Ultimately, a rotary kiln's temperature profile is not a single number but a carefully controlled gradient along its length. It is determined by two primary categories of factors: the intrinsic thermal properties of the material being processed and the mechanical operating parameters of the kiln itself. Understanding both is essential for achieving the desired chemical reaction and final product quality.
A successful temperature profile is achieved when you synchronize the material's required reaction temperatures with the kiln's physical ability to control heat exposure over time. The goal is to create distinct thermal zones that match each stage of the material's transformation.

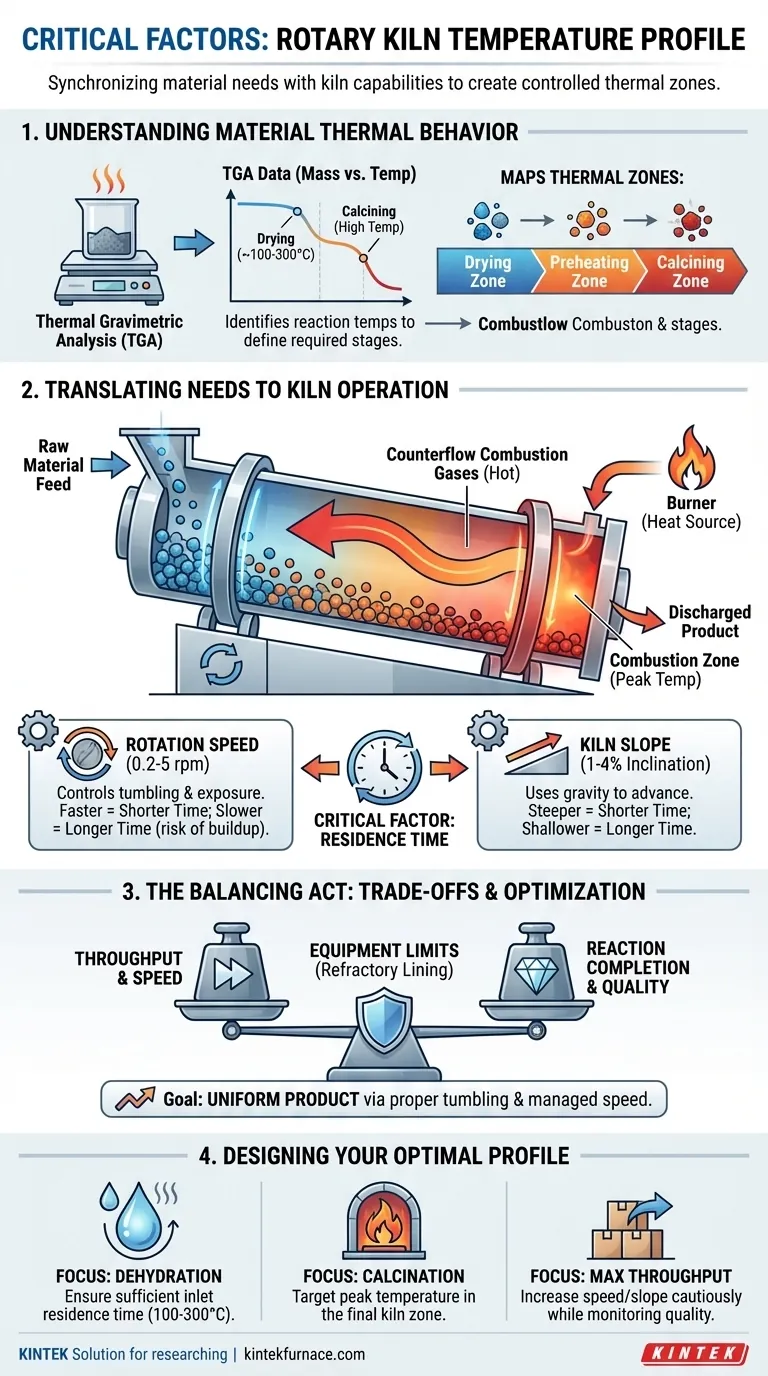
Understanding Your Material's Thermal Behavior
Before you can control the kiln, you must first understand the material. The temperature profile's primary purpose is to trigger specific physical or chemical changes in the material as it travels through the drum.
The Role of Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) is the foundational step. This lab technique measures a material's mass change as temperature increases, revealing the exact temperatures at which key reactions occur.
For example, TGA can show that free water vaporizes near 100°C, but more tightly bound chemical water might only be released at temperatures up to 260°C. This data provides the target temperatures for your process.
Identifying Necessary Reaction Zones
The TGA results allow you to map out the required thermal stages. A process might require a low-temperature drying zone to remove moisture, a medium-temperature preheating zone, and a high-temperature calcining zone to induce the final chemical transformation.
Translating Thermal Needs into Kiln Operation
Once you know the target temperatures, you must configure the kiln's mechanical systems to create and maintain them along the length of the shell.
The Burner and Heat Source
The primary heat source is the burner, typically located at the material discharge end of the kiln. It generates the highest temperatures in the system, creating the peak of the thermal profile in the combustion zone.
Heat Flow and Thermal Efficiency
Most modern kilns use a counterflow design. Hot combustion gases from the burner flow up the kiln, opposite to the direction of the material moving downward. This is highly efficient, as the hottest gases treat the most processed material, while cooler gases preheat the incoming raw feed.
The Critical Factor of Residence Time
Residence time—the duration the material spends inside the kiln—is arguably the most critical operational parameter. It dictates how long the material is exposed to the heat in each zone. It is controlled by two main factors.
The Impact of Rotation Speed
The kiln's rotation speed (typically 0.2 to 5 rpm) directly controls how quickly material tumbles through the drum.
- Too fast: Reduces residence time, meaning the material may exit before reactions are complete.
- Too slow: Can lead to material buildup, inefficient heat transfer, and potential "cold spots" that result in a non-uniform product.
The Influence of Kiln Slope
Rotary kilns are installed at a slight slope (usually 1% to 4% inclination). This downward angle uses gravity to help advance the material from the inlet to the discharge end. A steeper slope decreases residence time, while a shallower slope increases it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a temperature profile is an exercise in balancing competing factors. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is the most common source of process failure.
Speed vs. Heat Transfer
The central trade-off is between throughput and reaction completion. Increasing rotation speed and slope boosts the amount of material you can process, but it shortens the residence time, risking incomplete heating and chemical conversion.
Protecting the Equipment
The temperature profile cannot exceed the thermal limits of the kiln's internal refractory lining. This protective layer shields the outer steel shell from extreme heat. Pushing temperatures too high can cause catastrophic damage to this lining and the kiln structure.
Achieving Product Uniformity
A profile that is too aggressive or a rotation speed that is too slow can lead to an inconsistent product. Proper tumbling action, managed by rotation speed, is essential for ensuring every particle is exposed to the correct temperature for the right amount of time.
Designing Your Optimal Temperature Profile
There is no single "correct" profile; it must be tailored to your specific process objective. Use the following principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is complete dehydration: Ensure the kiln's inlet zone provides sufficient residence time at temperatures between 100°C and 300°C to drive off all free and bound water.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature calcination: Design the profile to reach its peak temperature in the final third of the kiln, ensuring the material has adequate time in that zone to fully react.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Carefully increase rotation speed and slope while monitoring the final product to find the sweet spot where residence time is minimized without sacrificing quality.
Ultimately, mastering your kiln's temperature profile is about synchronizing the material's chemical needs with the kiln's mechanical capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thermal Properties | Intrinsic behavior of the material under heat | Use TGA to identify reaction temperatures (e.g., drying at 100-300°C, calcining at high temps) |
| Kiln Operating Parameters | Mechanical settings controlling heat exposure | Adjust rotation speed (0.2-5 rpm), slope (1-4%), and burner position for residence time and efficiency |
| Thermal Zones | Segmented areas for different process stages | Design zones like drying, preheating, and calcining to match material transformation stages |
| Trade-offs | Balancing throughput, quality, and equipment safety | Optimize speed vs. heat transfer; avoid exceeding refractory limits for uniform product |
Struggling to optimize your rotary kiln's temperature profile? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your lab's unique needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. We help you achieve precise thermal control, enhance efficiency, and ensure product uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how we can design the perfect solution for your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency



















