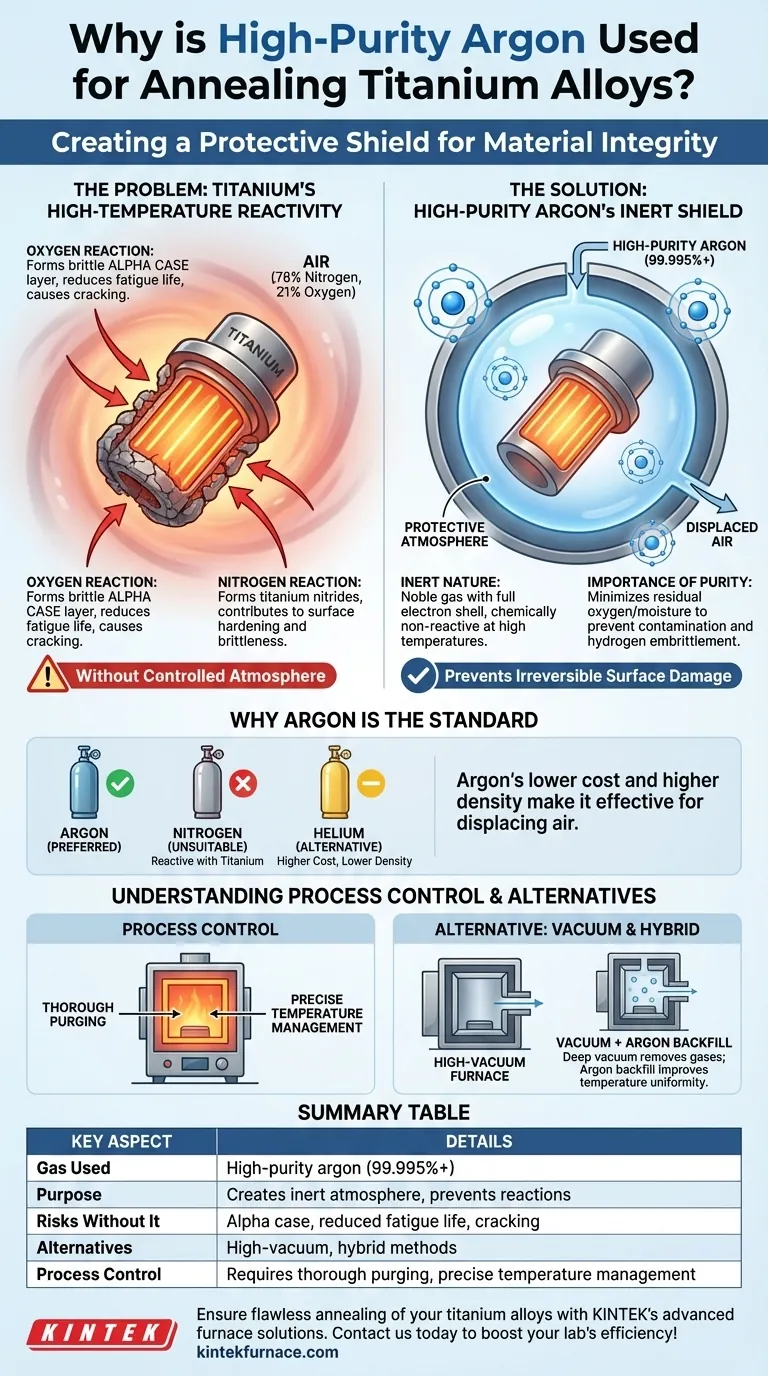
The standard gas used for annealing titanium alloys is high-purity argon. This is because titanium is extremely reactive at the high temperatures required for annealing. The argon, an inert gas, creates a protective atmosphere that displaces the oxygen and nitrogen present in the air, preventing chemical reactions that would otherwise damage the metal's surface and compromise its structural integrity.
The core challenge in annealing titanium is not the heat itself, but protecting the metal from atmospheric gases at high temperatures. Using an inert gas like argon is non-negotiable to prevent irreversible surface damage and preserve the alloy's critical properties.

The Core Problem: Titanium's Reactivity at High Temperatures
To understand the need for argon, you must first understand the aggressive nature of titanium when heated. Without a controlled atmosphere, the process does more harm than good.
Why Air is the Enemy
Normal air is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At room temperature, these gases are harmless to titanium. At annealing temperatures (typically above 700°C or 1300°F), titanium actively seeks to bond with them.
The Threat of Oxidation
When heated, titanium reacts rapidly with any available oxygen. This forms a hard, brittle, oxygen-enriched layer on the surface known as alpha case.
This alpha case layer is detrimental to the part's performance, as it dramatically reduces fatigue life and can create surface cracks during subsequent machining or while in service.
The Threat of Nitridation
In addition to oxygen, titanium also reacts with nitrogen at high temperatures. This forms titanium nitrides on the surface, which also contribute to surface hardening and brittleness, similar to the effects of oxidation.
Argon as the Solution: Creating a Protective Shield
The purpose of using argon is to create an environment that is completely free of these reactive gases. It acts as a neutral, invisible shield for the duration of the heating and cooling cycle.
What Makes Argon 'Inert'
Argon is a noble gas. Its atoms have a full outer shell of electrons, which makes it chemically non-reactive. It will not bond with titanium or any other element, even under the intense heat of an annealing furnace.
The Importance of 'High-Purity'
Simply using argon is not enough; its purity is critical. High-purity argon (e.g., 99.995% or higher) is specified to ensure that residual oxygen and moisture levels are exceptionally low.
Even trace amounts of oxygen or water vapor (which introduces hydrogen and oxygen) in the furnace can be enough to cause surface contamination and potential hydrogen embrittlement.
Why Not Other Gases?
Nitrogen, while often used as a cheap inerting gas for other processes, is unsuitable for titanium because it is reactive. Helium is also inert and can be used, but argon is the industry standard primarily due to its lower cost and higher density, which makes it more effective at displacing air from a furnace chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Control
While argon is the correct technical choice, its implementation requires careful process control and carries associated costs.
Vacuum as an Alternative
The other primary method for annealing titanium is to do it in a high-vacuum furnace. A vacuum also removes oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases.
In practice, many processes use a hybrid approach: a furnace is first pumped down to a deep vacuum to remove all air and moisture, and then it is partially or fully backfilled with high-purity argon. This argon backfill can improve temperature uniformity throughout the workload via convection.
The Risk of Insufficient Purging
A common failure mode is an incomplete purge. If the furnace is not thoroughly purged of air before the heating cycle begins, the protective argon atmosphere will be contaminated. This results in the very oxidation and nitridation the process was designed to prevent.
How to Ensure a Successful Annealing Process
Your choice of atmospheric control depends on your final goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum material integrity: Insist on using high-purity (99.999% or "UHP") argon or a high-vacuum process to completely eliminate the risk of alpha case formation.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for aerospace or medical parts: A vacuum furnace backfilled with argon provides the most reliable and repeatable environment for critical applications.
- If your primary focus is cost management: Recognize that while high-purity argon and proper furnace control are an expense, this investment prevents the far greater cost of scrapping a batch of valuable, but damaged, titanium components.
Ultimately, treating the furnace atmosphere with the same precision as the temperature profile is the key to successfully annealing titanium.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas Used | High-purity argon (99.995% or higher) |
| Purpose | Creates an inert atmosphere to prevent reactions with oxygen and nitrogen |
| Risks Without It | Formation of alpha case (brittle surface layer), reduced fatigue life, and potential cracking |
| Alternatives | High-vacuum furnaces or hybrid vacuum-argon methods for enhanced control |
| Process Control | Requires thorough purging and precise temperature management for success |
Ensure flawless annealing of your titanium alloys with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all customizable to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature expertise can protect your materials and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















