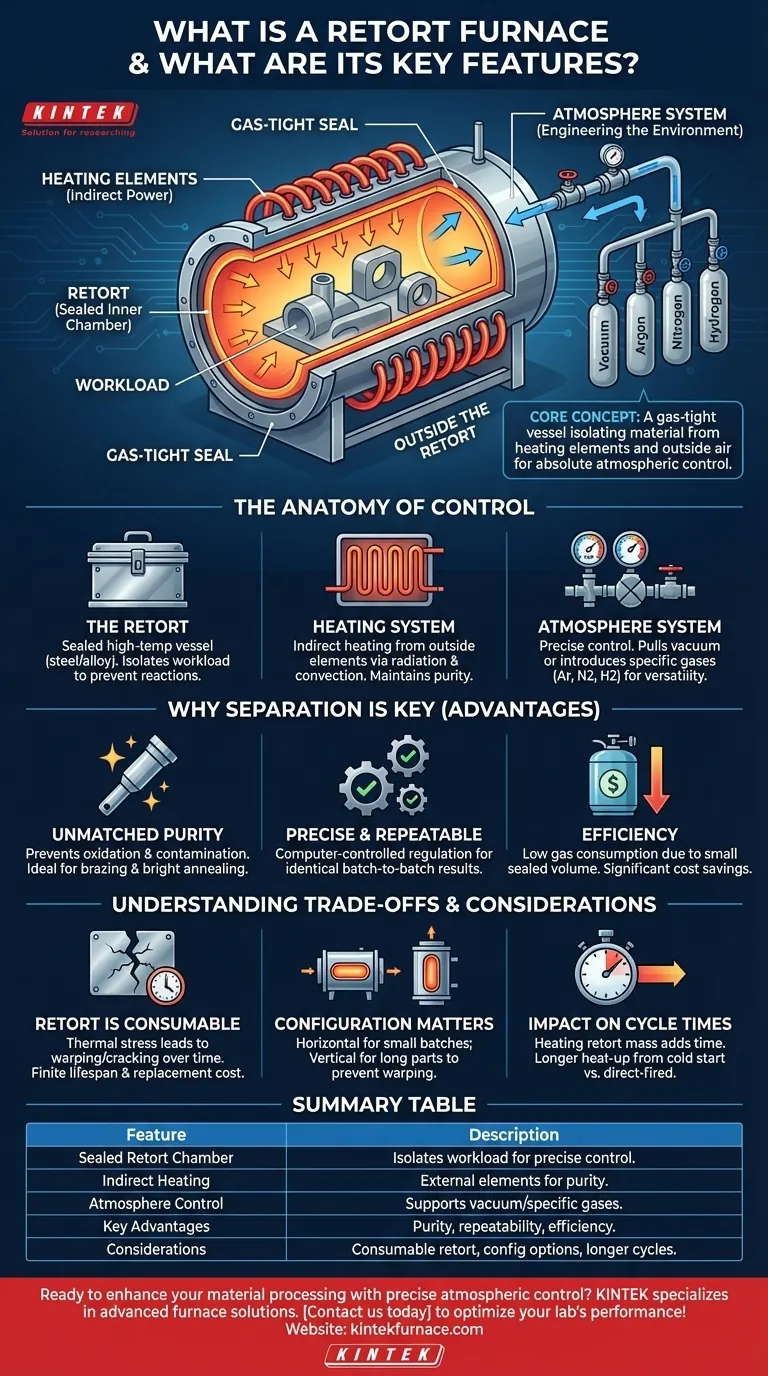
At its core, a retort furnace is a high-temperature industrial oven distinguished by a critical component: a sealed inner chamber, known as the retort. This gas-tight vessel isolates the material being processed from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air. This separation allows for absolute control over the atmospheric conditions during the heating cycle, which is essential for specialized manufacturing and material treatments.
The defining characteristic of a retort furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its sealed inner chamber. This design fundamentally separates the workload from the heat source, enabling precise control over the internal atmosphere to prevent contamination and achieve specific material properties.
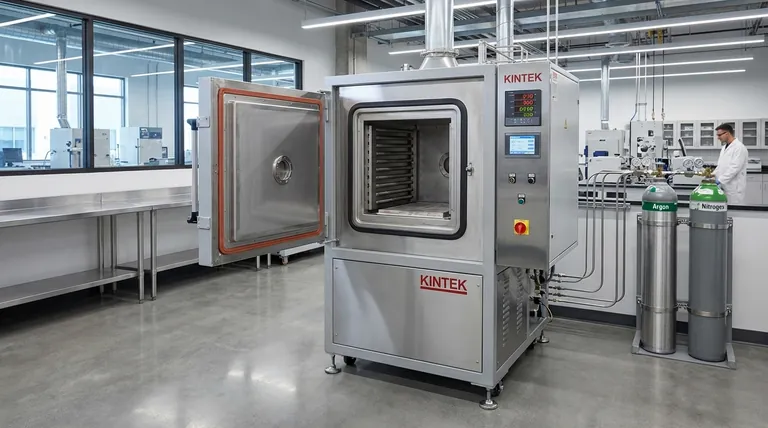

The Anatomy of a Retort Furnace
Understanding a retort furnace requires looking beyond the heat and focusing on its unique structural components that enable process control.
The Retort: A Chamber of Control
The heart of the furnace is the retort. This is a cylindrical or box-shaped vessel, typically made of high-temperature resistant steel or a nickel alloy.
Its sole purpose is to create a perfectly sealed environment for the parts being treated. By isolating the workload, it prevents unwanted reactions with oxygen or other gases.
The Heating System: Indirect Power
The heating elements, which can be electric or gas-fired, are located outside the retort.
They heat the walls of the retort, which then transfers that heat to the workload inside through radiation and convection. This indirect heating method is fundamental to maintaining the purity of the internal atmosphere.
The Atmosphere System: Engineering the Environment
This system allows operators to precisely manipulate the environment inside the retort.
It can be used to pull a vacuum or to introduce and maintain specific protective or reactive gases, such as Argon, Nitrogen, or Hydrogen. The ability to alter these conditions during a single firing cycle makes the furnace incredibly versatile.
Why Separation is the Key Advantage
The separation of the workload from the heating elements is not a minor detail; it is the furnace's primary value proposition, delivering tangible benefits in quality and efficiency.
Unmatched Purity and Product Quality
By creating a controlled atmosphere, a retort furnace effectively prevents oxidation and contamination of the material's surface. This is critical for processes like brazing, where clean surfaces are mandatory, and for producing bright, unblemished parts after annealing.
Precise and Repeatable Process Control
The sealed environment allows for exact, computer-controlled regulation of both temperature and gas composition. This ensures that every process is highly repeatable, delivering identical results from batch to batch.
Efficiency in Atmosphere Usage
Because the retort is a closed and relatively small volume, it requires very little process gas to purge the chamber and maintain the desired atmosphere. This low gas consumption results in significant operational cost savings compared to furnaces that are constantly flushed with gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, retort furnaces have specific operational characteristics that must be factored into any decision.
The Retort is a Consumable Component
The retort is subjected to immense thermal stress during every heating and cooling cycle. Over time, this stress leads to warping and cracking, making the retort a consumable item with a finite lifespan. Its eventual replacement represents a significant maintenance cost.
Configuration Matters: Horizontal vs. Vertical
Retort furnaces are available in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Horizontal furnaces are common for batch processing of many small parts. Vertical furnaces are often preferred for long, slender parts that could distort or warp under their own weight if supported horizontally at high temperatures.
Impact on Cycle Times
The retort itself has a significant thermal mass that must be heated along with the workload. While heat transfer to the parts can be very efficient within the sealed atmosphere, the overall time to heat the furnace from a cold start may be longer than a direct-fired furnace without a retort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace requires aligning the equipment's capabilities with your primary process goal.
- If your primary focus is process purity and preventing oxidation: A retort furnace is the definitive choice, as its sealed chamber offers the highest level of atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost heat treating where some surface discoloration is acceptable: A non-retort, direct-fired or open atmosphere furnace may be more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is versatility for multiple processes (e.g., brazing, sintering, annealing): The retort furnace's ability to precisely manage different atmospheres makes it an exceptionally flexible tool.
Ultimately, a retort furnace is an investment in control, delivering the process purity and repeatability that modern material science demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Sealed Retort Chamber | Isolates workload from heating elements, allowing precise atmospheric control to prevent contamination. |
| Indirect Heating | Heating elements outside the retort transfer heat through radiation and convection for purity. |
| Atmosphere Control | Supports vacuum or specific gases (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen) for versatile processes like brazing and annealing. |
| Key Advantages | Unmatched purity, repeatable results, low gas consumption, and efficiency in material treatments. |
| Considerations | Retort is consumable, available in horizontal/vertical orientations, and may have longer cycle times. |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precise atmospheric control? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring purity, repeatability, and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our retort furnaces can optimize your lab's performance and deliver superior results for applications like brazing, sintering, and annealing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















