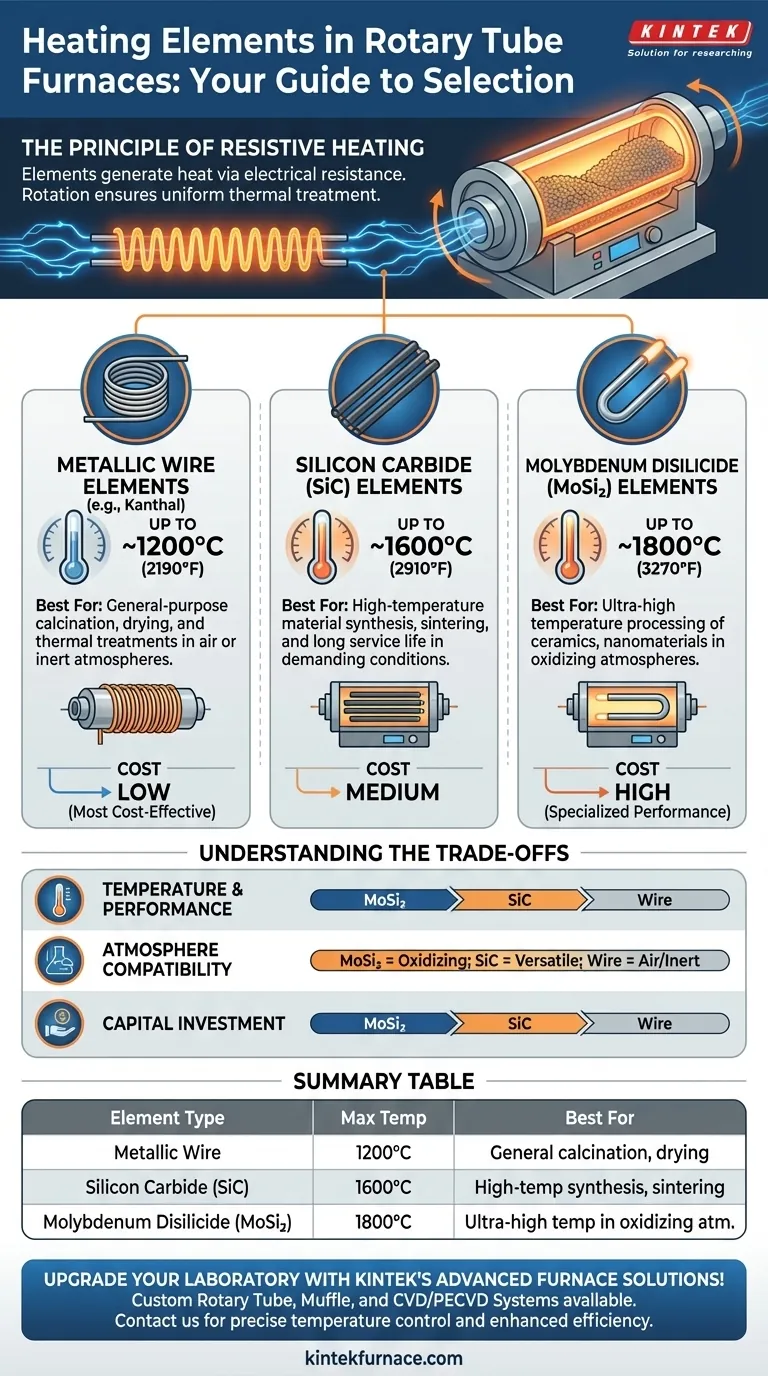
In rotary tube furnaces, the choice of heating element is dictated primarily by the required operating temperature and processing atmosphere. The most common types are metallic wire-wound elements, silicon carbide (SiC) rods, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements. Each is engineered for a specific performance envelope, ensuring the furnace can reliably and efficiently heat materials for a given application.
The selection of a heating element is not arbitrary; it is a critical design choice directly tied to the maximum temperature and atmosphere your process requires. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each element type is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and furnace longevity.

The Principle of Resistive Heating
The core function of a rotary tube furnace is to provide dynamic, uniform thermal treatment to granular or powdered materials. The heating elements are the engine that drives this process.
How Elements Generate Heat
All common heating elements operate on the principle of electrical resistance. When an electrical current is passed through the element, its inherent resistance causes it to heat up significantly. This radiant heat is then transferred to the furnace chamber and the rotating work tube.
Ensuring Uniformity
While the elements provide the heat, the furnace's rotation is what guarantees uniformity. By constantly tumbling the material, the system ensures that all particles are exposed evenly to the radiant heat, preventing hot spots and delivering highly consistent, reproducible results.
A Breakdown of Common Heating Elements
The specific element used in a furnace is a direct reflection of its intended operating range.
Metallic Wire Elements
These elements, often made from alloys like Kanthal (FeCrAl), are wound around the ceramic furnace tube. They are the standard for lower and moderate-temperature applications.
- Operating Temperature: Typically up to ~1200°C (2190°F).
- Best For: General-purpose calcination, drying, and thermal treatments in air or inert atmospheres where extreme temperatures are not required.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements
Silicon carbide elements are robust, self-supporting rods typically positioned parallel to the work tube. They represent a significant step up in temperature capability and durability from wire elements.
- Operating Temperature: Typically up to ~1600°C (2910°F).
- Best For: High-temperature material synthesis, sintering, and processes requiring long service life under demanding conditions.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements
These "U-shaped" elements are the premier choice for the highest temperature applications in oxidizing atmospheres. When heated in air, they form a protective surface layer of quartz glass (SiO₂) that allows them to function at extreme temperatures.
- Operating Temperature: Up to ~1800°C (3270°F).
- Best For: Ultra-high temperature processing of ceramics, nanomaterials, and specialty powders in an air or oxygen-rich environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and the specific needs of your material process. The heating element is central to this decision.
The Impact of Temperature
This is the single most important factor. Using an element beyond its maximum rated temperature will lead to rapid degradation and premature failure. Conversely, over-specifying a furnace with high-temperature elements for a low-temperature process results in unnecessary capital expense.
The Influence of Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace can react with the heating elements.
- MoSi₂ elements depend on an oxidizing atmosphere (like air) to form their protective layer and are generally not suitable for reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen).
- Metallic wire elements will slowly oxidize over time, which is a normal part of their aging process in air.
- SiC elements are relatively robust across different atmospheres but still have limitations.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost.
- Wire-wound furnaces are the most cost-effective.
- Silicon carbide represents a mid-range investment for higher performance.
- Molybdenum disilicide furnaces are the most expensive, reflecting their specialized, high-temperature capabilities.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Process
Your specific processing goals should guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose processing up to 1200°C: A furnace with metallic wire-wound elements offers the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing up to 1600°C: Silicon carbide (SiC) elements provide a durable and versatile option for more demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperatures (above 1600°C) in an air atmosphere: Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are required, representing the peak of performance for thermal processing.
Matching the heating element to your specific temperature and atmospheric needs is the foundational step toward achieving reliable and reproducible results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | Up to 1200°C | General-purpose calcination, drying in air or inert atmospheres |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | High-temperature synthesis, sintering, durable applications |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | Ultra-high temperature processing in oxidizing atmospheres |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable rotary tube furnaces featuring elements like metallic wire, SiC, and MoSi₂. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve precise temperature control and enhanced efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















