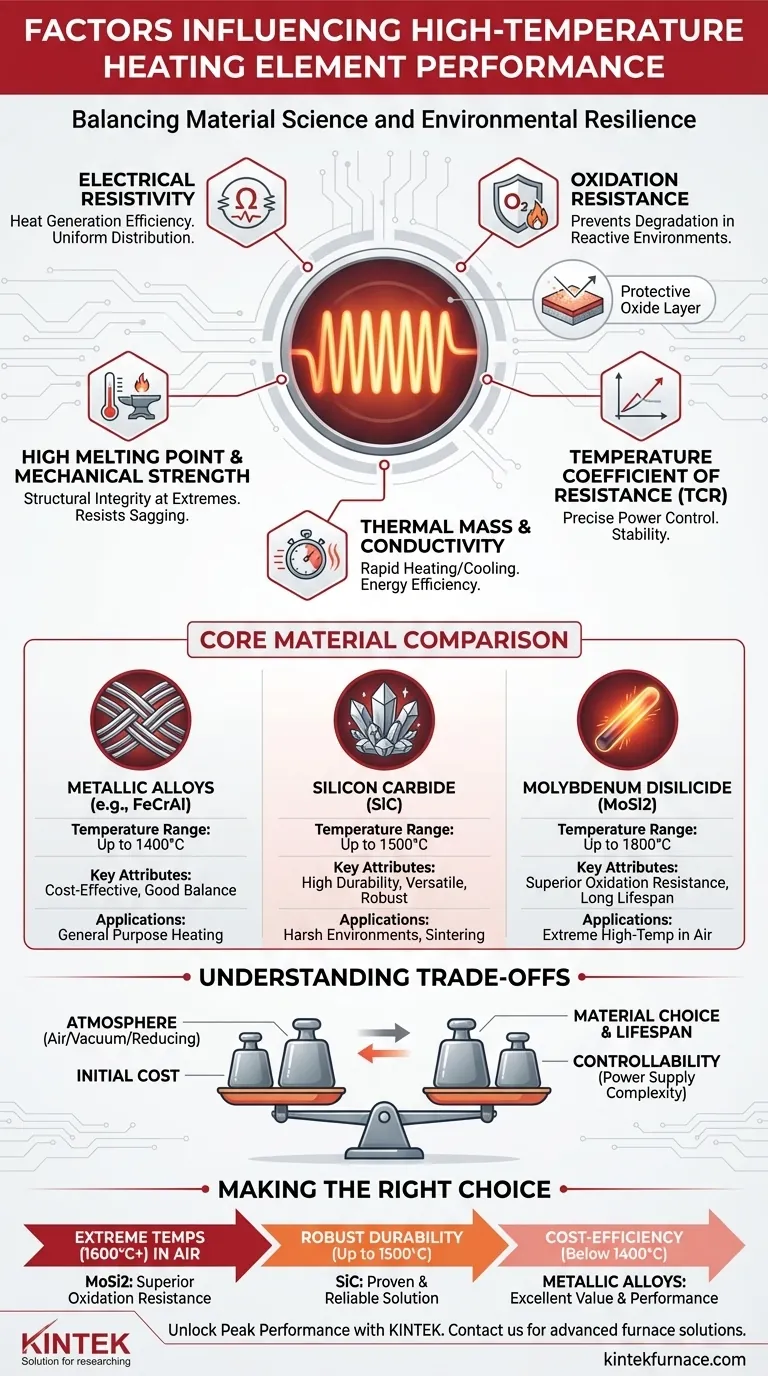
At its core, the performance of a high-temperature heating element is governed by a critical balance of material science and environmental resilience. The ideal element must not only generate heat efficiently through electrical resistance but also withstand the extreme chemical and physical stresses of its operating environment without degrading. Key factors include the material's resistivity, its resistance to oxidation, and how its electrical properties change with temperature.
The selection of a high-temperature heating element is not just about reaching a maximum temperature. It is a strategic decision that balances material lifespan, energy efficiency, and process control within a specific industrial application and atmosphere.

Core Material Properties that Define Performance
The choice of material is the single most important decision in heating element design. Its intrinsic properties dictate the element's efficiency, durability, and operational limits.
Electrical Resistivity
Resistivity is the property that allows the material to convert electrical energy into heat. An effective element has a resistivity high enough to generate significant heat but stable enough to prevent hotspots and ensure uniform temperature distribution.
Oxidation and Corrosion Resistance
At high temperatures, oxygen and other atmospheric gases become highly reactive. A premier heating element material, like molybdenum disilicide, forms a protective, self-healing oxide layer that prevents the underlying material from degrading, dramatically extending its service life.
High Melting Point and Mechanical Strength
This is a fundamental requirement. The material must maintain its solid form and structural integrity well above the maximum operating temperature. Support structures are often used, but the material itself must resist sagging or becoming brittle over thousands of hours.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR)
TCR describes how much a material's resistance changes as its temperature increases. A low, predictable TCR is desirable because it simplifies power control, allowing for precise and stable temperature management throughout the heating cycle.
Thermal Mass and Conductivity
Elements with low thermal mass, like many modern ceramic and metallic alloy designs, can heat up and cool down very rapidly. This provides exceptional process control and improves energy efficiency by minimizing wasted energy during thermal cycling.
A Comparison of Common High-Temperature Materials
Different materials are chosen for different temperature ranges and atmospheric conditions. Each has a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Metallic Alloys (e.g., FeCrAl)
These iron-chromium-aluminum alloys are the workhorses for applications up to approximately 1400°C. They offer an excellent balance of performance and cost-effectiveness but have clear temperature limitations compared to ceramics.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
SiC elements are extremely durable and can operate reliably in harsh environments for processes like sintering and melting. They are valued for their high strength and good thermal shock resistance, though their electrical resistance tends to increase gradually with age.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
For the highest temperature applications in air (often exceeding 1800°C), MoSi2 is the industry standard. Its ability to form a protective glass-like silica layer at high temperatures gives it exceptional oxidation resistance, but it can be more brittle at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" heating element. The optimal choice is always a compromise based on the specific demands of the application.
Atmosphere vs. Material Choice
An element that thrives in open air may fail rapidly in a vacuum or a reducing atmosphere. The chemical interaction between the element's surface and the surrounding gases is a critical factor that can dictate material selection.
Initial Cost vs. Lifespan
Advanced materials like MoSi2 carry a higher upfront cost than metallic alloys or even SiC. However, their longer lifespan and higher operating temperatures in the right application can lead to a lower total cost of ownership over time.
Controllability vs. Power Supply Complexity
Elements with a significant change in resistance as they heat up require more sophisticated, thyristor-based (SCR) power controllers to manage the power input. Simpler elements with a flat resistance curve can be run with less complex contactors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures (1600°C+) in air: MoSi2 elements are the clear technical choice due to their superior oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is robust durability and versatility up to 1500°C: SiC elements provide a proven, reliable solution for a wide range of industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for temperatures below 1400°C: High-performance metallic alloys deliver an excellent balance of performance and value.
Understanding these fundamental factors empowers you to select a heating element that not only meets your temperature requirements but also enhances the efficiency and reliability of your entire system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | Determines heat generation efficiency and uniformity | FeCrAl, SiC, MoSi2 |
| Oxidation Resistance | Prevents degradation in high-temperature environments | MoSi2 (forms protective layer) |
| Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) | Affects power control stability | Low TCR for precise control |
| Melting Point and Strength | Ensures structural integrity at high temperatures | All materials with high melting points |
| Thermal Mass and Conductivity | Influences heating/cooling speed and energy efficiency | Ceramics, metallic alloys |
Unlock Peak Performance for Your Laboratory
Choosing the right high-temperature heating element is crucial for achieving precise thermal control and extending equipment lifespan. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With our strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure your specific experimental requirements are met with precision.
Don't let suboptimal heating elements limit your lab's potential—contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















