In essence, a vacuum furnace is an electrically heated industrial furnace that processes materials within a high-vacuum environment. By removing the air and its reactive gases, it allows for high-temperature treatments like annealing, brazing, and sintering without the risk of oxidation or contamination that would otherwise degrade the material's surface and structural properties.
The critical insight is that a vacuum furnace is not just a heating chamber; it's a precision materials processing tool. By creating an inert environment, it enables the creation of parts with higher purity, superior structural integrity, and cleaner surfaces than is possible with conventional atmospheric furnaces.

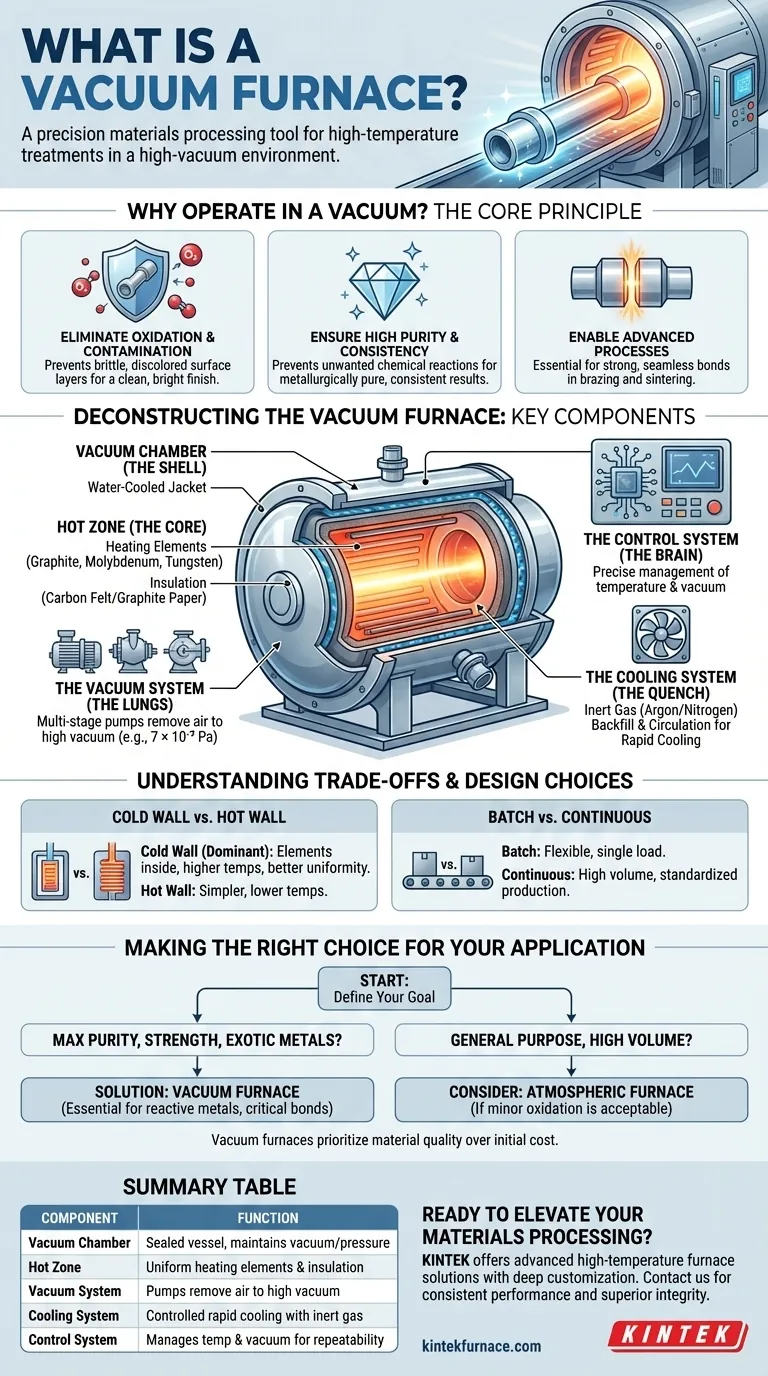
The Core Principle: Why Operate in a Vacuum?
The decision to use a vacuum is fundamental to achieving specific material outcomes. The absence of atmosphere is not passive; it is an active component of the process.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, metals readily react with oxygen and other gases present in the air. This reaction, known as oxidation, creates a brittle, discolored layer on the part's surface.
A vacuum furnace physically removes these reactive gases, preventing oxidation and ensuring the material's surface remains clean and bright.
Ensuring High Purity and Consistency
By preventing unwanted chemical reactions, the furnace ensures the integrity of the base metal and any alloys.
This results in a final product that is metallurgically pure, structurally sound, and highly consistent from one batch to the next.
Enabling Advanced Processes
Processes like high-temperature brazing and sintering depend on perfectly clean surfaces to form strong, seamless metallurgical bonds.
The vacuum environment is a prerequisite for these applications, as even microscopic levels of contamination can compromise the joint or part quality.
Deconstructing the Vacuum Furnace: Key Components
A vacuum furnace is a complex system where each component serves a critical function in maintaining a controlled environment of extreme heat and near-perfect vacuum.
The Vacuum Chamber (The Shell)
This is the sealed, airtight vessel that contains the entire process. It is typically built from high-strength steel or stainless steel alloys to withstand the immense external atmospheric pressure.
Most modern designs feature a double-layer, water-cooled jacket, which keeps the exterior of the furnace cool and safe to touch even when the interior is at thousands of degrees.
The Hot Zone (The Core)
Located inside the chamber, the hot zone is where the actual heating takes place. It consists of two main parts: heating elements and insulation.
The heating elements are made from materials like graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten, which can operate at extremely high temperatures without degrading in a vacuum. They are often arranged for 360-degree heating to ensure temperature uniformity.
Insulation, typically made of rigid carbon felt or flexible graphite paper, lines the hot zone to contain the heat. This efficient insulation allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles and minimizes energy loss.
The Vacuum System (The Lungs)
This is not a single pump but a multi-stage system designed to remove air from the chamber.
It starts with one or more mechanical "roughing" pumps to remove the bulk of the air. Then, high-vacuum pumps like diffusion, turbomolecular, or Roots pumps take over to achieve the final required vacuum level, which can be as low as 7 × 10⁻³ Pa.
The Cooling System (The Quench)
After the heating cycle, parts often need to be cooled rapidly in a controlled manner.
This is accomplished by turning off the heating elements and backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen. A powerful fan circulates this gas, transferring heat from the parts to the water-cooled walls of the chamber.
The Control System (The Brain)
A sophisticated system of power supplies, controllers, and sensors precisely manages both the temperature profile and the vacuum level throughout the entire process. This automation ensures the treatment is stable, repeatable, and meets exact specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Choices
Not all vacuum furnaces are the same. The design is tailored to the specific application, involving critical trade-offs in performance and cost.
Cold Wall vs. Hot Wall Designs
The most significant design choice is between a "cold wall" and "hot wall" furnace.
Cold wall furnaces, the dominant design for high-performance applications, place the heating elements and insulation inside a water-cooled vacuum chamber. This allows for very high operating temperatures, rapid heating and cooling, and superior temperature uniformity.
Hot wall furnaces, which are less common, heat the entire vacuum chamber from the outside. They are simpler but limited in maximum temperature and cycle speed.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Furnaces can be designed for either batch or continuous operation. Batch furnaces process a single load at a time and are highly flexible. Continuous furnaces move parts through different heating and cooling zones, ideal for high-volume, standardized production.
Cost and Complexity
The primary trade-off is cost. The components required to create and maintain a high vacuum—including the sealed chamber, complex pumping systems, and advanced controls—make vacuum furnaces significantly more expensive and complex to operate than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and strength: A vacuum furnace is essential for eliminating oxidation and ensuring clean, strong metallurgical bonds in processes like brazing or medical implant manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or exotic metals: The controlled, inert environment of a vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for materials like titanium, zirconium, and superalloys that are highly susceptible to atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-volume heat treatment: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more cost-effective solution if minor surface oxidation is acceptable for your application.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize final material quality and process control over initial equipment cost.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed vessel to maintain vacuum and withstand pressure |
| Hot Zone | Area with heating elements and insulation for uniform heating |
| Vacuum System | Pumps to remove air and achieve high vacuum levels |
| Cooling System | Uses inert gas for controlled rapid cooling |
| Control System | Manages temperature and vacuum for repeatable processes |
Ready to elevate your materials processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're working with reactive metals or require high-purity outcomes, our furnaces deliver consistent performance and superior structural integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory processes and achieve your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















