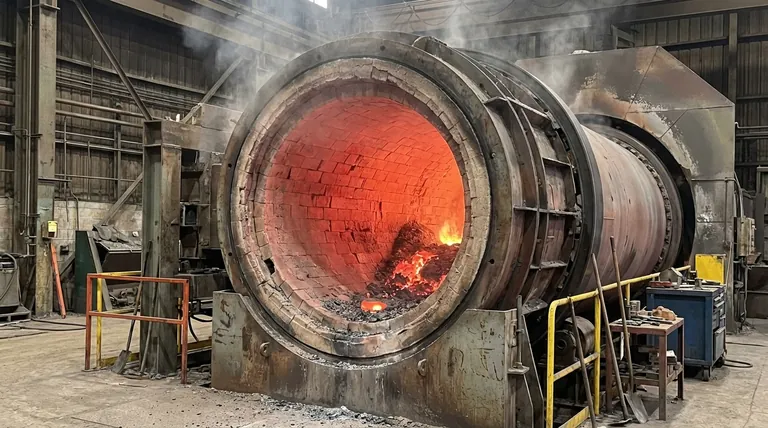
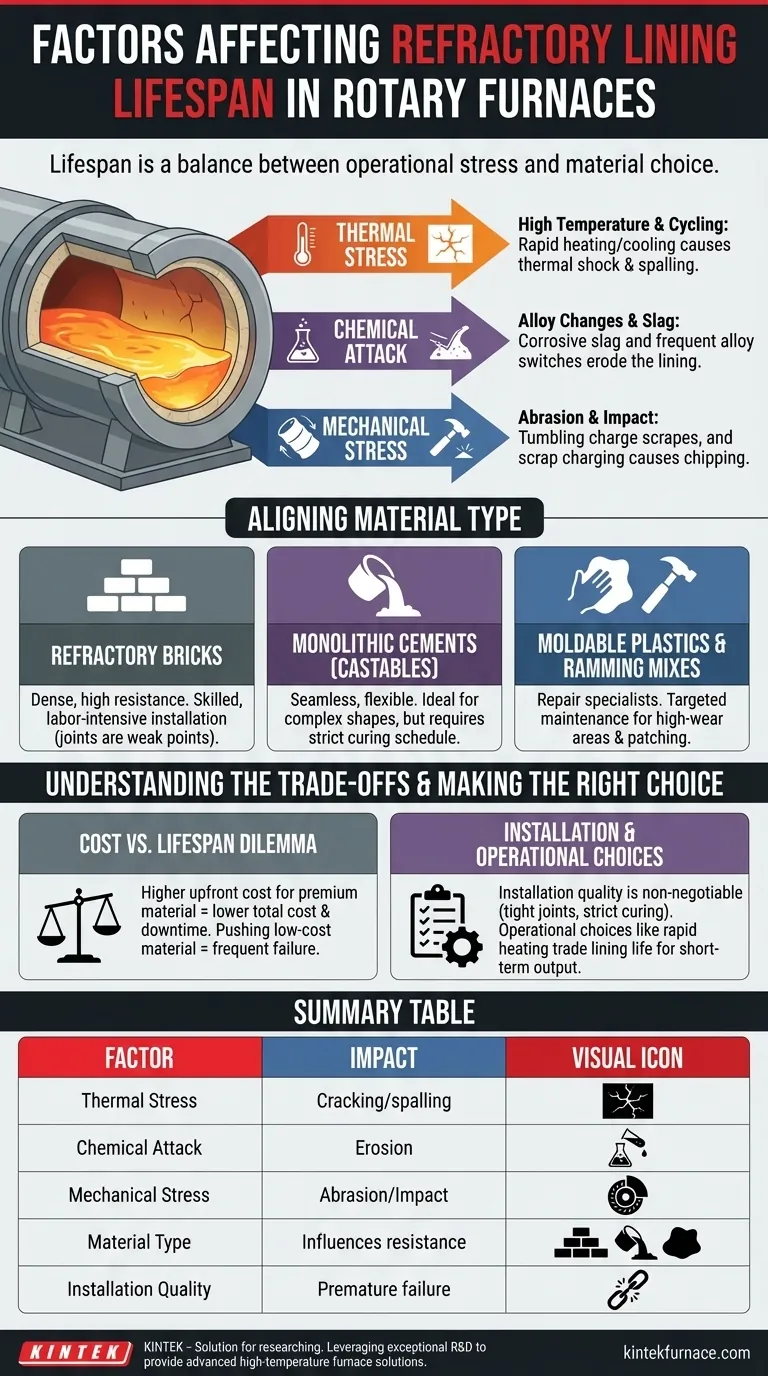
The lifespan of a refractory lining in a rotary furnace is determined by a direct and often brutal interaction between your operational practices and your choice of material. The primary factors dictating this lifespan are the operating temperature, the chemical aggression from different alloys and slag, the physical stress from heating and cooling cycles, and the inherent properties of the refractory material itself.
Your refractory lining does not fail from one single cause. Instead, its lifespan is a direct reflection of how well the chosen material's properties are aligned with the combined thermal, chemical, and mechanical stresses of your specific furnace operation.
The Primary Stress Factors on Refractory Linings
Understanding how a lining degrades requires looking at the distinct forces working against it during every cycle. These factors rarely act in isolation.
Thermal Stress: Temperature and Cycling
The most obvious stress is high operating temperature, which accelerates wear and can approach the material's service limit.
However, the frequency and speed of heating and cooling cycles are often more destructive. This thermal cycling causes the refractory to expand and contract, inducing internal stress that leads to cracking and spalling—a failure known as thermal shock.
Chemical Attack: Alloy Changes and Slag
Each alloy melted produces a unique slag chemistry. Some slags are highly corrosive and will actively seek to penetrate and erode the refractory lining.
Frequent changes between different alloys can expose a lining designed for one chemical environment to another, more aggressive one. This accelerates chemical wear and degradation significantly.
Mechanical Stress: Abrasion and Impact
The very nature of a rotary furnace introduces mechanical wear. The tumbling or rolling action of the furnace charge constantly scrapes and grinds against the hot face of the lining.
The initial charging of scrap metal can also cause direct impact damage, chipping, or cracking the refractory material before the melting process even begins.
Aligning Material Type with Operational Reality
The refractory material you select is your primary defense against these stresses. Each type offers a different balance of properties, installation complexity, and cost.
Refractory Bricks: The Standard for Durability
Bricks are pre-fired, dense shapes that generally offer excellent resistance to high temperatures and abrasion. Materials like high-alumina brick are a common choice for demanding applications.
Their primary drawback is installation. Laying brick is a skilled, labor-intensive process, and the joints between bricks can become weak points for slag penetration.
Monolithic Cements (Castables): The Advantage of Flexibility
Monolithic refractories, such as castable cements, are installed like concrete. They are mixed with water and then poured, pumped, or cast into place, creating a seamless, joint-free lining.
This monolithic structure eliminates the weakness of joints and makes them ideal for complex furnace geometries. Certain formulations offer superior resistance to thermal shock.
Moldable Plastics and Ramming Mixes: The Repair Specialists
These materials have a clay-like consistency and are typically rammed or hammered into place.
While not always used for a full lining, they are essential for creating complex shapes like spouts or for performing critical hot or cold repairs. They allow for targeted maintenance that can extend the life of a full lining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a refractory is not about finding a single "best" material, but about making an informed compromise.
The Cost vs. Lifespan Dilemma
High-performance materials come with a higher upfront cost but can deliver a lower total cost of ownership by extending campaign life and reducing costly downtime.
Conversely, a lower-cost material may be perfectly adequate for a less demanding process but will fail quickly if pushed beyond its design limits, leading to frequent and expensive relines.
Installation Quality is Non-Negotiable
Even the most advanced refractory will fail if installed improperly. For castables, this means precise water ratios and, most critically, adhering to a strict curing and dry-out schedule. Rushing the dry-out is a primary cause of premature failure.
For bricks, tight joints and the correct mortar are essential to prevent metal and slag penetration.
The Hidden Cost of Operational Choices
Pushing a furnace to its thermal limit or accelerating heat-up times to meet production targets directly trades lining life for short-term output. This is a business decision with a very real maintenance cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the optimal refractory strategy requires balancing your operational goals with material capabilities and installation discipline.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput at high temperatures: Invest in premium, high-density refractory bricks or a specialized high-strength castable, and enforce controlled heating and cooling procedures.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility with frequent alloy changes: Select a robust monolithic castable specifically formulated for high chemical resistance and excellent thermal shock properties.
- If your primary focus is patching and extending campaign life: Keep appropriate moldable plastics or ramming mixes on hand for rapid, targeted repairs to high-wear areas.
A successful refractory management program is a proactive partnership between material science and disciplined operational procedure.

Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stress | Causes cracking and spalling from heating/cooling cycles |
| Chemical Attack | Erodes lining due to corrosive slags and alloy changes |
| Mechanical Stress | Leads to abrasion and impact damage from furnace operation |
| Material Type | Influences resistance to stress; bricks, castables, or plastics |
| Installation Quality | Poor installation can cause premature failure |
Ready to extend your rotary furnace's refractory lining lifespan? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to optimize your furnace performance and reduce downtime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What distinguishes direct from indirect rotary kilns? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Material
- What are the primary applications of an electric rotary kiln? Achieve High-Purity Material Processing with Precision
- What data is necessary to design a rotary kiln? Essential Factors for Efficient Thermal Processing
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- What types of physical and chemical transformations occur in a rotary kiln? Master Material Processing for Superior Results



















