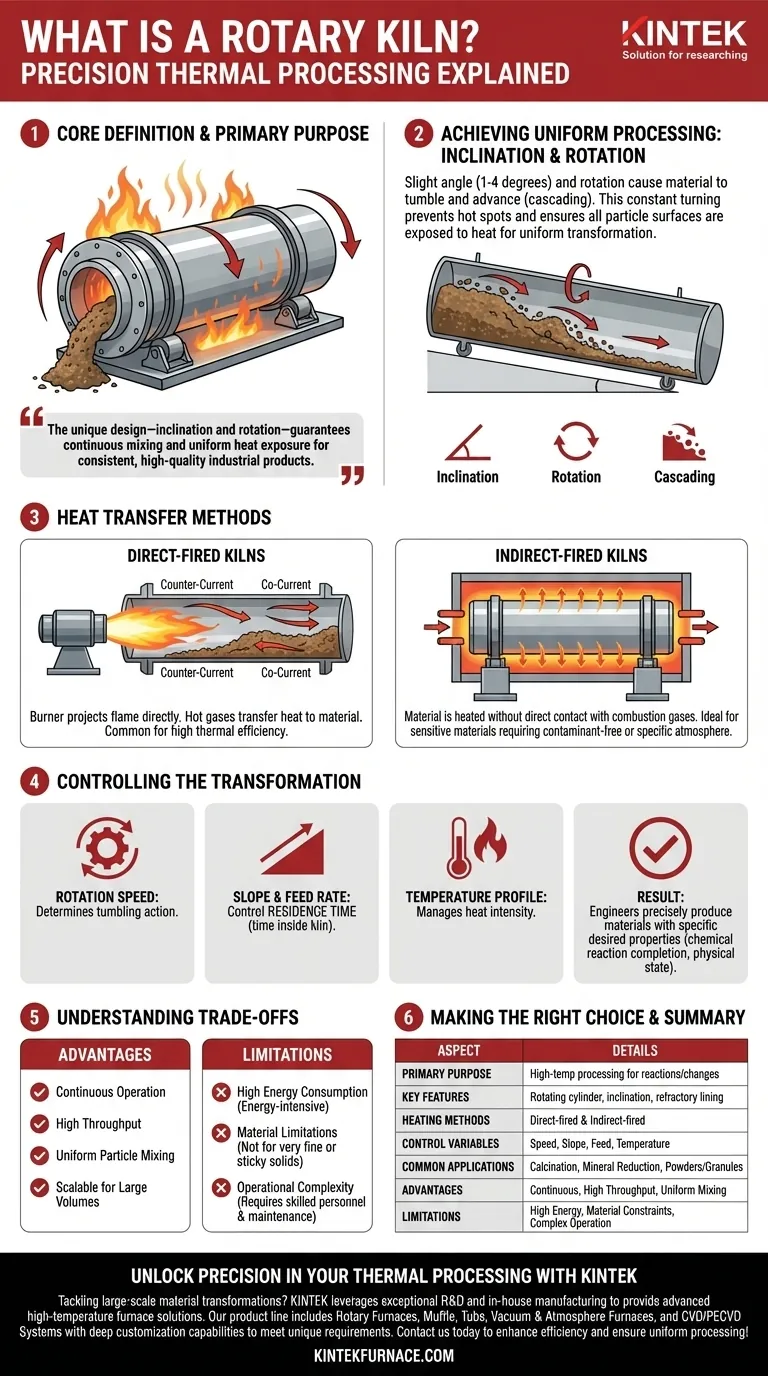
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, rotating industrial furnace designed for the high-temperature processing of solid materials. It consists of a long, cylindrical steel shell lined with refractory bricks, which is mounted at a slight angle and rotates slowly on its axis. Its primary purpose is to induce specific chemical reactions or physical changes in a material by subjecting it to controlled, extreme heat for a precise duration.
The genius of the rotary kiln isn't just its ability to generate high temperatures. Its true value lies in its unique design—the combination of inclination and rotation—which guarantees that every particle of material is continuously mixed and uniformly exposed to heat, ensuring a consistent and high-quality final product on an industrial scale.

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Uniform Processing
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln stems from a few fundamental engineering principles working in concert. The design is deliberately simple but highly effective for its intended purpose.
The Role of Inclination and Rotation
The kiln is positioned at a slight angle to the horizontal, typically between 1 and 4 degrees. As the cylinder rotates, material fed into the higher end tumbles and mixes as it gradually advances down the length of the kiln toward the discharge end.
This tumbling action, known as cascading, is critical. It ensures that the material bed is constantly being turned over, preventing hot spots and exposing all particle surfaces to the heat source for a uniform transformation.
The Principle of Heat Transfer
Heat is introduced to facilitate the desired reaction. This is primarily achieved through two methods: direct and indirect heating.
Direct-fired kilns are the most common. A burner projects a flame directly into the kiln, and the hot combustion gases pass through the cylinder, transferring heat directly to the material. The gas flow can be either counter-current (against the material flow) for maximum thermal efficiency or co-current (with the material flow).
Indirect-fired kilns heat the material without direct contact with combustion gases. The rotating cylinder is enclosed in an external furnace or fitted with heating elements, transferring heat through the shell wall. This method is essential for processing materials that cannot be exposed to contaminants or require a specific atmospheric composition.
Controlling the Transformation
Operators have precise control over the process by manipulating key variables. The rotation speed determines how much the material tumbles, while the slope and feed rate control the residence time—the amount of time the material spends inside the kiln.
By carefully managing these variables along with the temperature profile, engineers can reliably produce materials with specific desired properties, whether it's driving a chemical reaction to completion or achieving a particular physical state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary kiln is not a universal solution. Its design comes with specific operational considerations and limitations that must be understood.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Rotary kilns are inherently energy-intensive due to the high temperatures required and heat loss through the shell and exhaust gases. Modern operations often incorporate complex heat recovery systems, such as preheaters, to capture waste heat from the exhaust and use it to pre-process the incoming raw material, significantly improving thermal efficiency.
Material Limitations
The technology is optimized for granular, free-flowing solids. Materials that are very fine can become entrained in the gas flow and be carried out of the kiln prematurely. Conversely, materials that are sticky or have a tendency to agglomerate at high temperatures can build up on the kiln walls, disrupting flow and heat transfer.
Operational Complexity and Maintenance
Operating a rotary kiln is a complex task that requires skilled personnel to manage temperatures, feed rates, and rotational speeds. The harsh operating environment—high temperatures, abrasive materials, and constant rotation—leads to significant wear and tear, necessitating a robust and often costly maintenance program for the refractory lining, drive system, and support structures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on the material you are processing and the outcome you need to achieve. A rotary kiln is a specialized tool for specific, large-scale tasks.
- If your primary focus is large-scale calcination or mineral reduction: The rotary kiln is the undisputed industry standard due to its high throughput, continuous operation, and ability to handle abrasive materials.
- If your primary focus is processing temperature-sensitive or contamination-prone materials: An indirect-fired rotary kiln is the superior choice, as it isolates the product from direct contact with combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest degree of product uniformity for powders or granules: The continuous tumbling action of a rotary kiln provides more consistent particle-level heat treatment than a static batch furnace.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln remains a cornerstone of modern industry because it provides a reliable and scalable method for precisely transforming raw materials with heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | High-temperature processing to induce chemical reactions or physical changes in materials |
| Key Design Features | Rotating cylinder, slight inclination, refractory lining for uniform heat exposure |
| Heating Methods | Direct-fired (common, with counter/co-current gas flow) and indirect-fired (for contamination-sensitive materials) |
| Control Variables | Rotation speed, slope, feed rate, and temperature to manage residence time and product quality |
| Common Applications | Calcination, mineral reduction, processing powders/granules on an industrial scale |
| Key Advantages | Continuous operation, high throughput, uniform particle mixing, scalability for large volumes |
| Limitations | High energy consumption, not suitable for very fine or sticky materials, requires skilled operation and maintenance |
Unlock Precision in Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Are you tackling large-scale material transformations like calcination or mineral reduction? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and industrial requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our rotary kilns and other solutions can enhance your efficiency, ensure uniform processing, and drive your projects to success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















