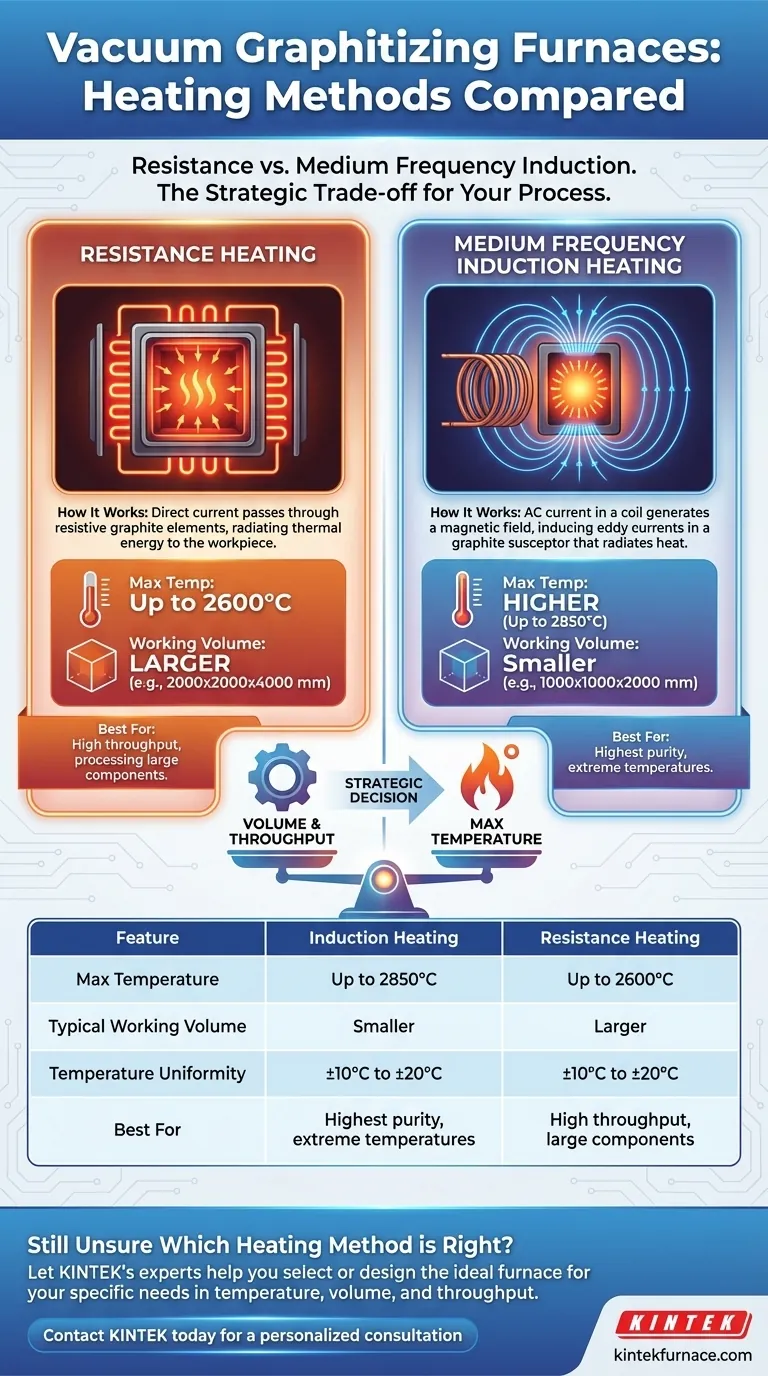
At its core, a vacuum graphitizing furnace can be equipped with one of two primary heating methods. The choice depends on the specific configuration and operational requirements, centering on a trade-off between maximum temperature and the size of the working volume. The two methods are medium frequency induction heating and resistance heating.
The central decision between heating methods is a strategic one: Induction heating achieves higher maximum temperatures, making it ideal for the most demanding graphitization processes, while resistance heating enables significantly larger furnace volumes, prioritizing throughput and the processing of large components.
How Each Heating Method Works
To understand the trade-offs, you must first understand the fundamental principles behind how each method generates heat within the vacuum environment. Both are effective, but they achieve their goal in distinct ways.
Resistance Heating
Resistance heating is a direct and robust method. It works by passing a high electrical current through heating elements made of a material with high electrical resistance, typically graphite.
These graphite elements are arranged around the furnace's "hot zone," surrounding the material being processed. As current flows through them, they heat up due to the Joule effect and radiate thermal energy to the workpiece and the graphite retort holding it.
Medium Frequency Induction Heating
Induction heating is an indirect method that uses electromagnetism. A high-frequency alternating current is passed through a copper coil, which is typically located outside the vacuum chamber or is water-cooled inside it.
This coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field. The magnetic field penetrates the furnace and induces powerful electrical eddy currents within a graphite susceptor or muffle inside the hot zone. It is this graphite susceptor that heats up intensely and, in turn, radiates heat to the material being processed.
Key Differences: A Head-to-Head Comparison
While both methods achieve the high temperatures needed for graphitization, the references highlight critical differences in their performance specifications that directly impact their suitability for different applications.
Maximum Temperature
Induction heating holds a clear advantage in peak temperature capability. Furnaces using this method can reach up to 2850°C.
Resistance heating, while still capable of extremely high temperatures, typically maxes out at a slightly lower 2600°C. This difference can be critical for specific advanced material processes.
Available Working Volume
This is where resistance heating excels. Resistance-heated furnaces can be constructed with very large working zones, with examples reaching up to 2000x2000x4000 mm.
Induction heating systems, due to the physics of generating a uniform magnetic field, are generally limited to smaller working volumes, such as 1000x1000x2000 mm or less.
Temperature Uniformity
Both methods provide excellent temperature uniformity, which is critical for consistent material properties.
The stated uniformity for both is in the range of ±10°C to ±20°C, depending on the specific furnace design and control systems. Resistance heating has a slight potential edge at the lower end of this range, but both are considered highly uniform.
Construction and Materials
The choice of heating method is just one piece of the furnace system. The references note that the furnace design also includes choices for insulation materials (soft felt vs. rigid composite felt) and the quality of the heater and muffle materials themselves (e.g., isostatic vs. fine-grain graphite).
These choices interact with the heating method to determine the furnace's overall performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision is not about which method is "better" in a vacuum, but which is better for a specific goal. Choosing the wrong system can lead to process limitations or unnecessary capital expenditure.
The primary trade-off is maximum temperature vs. furnace volume. If your process absolutely requires temperatures above 2600°C, induction heating is your only viable option. However, this choice constrains you to a smaller processing volume per batch.
Conversely, if your priority is high throughput or processing very large monolithic parts, a resistance-heated furnace provides the necessary scale. You must accept a slightly lower maximum operating temperature in exchange for this volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements for temperature, part size, and production volume are the only factors that matter.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material purity and crystalline structure: Choose an induction furnace for its superior maximum temperature capability (up to 2850°C).
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput or processing large components: Choose a resistance furnace for its ability to accommodate significantly larger working volumes.
- If your process falls comfortably below 2600°C and involves moderately sized parts: Both options are viable, and the decision may come down to secondary factors like cost, existing infrastructure, and manufacturer preference.
By understanding this core trade-off, you can specify a furnace that is precisely matched to your operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Resistance Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 2850°C | Up to 2600°C |
| Typical Working Volume | Smaller (e.g., 1000x1000x2000 mm) | Larger (e.g., 2000x2000x4000 mm) |
| Temperature Uniformity | ±10°C to ±20°C | ±10°C to ±20°C |
| Best For | Highest purity, extreme temperatures | High throughput, large components |
Still Unsure Which Heating Method is Right for Your Graphitization Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let our experts help you select or design the ideal furnace for your specific needs in temperature, volume, and throughput.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?



















