The industries where material failure is simply not an option are the ones that benefit most from vacuum furnace technology. This includes demanding sectors like aerospace, medical, tool and die manufacturing, and advanced electronics, where the absolute purity and structural integrity of components are paramount for safety and performance.
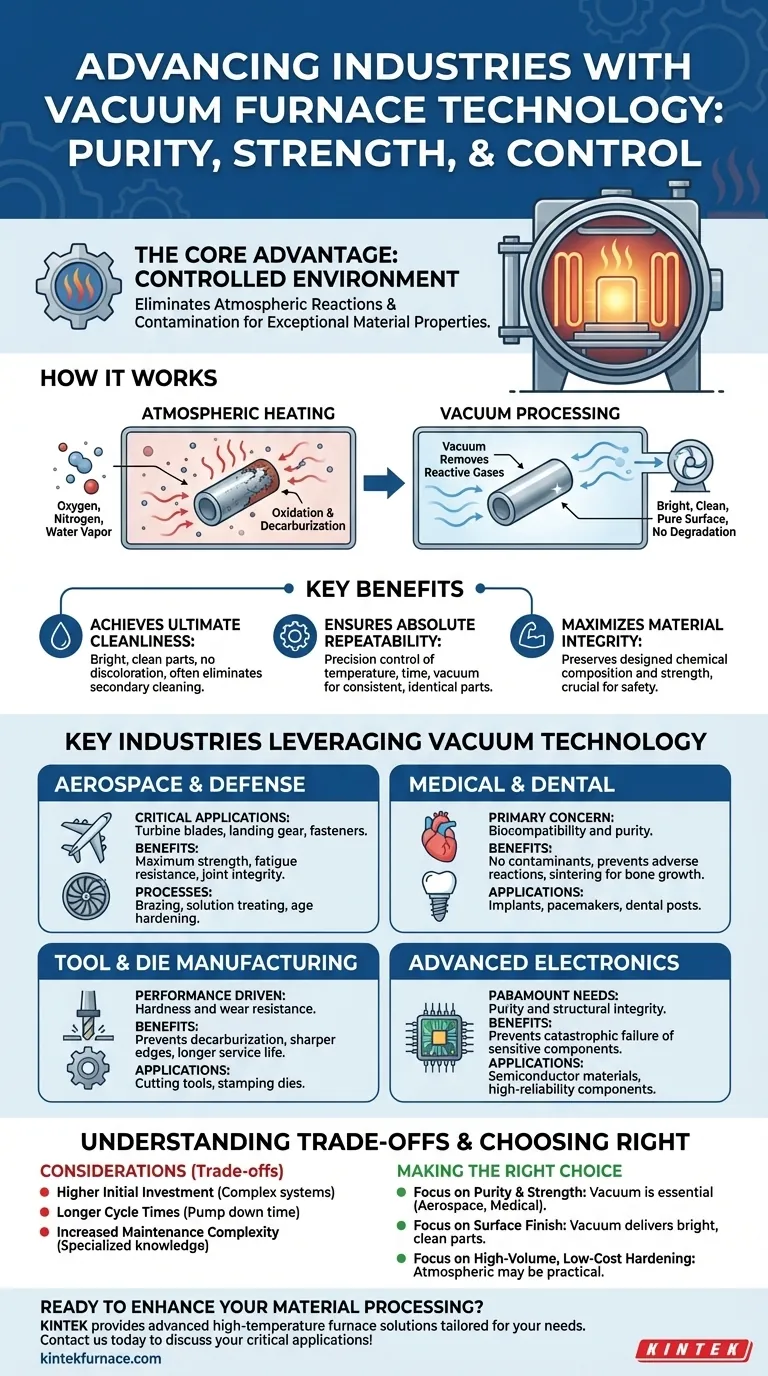
The core value of a vacuum furnace isn't just about heat; it's about control. By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, enabling the creation of materials with exceptional purity, strength, and specific properties that are impossible to achieve otherwise.
The Fundamental Advantage: Controlling the Environment
At its heart, a vacuum furnace solves one of the biggest challenges in metallurgy: contamination. When metals are heated in the presence of air, they react with oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. A vacuum furnace creates a controlled, chemically inert environment.
Eliminating Atmospheric Reactions
At high temperatures, the oxygen in the air aggressively attacks metal surfaces. This leads to oxidation (scaling) and decarburization—a process where carbon is stripped from the surface of steel alloys, making them weaker.
A vacuum removes these reactive gases. This prevents surface degradation, ensuring the material retains its designed chemical composition and strength from its core to its surface.
Achieving Ultimate Cleanliness
Because there are no reactions with atmospheric gases, parts emerge from a vacuum furnace bright, clean, and free of discoloration.
This level of cleanliness is not just cosmetic. For a medical implant or a sensitive electronic component, any surface contamination could cause catastrophic failure. This process often eliminates the need for subsequent chemical or mechanical cleaning.
Ensuring Absolute Repeatability
A vacuum is a highly measurable and controllable process variable. Modern furnace controls can replicate processing parameters—temperature, time, and vacuum level—with incredible precision.
This process repeatability is essential for industries with stringent quality control standards, ensuring that the ten-thousandth part has the exact same metallurgical properties as the first.
How Key Industries Leverage Vacuum Technology
The theoretical benefits of vacuum processing translate into critical, real-world advantages for high-stakes manufacturing.
Aerospace and Defense
For mission-critical components like turbine blades, landing gear, and structural fasteners, failure can be catastrophic. These parts are often made from superalloys that require complex heat treatment.
Vacuum furnaces are used for processes like brazing, solution treating, and age hardening. The controlled environment ensures maximum material strength, fatigue resistance, and joint integrity.
Medical and Dental
Biocompatibility is the primary concern for any material placed inside the human body. Medical implants like artificial joints, pacemakers, and dental posts must be perfectly pure.
Vacuum heat treating ensures these devices are free of surface oxides or contaminants that could trigger an adverse reaction. It is also used for sintering porous coatings that allow bone to grow into the implant, a process that requires extreme cleanliness.
Tool & Die Manufacturing
The performance of a cutting tool or a stamping die is determined by its hardness and wear resistance. These properties are achieved through precise hardening processes.
Using a vacuum furnace prevents the decarburization that weakens the cutting edge of a tool. This results in tools that stay sharper for longer, have a tougher core to resist chipping, and exhibit a significantly longer service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
As a trusted advisor, it's my duty to present a complete picture. While powerful, vacuum technology is not universally superior for every application.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex than their atmospheric counterparts. The vacuum chamber, pumping systems, and sophisticated controls lead to a significantly higher upfront capital cost.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber adds to the overall process cycle time, which can impact throughput for high-volume production.
Increased Maintenance Complexity
The systems that create and maintain the vacuum—including pumps, seals, and instrumentation—require specialized knowledge for routine maintenance and troubleshooting, adding to the operational overhead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace must be driven by the specific requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and strength: Vacuum processing is essential for mission-critical applications in aerospace, defense, and medical fields.
- If your primary focus is a perfect surface finish: Vacuum furnaces deliver parts that are bright and clean, often eliminating the cost and complexity of secondary cleaning steps.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost hardening: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more practical and economical choice, provided minor surface oxidation is acceptable.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum technology is an investment in certainty—the certainty of material integrity, process consistency, and superior final performance.

Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Aerospace and Defense | Maximum strength, fatigue resistance, joint integrity for turbine blades, landing gear |
| Medical and Dental | Biocompatibility, purity for implants, no contaminants, sintering for bone growth |
| Tool and Die Manufacturing | Hardness, wear resistance, longer tool life, prevention of decarburization |
| Advanced Electronics | Purity, structural integrity for sensitive components, prevention of failure |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and tool manufacturing. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can deliver purity, strength, and repeatability for your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















