At its core, a rotary kiln is an industrial furnace designed for the continuous thermal processing of solid materials. It consists of a long, rotating cylindrical tube inclined at a slight angle, which simultaneously heats and transports material from an upper feed end to a lower discharge end, inducing specific chemical reactions or physical changes.
The true value of a rotary kiln lies not just in its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but in its unique design that uses rotation and gravity to guarantee every particle of material is mixed and heated with unparalleled uniformity on a massive industrial scale.
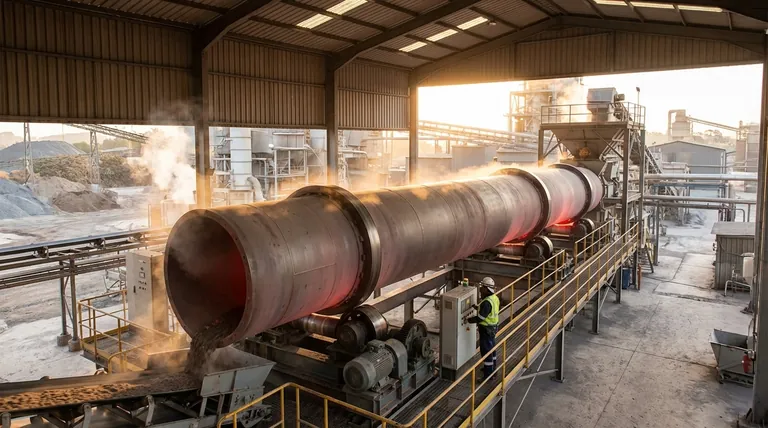

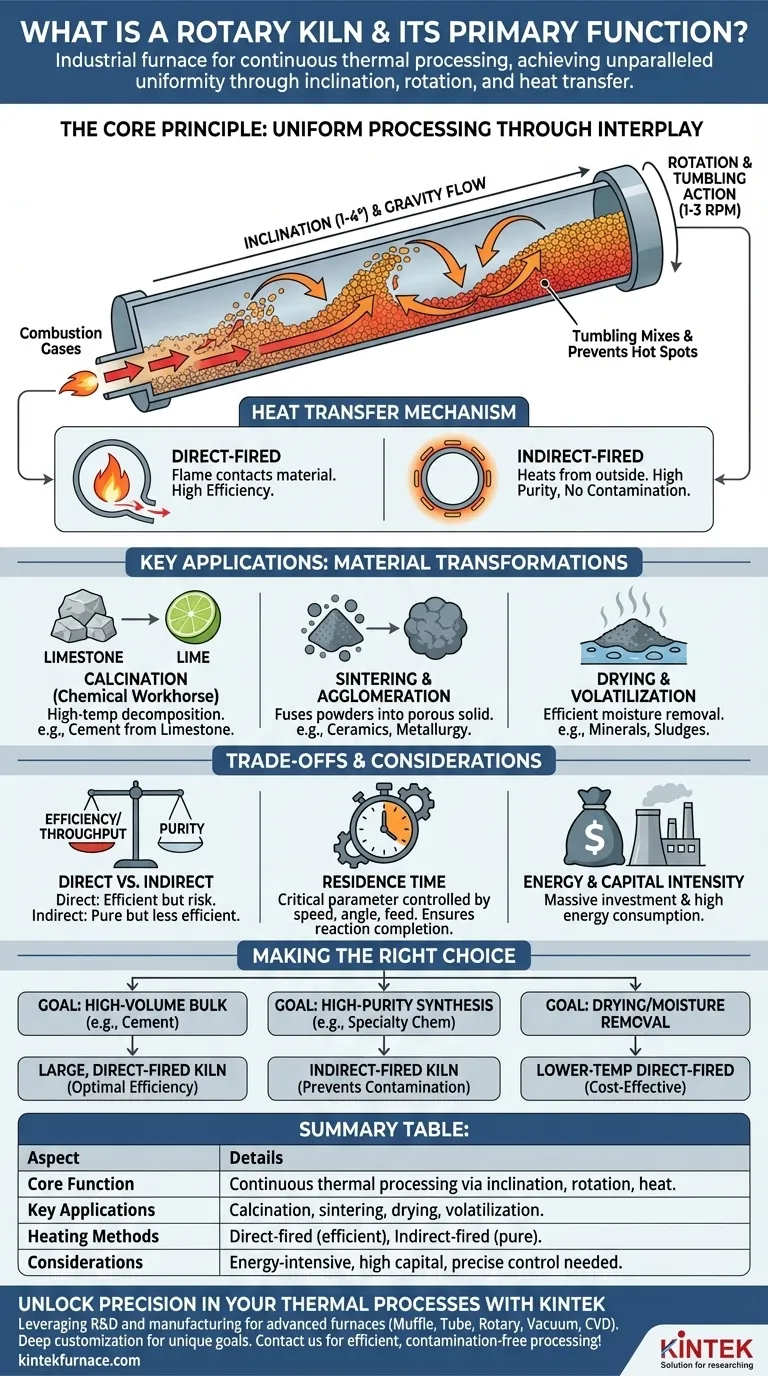
The Core Principle: How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Uniform Processing
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from the elegant interplay of three simple physical principles: inclination, rotation, and heat transfer. This combination solves the difficult challenge of processing large volumes of solids continuously and evenly.
The Role of Inclination and Gravity
The kiln is mounted on a slight downward slope, typically between 1 and 4 degrees. This gentle incline uses gravity to ensure a consistent, predictable flow of material from the point of entry to the point of exit.
This continuous movement is a key advantage over "batch" processes, where materials are loaded, heated, and then unloaded in separate steps.
The Tumbling Action: Ensuring Uniformity
As the kiln slowly rotates (usually 1-3 revolutions per minute), the bed of material inside is constantly lifted up the side of the shell before cascading, or "tumbling," back down.
This tumbling action is the kiln's most critical feature. It thoroughly mixes the solids, preventing hot spots and ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source. This eliminates the "uneven firing" common in static furnaces.
The Heat Transfer Mechanism
Heat is introduced to create the necessary reaction environment. Kilns are primarily heated in one of two ways, depending on the process requirements.
- Direct-Fired Kilns: A flame and hot combustion gases are generated by a burner at the lower end and flow directly through the kiln, coming into contact with the material. This is highly efficient and common in industries like cement manufacturing.
- Indirect-Fired Kilns: The kiln shell is heated from the outside, often using electric heating elements or an external furnace. The material inside never contacts the combustion byproducts, which is essential for high-purity applications where contamination must be avoided.
Key Applications and Material Transformations
The primary function of a rotary kiln is to facilitate specific physical and chemical changes in a material. These transformations are the reason for its widespread use across heavy industry.
Calcination: The Chemical Workhorse
Calcination is a high-temperature process that drives off a volatile component or causes a chemical decomposition. The most prominent example is the production of cement, where limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated in a kiln to produce lime (calcium oxide).
Sintering and Agglomeration
Sintering uses heat to fuse fine powders into a solid, porous mass without melting them completely. This process strengthens materials and is used in metallurgy and the production of ceramics and lightweight aggregate.
Drying and Volatilization
At lower temperatures, a rotary kiln functions as a highly efficient industrial dryer. Its tumbling action and high throughput are ideal for removing moisture from minerals, ores, sludges, and other bulk solids.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. Their design and operation involve critical trade-offs that impact efficiency, cost, and product quality.
Direct-Fired vs. Indirect-Fired Kilns
The choice between heating methods is a fundamental trade-off. Direct firing offers superior thermal efficiency and higher throughput but introduces the risk of product contamination from the fuel source. Indirect firing guarantees product purity but is less energy-efficient and limited by the temperature the outer shell material can withstand.
Material Residence Time
The "residence time"—how long the material spends inside the kiln—is a critical operating parameter. It is controlled by the kiln's rotational speed, its angle of inclination, and the feed rate. Achieving the correct residence time is essential for ensuring the desired chemical reaction or physical change is fully completed.
Energy and Capital Intensity
Rotary kilns are massive pieces of industrial machinery. They represent a significant capital investment and are extremely energy-intensive to operate, often constituting the single largest energy consumer in an entire plant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate kiln configuration depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired final product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing (e.g., cement or minerals): A large, direct-fired kiln is the optimal choice for its unmatched thermal efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis (e.g., specialty chemicals or advanced ceramics): An indirect-fired kiln is necessary to prevent contamination from combustion byproducts, even at the cost of lower energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is drying or removing moisture: A lower-temperature direct-fired design often provides the most cost-effective and efficient solution for handling large volumes of wet material.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln remains a cornerstone of modern industry because it provides a reliable, continuous, and scalable method for precisely engineering the properties of raw materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Continuous thermal processing of solid materials via inclination, rotation, and heat transfer. |
| Key Applications | Calcination (e.g., cement production), sintering, drying, and volatilization. |
| Heating Methods | Direct-fired (high efficiency, risk of contamination) and indirect-fired (high purity, lower efficiency). |
| Advantages | Uniform heating, scalability, continuous operation, and high throughput for industrial use. |
| Considerations | Energy-intensive, high capital cost, requires precise control of residence time and temperature. |
Unlock Precision in Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in cement, ceramics, or specialty chemicals, our expertise ensures efficient, contamination-free processing tailored to your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your industrial thermal applications and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















