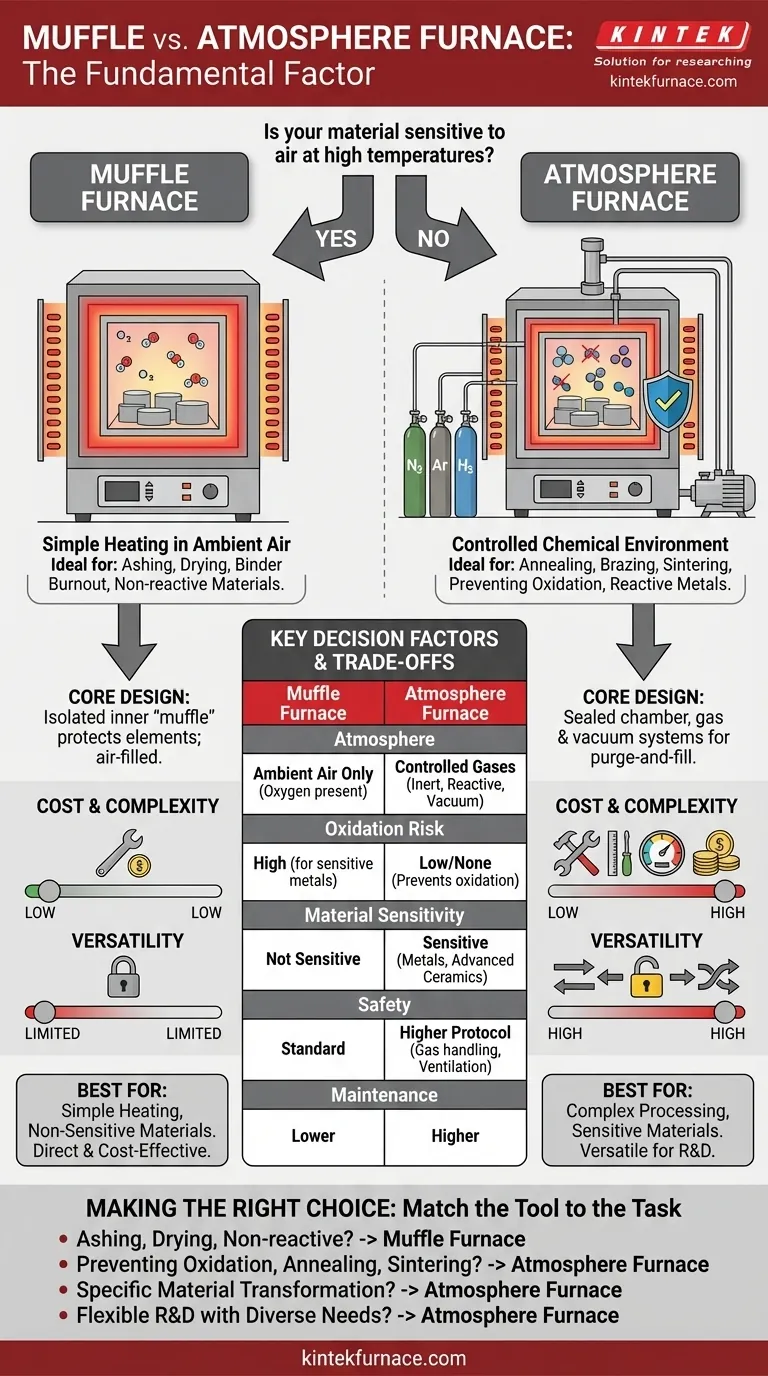
The fundamental factor in choosing between a muffle furnace and an atmosphere furnace is whether your process simply requires high heat or if it demands a controlled chemical environment. A muffle furnace provides high-temperature heating in ambient air, while an atmosphere furnace gives you precise control over the gas surrounding your sample, preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
The decision boils down to one critical question: Is your material sensitive to air at high temperatures? If the answer is yes, an atmosphere furnace is necessary. If not, a simpler muffle furnace is the more direct and cost-effective tool for the job.

Deconstructing the Furnaces: Core Design Differences
To make an informed choice, you must first understand how these furnaces are constructed and what capabilities arise from their designs. While related, their internal systems serve fundamentally different purposes.
The Muffle Furnace: A High-Temperature Oven
A muffle furnace is the most straightforward type of high-temperature laboratory furnace. Its core component is a "muffle"—an isolated inner chamber made of a thermally resistant material that holds your samples.
Heating elements are typically positioned on the outside of this muffle. This design protects the heating elements from any potential off-gassing from the sample and prevents contamination of the sample by the elements.
The crucial point is that the atmosphere inside is simply ambient air. These furnaces are ideal for processes like ashing, drying, or heat-treating materials that are not reactive with oxygen.
The Atmosphere Furnace: A Controlled Chemical Environment
An atmosphere furnace builds upon the basic design of a muffle furnace but adds critical systems for atmospheric control. It is essentially a sealed chamber designed for high-purity processing.
These furnaces include a gas delivery system to introduce specific gases (e.g., inert nitrogen or argon, or reactive hydrogen) and a vacuum system to first remove the air from the chamber.
This purge-and-fill capability is the furnace's defining feature. By removing oxygen and other atmospheric gases, it allows you to heat materials without causing oxidation or other unwanted chemical changes.
Key Decision Factors: Matching the Tool to the Task
Your choice depends entirely on the requirements of your material and your process. Answering the following questions will guide you to the correct furnace.
What is the Goal of Your Process?
Are you simply trying to heat something up, or are you trying to induce a specific material transformation?
For processes like ashing (burning off organic material), drying, or binder burnout, a muffle furnace is sufficient because the presence of oxygen is either benign or required.
For metallurgical processes like annealing, brazing, or sintering, controlling the atmosphere is non-negotiable. These processes require specific environments—often inert or reducing—to achieve the desired material properties and prevent surface defects.
How Sensitive is Your Material to Air?
This is the most important consideration. Most metals (with the exception of noble metals) will oxidize rapidly when heated in air, forming a layer of scale that compromises the material's surface finish and integrity.
If you are working with reactive metals, certain advanced ceramics, or powders that must remain pure, an atmosphere furnace is essential. If you are working with stable ceramics, glass, or performing gravimetric analysis through ashing, a muffle furnace is perfectly adequate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability against complexity and cost. An atmosphere furnace offers more versatility, but this comes with significant trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
An atmosphere furnace is inherently more complex. It requires a vacuum pump, gas flow controllers, sealed fittings, and more sophisticated control systems. This results in a significantly higher initial cost and more demanding maintenance requirements.
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is a relatively simple machine with fewer failure points and a much lower barrier to entry.
Versatility vs. Specificity
An atmosphere furnace can do everything a muffle furnace can do; you can simply choose not to run the vacuum or gas systems and heat it in air. The reverse is not true.
This makes the atmosphere furnace a more versatile tool for research and development, where process requirements may change. However, if your work only ever requires heating in air, paying for this unused capability is inefficient.
Safety and Facility Requirements
Introducing process gases, especially flammable ones like hydrogen, adds a significant layer of safety protocol. It requires proper ventilation, leak detection, and operator training that are not concerns with a standard muffle furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific process goal as the final determinant.
- If your primary focus is ashing, drying, or heat-treating non-reactive materials: A muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of metals or other sensitive samples: An atmosphere furnace is essential to maintain material integrity.
- If your primary focus is executing specific processes like annealing, sintering, or brazing: An atmosphere furnace provides the necessary environmental control for successful and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is flexible research with diverse and evolving material needs: An atmosphere furnace offers the versatility to handle both air and controlled-atmosphere processes in a single unit.
Understanding this core distinction between simple heating and controlled processing ensures you invest in a tool that enables your work, rather than limits it.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Muffle Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Ambient air only | Controlled gases (e.g., inert, reactive) |
| Ideal For | Ashing, drying, non-reactive materials | Preventing oxidation, annealing, sintering |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler design | Higher cost, more complex systems |
| Material Sensitivity | Not sensitive to air | Sensitive to air (e.g., metals, ceramics) |
| Versatility | Limited to air processes | Can handle air and controlled atmospheres |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements—whether you need simple heating or complex controlled environments. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















