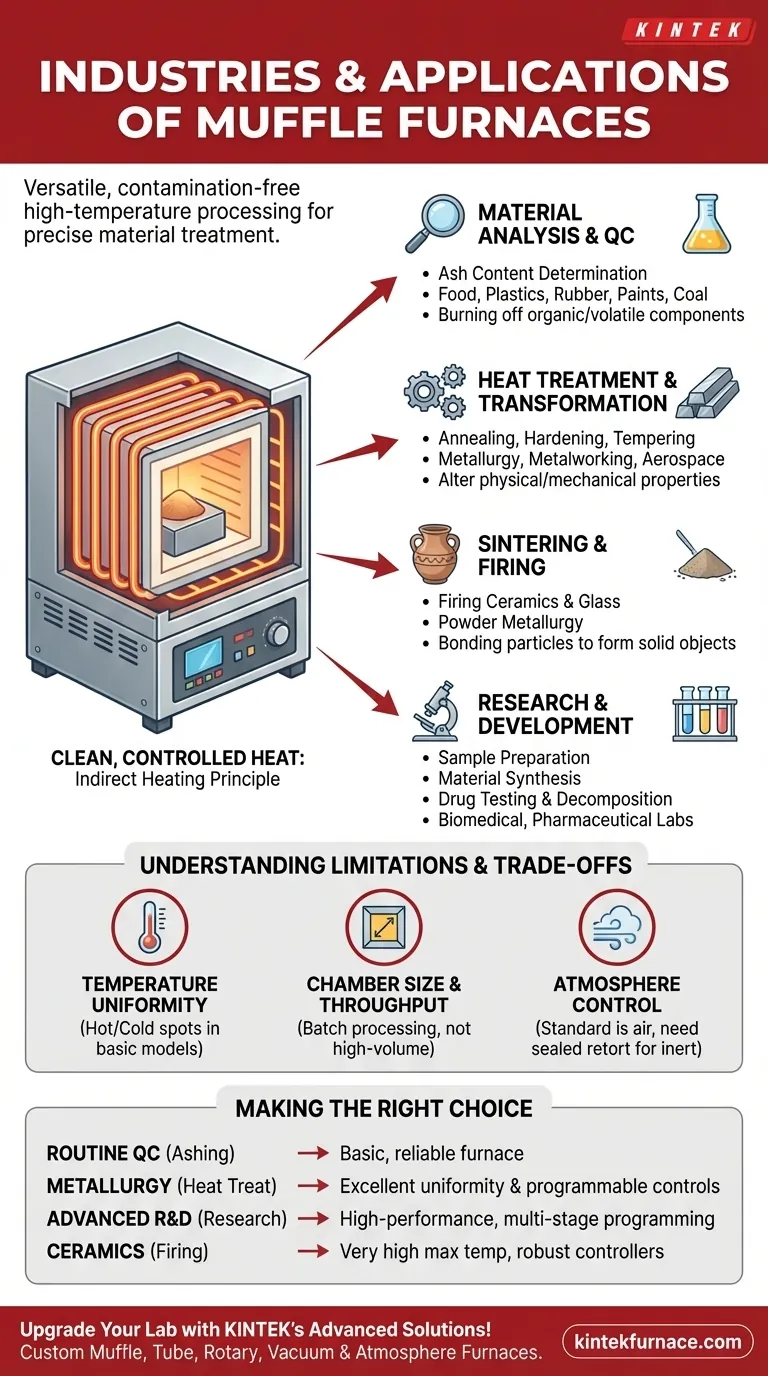
In short, muffle furnaces are used across a vast range of sectors, including research laboratories, metallurgy, aerospace, ceramics, plastics, and biomedical fields. Their versatility stems from the ability to perform high-temperature processes like material testing, heat treatment, and sample analysis in a highly controlled, contamination-free environment.
The core value of a muffle furnace isn't just high heat; it's the ability to apply that heat precisely and cleanly. By separating the material being heated from the furnace's heating elements, it ensures that the only variable affecting the sample is the temperature itself.
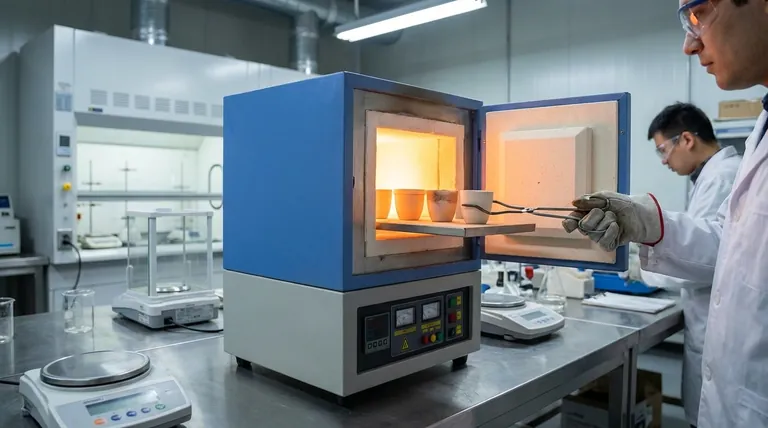

The Core Function: Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
To understand why so many industries rely on muffle furnaces, you must first understand their fundamental design principle.
What is a "Muffle"?
A muffle furnace contains a primary chamber made of a high-temperature, non-corrosive material, often a type of ceramic. This chamber, the "muffle," is what holds the material or sample.
The heating elements are located outside of this muffle. They heat the chamber, which in turn radiates heat to the sample inside.
Why This Design is Critical
This indirect heating method is the key to the furnace's utility. It isolates the sample from any byproducts of combustion or contamination from the heating elements themselves.
This ensures that any changes to the material—whether it's burning away organic matter or altering a metal's crystal structure—are a direct result of the controlled temperature profile, not a chemical reaction with the heat source.
Key Applications Across Industries
Different industries use this core function of clean, precise heating to achieve specific goals. We can group these applications into several major categories.
Material Analysis and Quality Control
This is one of the most common uses, where the goal is to analyze a material's composition by burning it under controlled conditions.
Industries like food, plastics, rubber, paints, and coal analysis use muffle furnaces for ash content determination. By heating a sample to a high temperature, all organic and volatile components are burned off, leaving only the non-combustible ash (e.g., minerals, fillers), which can then be weighed and analyzed.
Heat Treatment and Material Transformation
The metallurgy, metalworking, and aerospace industries depend on muffle furnaces for precise heat treatment to alter the physical and mechanical properties of metals.
Key processes include:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a metal to make it more ductile and less brittle.
- Hardening: Heating a metal and then rapidly cooling (quenching) it to increase its hardness.
- Tempering: Re-heating a hardened part to a lower temperature to reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness.
Sintering and Firing
This application involves heating powdered materials to a point where their particles bond together to form a solid, coherent object without melting completely.
The ceramics industry uses muffle furnaces extensively for firing everything from pottery to advanced technical ceramics. It is also critical in glass manufacturing for certain treatments and in powder metallurgy for creating complex metal parts.
Research and Development
Nearly every research laboratory—whether academic, biomedical, or pharmaceutical—benefits from a muffle furnace. Its versatility makes it a workhorse for a wide array of tasks.
These include preparing samples for analysis, synthesizing new materials, testing material stability at high temperatures, and performing drug testing and decomposition studies in the biomedical and pharmaceutical sectors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly useful, muffle furnaces are not a universal solution for all high-temperature needs. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Temperature Uniformity
For processes like heat treating or sensitive materials synthesis, the temperature must be perfectly uniform throughout the entire chamber. Basic models may have hot or cold spots, while high-performance furnaces incorporate multiple heating zones and advanced controls to ensure uniformity.
Chamber Size and Throughput
Muffle furnaces are typically designed for batch processing, not continuous, high-volume manufacturing. Their size limits the throughput, making them ideal for labs, quality control, or the production of smaller, high-value parts.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. While the sample is protected from heating element contamination, it is still exposed to oxygen. For processes that require an inert (e.g., argon, nitrogen) or reactive atmosphere, a specialized, sealed retort furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right tool, match the furnace's capabilities to your primary application.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control (e.g., ashing): A basic, reliable furnace with good temperature stability is sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy or heat treating: Prioritize a furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and programmable controls for precise heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: You need a high-performance model, likely with multi-stage programming and potential options for atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is ceramics or glass firing: A furnace with a very high maximum temperature and robust, programmable controllers for long, complex firing schedules is essential.
Understanding that a muffle furnace's true purpose is to provide clean, controlled heat empowers you to choose the exact tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ash content determination in food, plastics, rubber, paints, coal |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, tempering in metallurgy, aerospace |
| Sintering and Firing | Firing ceramics, glass manufacturing, powder metallurgy |
| Research and Development | Sample prep, material synthesis, drug testing in labs, biomedical |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your industry applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















