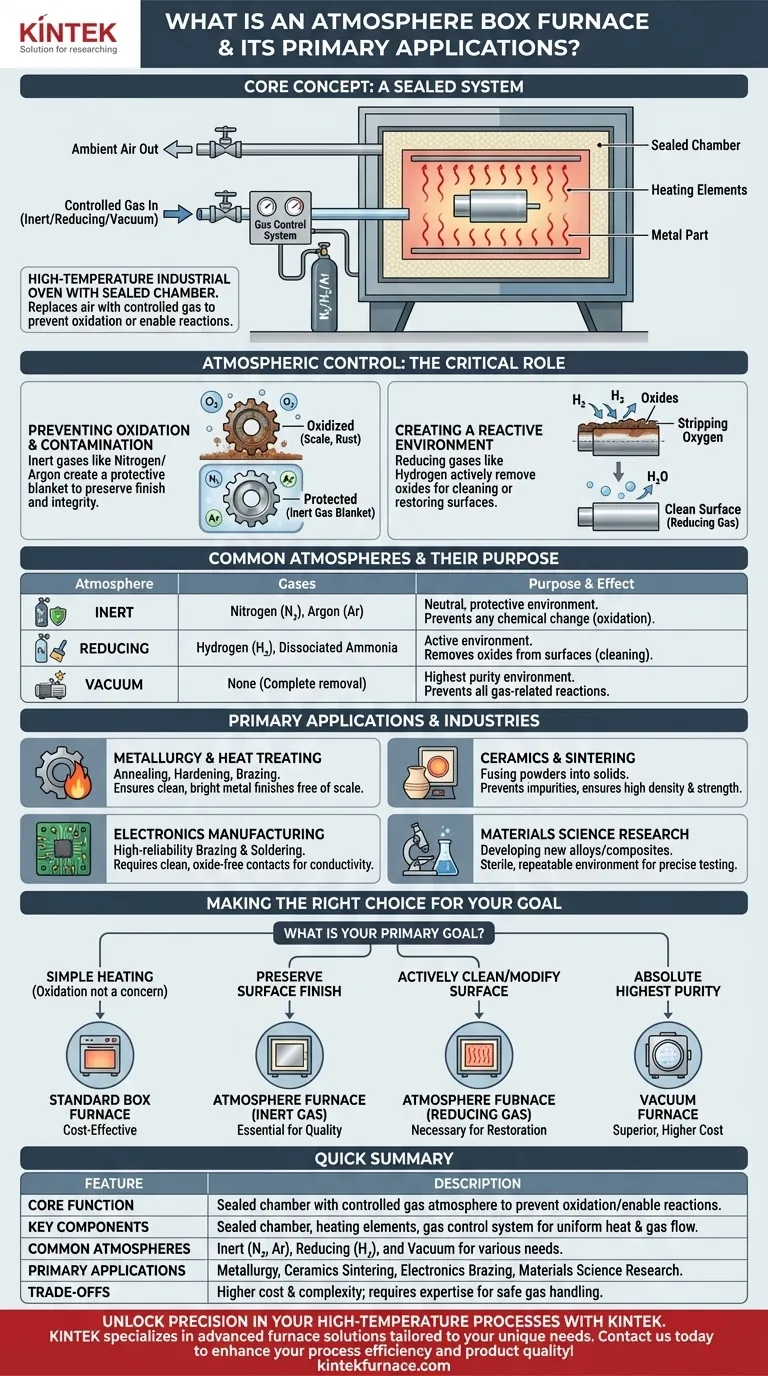
In short, an atmosphere box furnace is a high-temperature industrial oven with a critical added capability: the ability to replace the air inside its sealed chamber with a specific, controlled gas. This function is essential for processes where exposure to oxygen or other airborne contaminants at high temperatures would ruin the final product.
The core function of an atmosphere furnace is not just to heat a material, but to precisely control its chemical environment during heating. This prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation (rusting or scaling) and allows for the creation of materials with specific, highly-engineered properties.
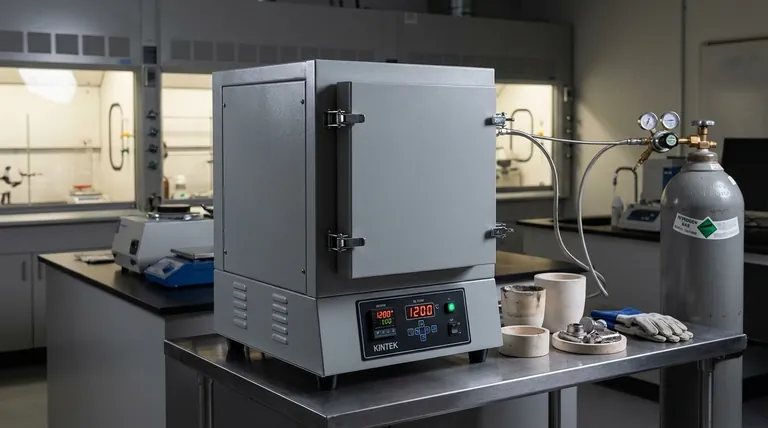

How an Atmosphere Box Furnace Works
The Core Concept: A Sealed System
A standard furnace heats materials in ambient air. An atmosphere furnace, sometimes called a muffle furnace, operates within a tightly sealed, box-shaped chamber.
This sealed design allows operators to first remove the ambient air and then introduce a specific gas or create a vacuum, establishing a controlled "atmosphere."
Key Components
The system is built around three primary components:
- The Sealed Chamber: A high-temperature-resistant box, often lined with ceramic insulation, designed to prevent gas from leaking in or out.
- Heating Elements: These surround the chamber to provide uniform, precisely controlled heat, often reaching very high temperatures.
- Gas Control System: A system of pipes, valves, and gauges that purges the chamber of air and feeds in the desired gas at a controlled rate.
Advanced models include programmable controllers for automating temperature and gas flow cycles, ensuring process repeatability and safety.
The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
Controlling the atmosphere is essential for preventing destructive chemical reactions and, in some cases, promoting beneficial ones.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, most metals and many other materials react aggressively with oxygen. This process, oxidation, creates a layer of scale or oxide on the material's surface, altering its dimensions, finish, and properties.
By replacing air with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, the furnace creates a protective blanket around the material, preventing oxidation entirely.
Creating a Reactive Environment
Sometimes, the goal is not to prevent a reaction but to cause a specific one.
A furnace can be filled with a reducing gas, such as hydrogen, to actively strip oxygen atoms from a material's surface. This is a common technique for cleaning or restoring oxidized components.
Common Atmospheres and Their Purpose
- Inert (Nitrogen, Argon): A neutral, protective environment to prevent any chemical change.
- Reducing (Hydrogen, Dissociated Ammonia): An active environment used to remove oxides from a material's surface.
- Vacuum: The complete removal of all gases, providing the purest possible processing environment and preventing any gas-related reactions.
Primary Applications and Industries
The ability to control a material's environment at high temperatures makes these furnaces indispensable in advanced manufacturing and research.
Metallurgy and Heat Treating
Atmosphere furnaces are used for processes like annealing, hardening, and brazing metals. They ensure the components emerge from the heat with a clean, bright finish, free from the scale and discoloration caused by oxidation.
Ceramics and Sintering
Sintering is the process of fusing powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) into a solid mass using heat. Performing this in a controlled atmosphere prevents impurities from becoming trapped in the final product and ensures superior density and strength.
Electronics Manufacturing
When joining electronic components, any oxidation on the metal contacts can impede electrical conductivity. An atmosphere furnace provides the clean environment needed for high-reliability brazing and soldering.
Materials Science Research
For scientists developing new alloys, composites, or advanced materials, an atmosphere furnace provides a sterile, repeatable environment. It allows them to test how a material behaves under precise thermal and chemical conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is not always the right tool for the job.
Increased Complexity and Cost
The seals, gas plumbing, and control systems make these furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than a standard air-circulating furnace.
Operational Demands
Operating an atmosphere furnace requires more expertise. Managing gas flow, ensuring the chamber is properly purged of air, and maintaining a perfect seal are critical for success. Working with flammable gases like hydrogen also introduces significant safety protocols.
Batch Processing Limitations
As a type of box furnace, materials are loaded, processed, and unloaded in individual batches. This "intermittent" operation is less suited for high-volume, continuous production lines where conveyor-style furnaces are more efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether you need an atmosphere furnace comes down to the required quality of your final part.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a material where surface oxidation is not a concern: A standard, non-atmosphere box furnace is more cost-effective and simpler to operate.
- If your primary focus is to preserve the material's surface finish and integrity at high temperature: An atmosphere furnace using an inert gas (nitrogen or argon) is essential.
- If your primary focus is to actively clean or modify the material's surface chemistry: A furnace capable of handling a reducing gas (like hydrogen) is necessary.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest purity with zero atmospheric interaction: A vacuum furnace is the superior, though often more expensive, choice.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace depends on whether you are simply applying heat or precisely engineering a material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Sealed chamber with controlled gas atmosphere to prevent oxidation and enable specific chemical reactions during heating. |
| Key Components | Sealed chamber, heating elements, gas control system for uniform heat and gas flow. |
| Common Atmospheres | Inert (e.g., nitrogen, argon), reducing (e.g., hydrogen), and vacuum for various processing needs. |
| Primary Applications | Metallurgy (annealing, hardening), ceramics sintering, electronics brazing, and materials science research. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and complexity than standard furnaces; requires expertise for safe operation with gases like hydrogen. |
Unlock Precision in Your High-Temperature Processes with KINTEK
Are you facing challenges with material oxidation or inconsistent results in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you're in metallurgy, ceramics, electronics, or materials science research.
Don't let atmospheric issues hold back your innovations—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance



















