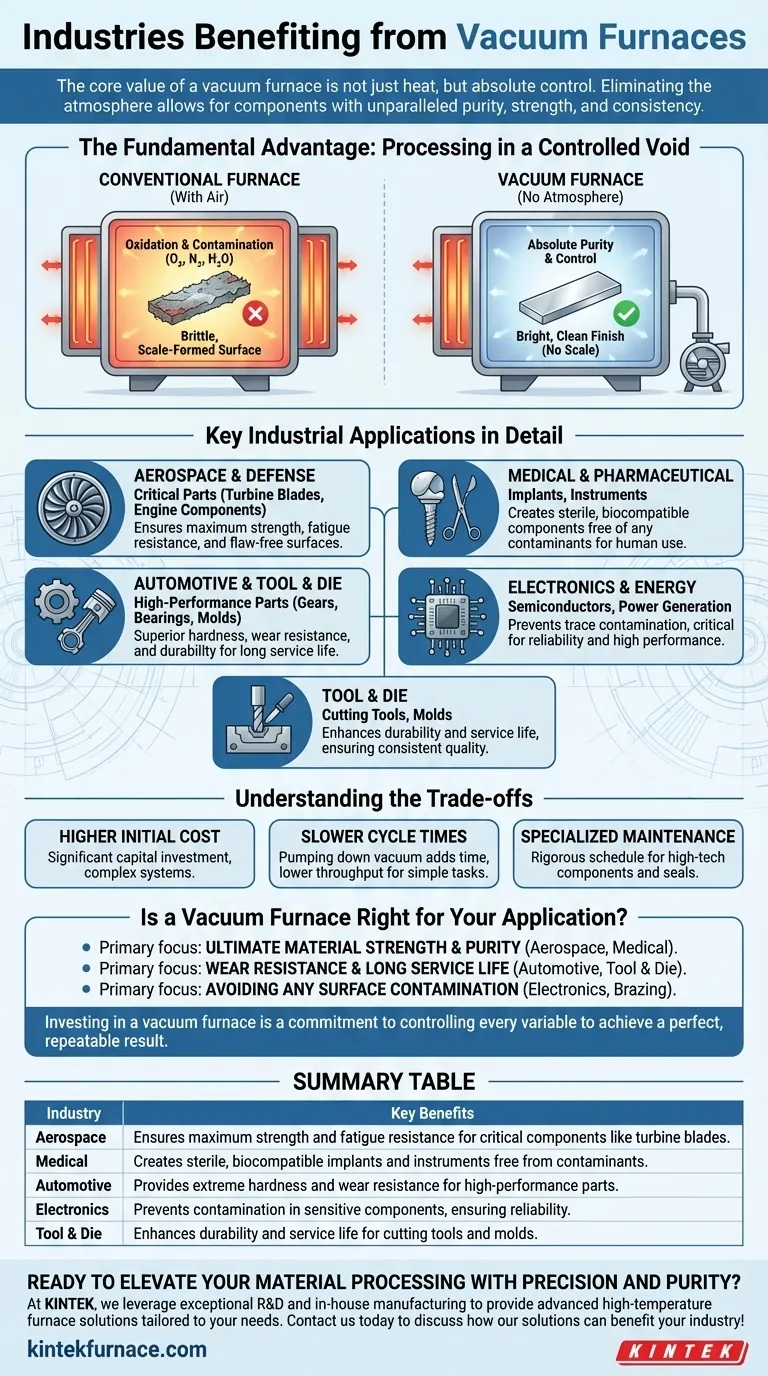
In short, any industry requiring heat treatment of materials without surface oxidation or contamination benefits from vacuum furnaces. Key sectors include aerospace, medical, automotive, tool and die, and electronics, where the structural integrity and purity of components are absolutely critical for performance and safety.
The core value of a vacuum furnace is not just heat, but absolute control. By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate unpredictable reactions like oxidation, allowing for the creation of components with unparalleled purity, strength, and consistency.

The Fundamental Advantage: Processing in a Controlled Void
To understand why these industries invest in vacuum technology, you must first grasp the problem it solves. A conventional furnace heats materials in the presence of air, which is rich in oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. At high temperatures, these gases aggressively react with the material's surface.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The most significant benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen. When heated, metals readily react with oxygen to form a brittle, flaky layer of oxide scale. This scale compromises surface finish, alters component dimensions, and can create points of weakness.
A vacuum environment effectively prevents this, resulting in bright, clean parts that often require no post-processing cleanup.
Ensuring Metallurgical Purity
Beyond oxidation, the controlled atmosphere prevents other unwanted reactions. For example, it stops decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel—which reduces hardness and wear resistance. By processing in a vacuum, the material's carefully engineered chemical composition is perfectly preserved from the core to the surface.
Achieving Absolute Process Control
Modern vacuum furnaces offer unparalleled computer control over the entire heat treatment cycle. Engineers can program precise temperature ramp rates, soak times, and cooling (quenching) profiles. This digital repeatability ensures that every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, receives the exact same metallurgical treatment, guaranteeing consistent quality.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The demand for control and purity drives the adoption of vacuum furnaces across several high-stakes industries.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, component failure is not an option. Vacuum furnaces are used for the solution heat treating, aging, and brazing of critical parts like turbine blades, engine components, and structural elements. The process guarantees maximum material strength and fatigue resistance, free from microscopic surface flaws that could propagate into cracks.
Medical and Pharmaceutical
Any device intended for the human body, such as orthopedic implants, pacemakers, and surgical instruments, must be impeccably clean and biocompatible. Vacuum heat treatment creates strong, sterile components with a pure surface, free of any contaminants that could cause an adverse reaction.
Automotive and Tool & Die
High-performance automotive parts like gears, bearings, and fuel injectors demand extreme hardness and wear resistance. Vacuum carburizing and hardening create a superior case depth and material toughness. Similarly, in the tool and die industry, vacuum treatment gives cutting tools and molds the durability needed for a long service life.
Electronics and Energy
The semiconductor industry relies on vacuum furnaces for processes like annealing and brazing, where even trace amounts of contamination can ruin sensitive electronic components. In the energy sector, equipment for power generation requires robust, high-performance materials that can withstand extreme conditions, which are perfected through vacuum heat treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Their adoption involves specific considerations.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. The systems involve complex vacuum pumps, seals, and control instrumentation that add to the upfront cost.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to each cycle. For simple heat treatments where surface oxidation is not a major concern, an atmospheric furnace may offer faster throughput.
Specialized Maintenance
The high-tech components of a vacuum furnace, particularly the pumping systems and seals, require a rigorous and specialized maintenance schedule to ensure performance and prevent costly downtime.
Is a Vacuum Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing this technology is a strategic decision based on the final properties your component requires.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material strength and purity: A vacuum furnace is essential, as seen in aerospace and medical applications where performance and safety are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and long service life: Vacuum heat treating provides superior hardness and durability for high-performance automotive parts and industrial tools.
- If your primary focus is avoiding any surface contamination: A vacuum is the only way to guarantee a perfectly clean, bright finish, which is critical for electronics and brazing applications.
Ultimately, investing in a vacuum furnace is a commitment to controlling every variable to achieve a perfect, repeatable result.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Ensures maximum strength and fatigue resistance for critical components like turbine blades. |
| Medical | Creates sterile, biocompatible implants and instruments free from contaminants. |
| Automotive | Provides extreme hardness and wear resistance for high-performance parts. |
| Electronics | Prevents contamination in sensitive components, ensuring reliability. |
| Tool & Die | Enhances durability and service life for cutting tools and molds. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, automotive, or electronics, we can help you achieve unparalleled control and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your industry!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum annealing furnace improve material performance? Achieve Purity and Strength in Materials
- How is cooling achieved in a vacuum furnace after the desired process? Master Gas Quenching for Precision Results
- What is the technical purpose of a vacuum distillation system in VMPPS synthesis? Enhance Polymer Weight and Purity
- How does a vacuum heat treating furnace improve the condition of metal alloys? Achieve Superior Metal Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in processing mixed TiB2-SiC slurries? Protect Material Integrity
- How is a laboratory vacuum drying oven utilized in the production of shape-stabilized phase change materials?
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven? Essential Benefits for Graphene Composite Powders
- Why must a vacuum system maintain 3.6 mbar for plasma nitriding? Master Precision Surface Hardening



















