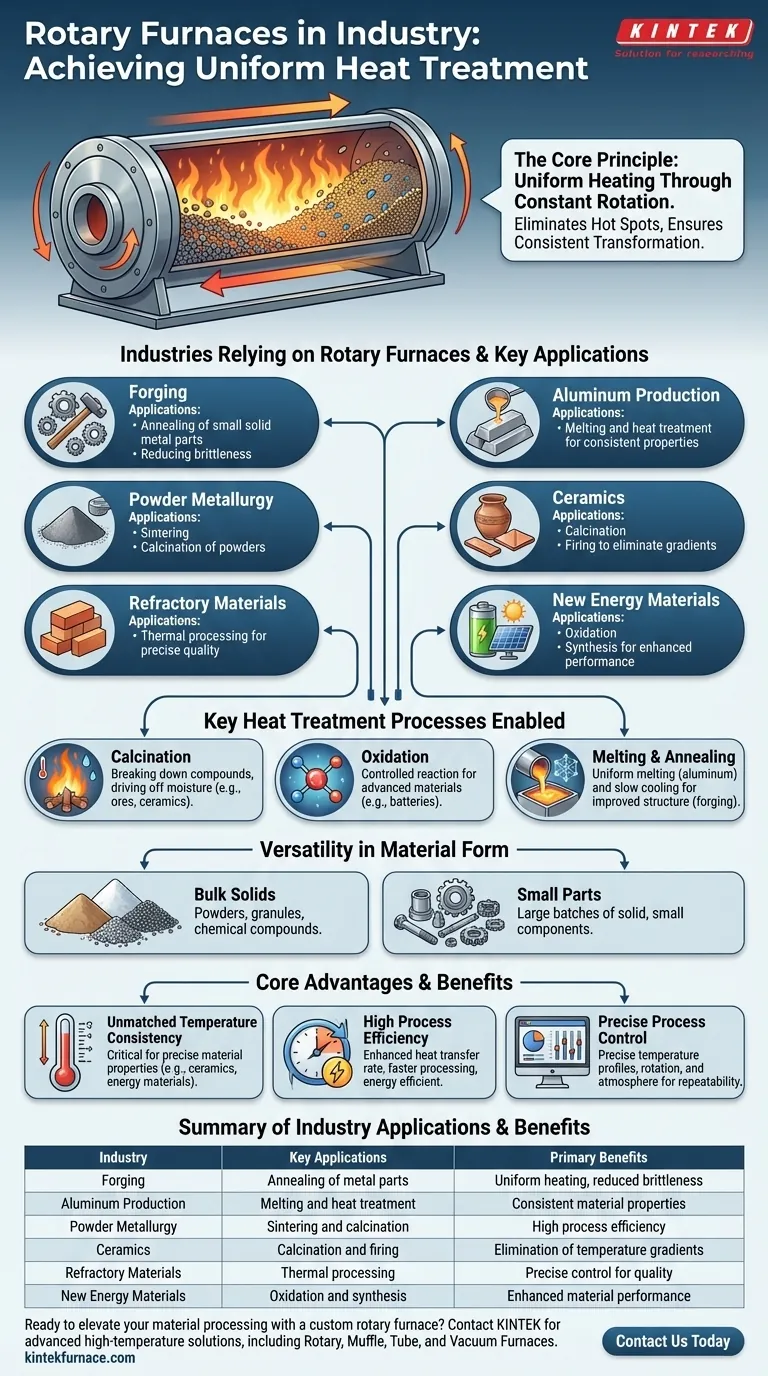
Rotary furnaces are a cornerstone technology for industries that depend on the precise thermal transformation of materials. They are most commonly used in forging, aluminum production, powder metallurgy, ceramics, refractory materials, and the development of new energy materials.
The core reason these industries rely on rotary furnaces is their unique ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heating. The constant rotation tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the same temperature, which is critical for processes like calcination, oxidation, and annealing.

Why These Industries Rely on Rotary Furnaces
The choice of a rotary furnace is not arbitrary; it is a direct solution to the challenge of achieving consistent material properties on an industrial scale. The furnace's design directly enables the specific chemical and physical changes these industries require.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
A rotary furnace is a cylindrical chamber that rotates along its horizontal axis. As material moves through it, it is continuously tumbled and mixed.
This constant motion is the key. It prevents temperature gradients and "hot spots" that can occur in static furnaces, ensuring every part of the material batch receives the exact same heat treatment.
This uniformity is directly linked to higher quality, greater consistency, and less product waste.
Key Heat Treatment Processes Enabled
Rotary furnaces excel at several high-temperature processes that are fundamental to materials science and manufacturing.
Calcination is a process of thermal decomposition. It uses heat to break down compounds, such as driving off moisture from ores or creating the base materials for ceramics.
Oxidation is a controlled chemical reaction used to alter a material's properties. This is especially critical in creating advanced materials, such as those used in batteries and other new energy applications.
Melting and Annealing are essential in metallurgy. Uniform melting is required for aluminum production, while annealing—a process of heating and slow cooling—improves the structure and reduces the brittleness of forged metal parts.
Versatility in Material Form
A significant advantage of rotary furnaces is their ability to process a wide range of material forms.
They are highly effective for powders, granules, and other bulk solids, which are common in the ceramics, powder metallurgy, and chemical industries. They can also effectively heat-treat large batches of small, solid parts for the forging industry.
Understanding the Core Advantages
While other furnace types exist, the rotary furnace is chosen when certain outcomes are non-negotiable. Its advantages are rooted in its fundamental design.
Unmatched Temperature Consistency
The primary benefit is the elimination of temperature differences within the material batch. For processes where a few degrees can alter the final product's performance—such as in ceramics or new energy materials—this consistency is paramount.
High Process Efficiency
The tumbling action not only ensures uniform temperature but also enhances the rate of heat transfer. This can lead to faster processing times and greater energy efficiency compared to static batch furnaces.
Precise Process Control
Modern rotary furnaces are integrated with computer systems that allow for precise control over temperature profiles, rotation speed, and atmospheric conditions within the furnace. This level of control is crucial for repeatable, high-quality production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core function of a rotary furnace helps clarify its application in your specific field.
- If your primary focus is transforming granular or powdered raw materials: A rotary furnace is ideal for calcination or oxidation, as its mixing action ensures every particle is transformed uniformly.
- If your primary focus is heat treating batches of small, solid metal parts: The tumbling motion guarantees that all surfaces of each part are evenly heated during annealing, resulting in consistent structural properties.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced chemical or energy materials: The precise control over temperature and atmosphere makes a rotary furnace essential for creating materials with specific, highly-engineered compositions.
Ultimately, selecting a rotary furnace is a decision to prioritize material uniformity and precise process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Forging | Annealing of metal parts | Uniform heating, reduced brittleness |
| Aluminum Production | Melting and heat treatment | Consistent material properties |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintering and calcination | High process efficiency |
| Ceramics | Calcination and firing | Elimination of temperature gradients |
| Refractory Materials | Thermal processing | Precise control for quality |
| New Energy Materials | Oxidation and synthesis | Enhanced material performance |
Ready to elevate your material processing with a custom rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering unmatched uniformity, efficiency, and control for industries like forging, aluminum production, and new energy materials. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















