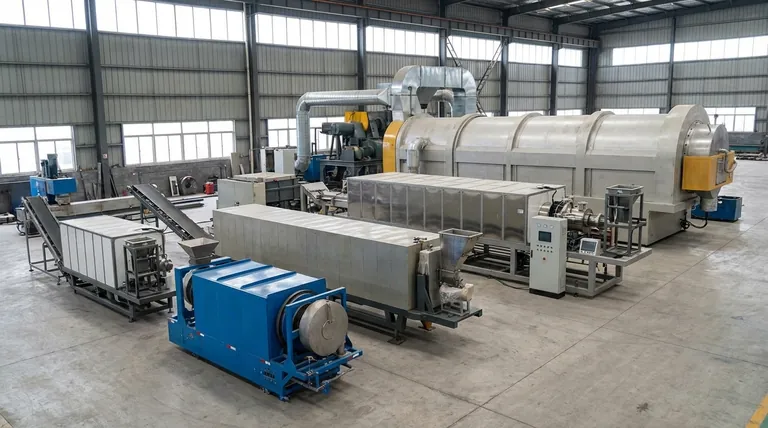
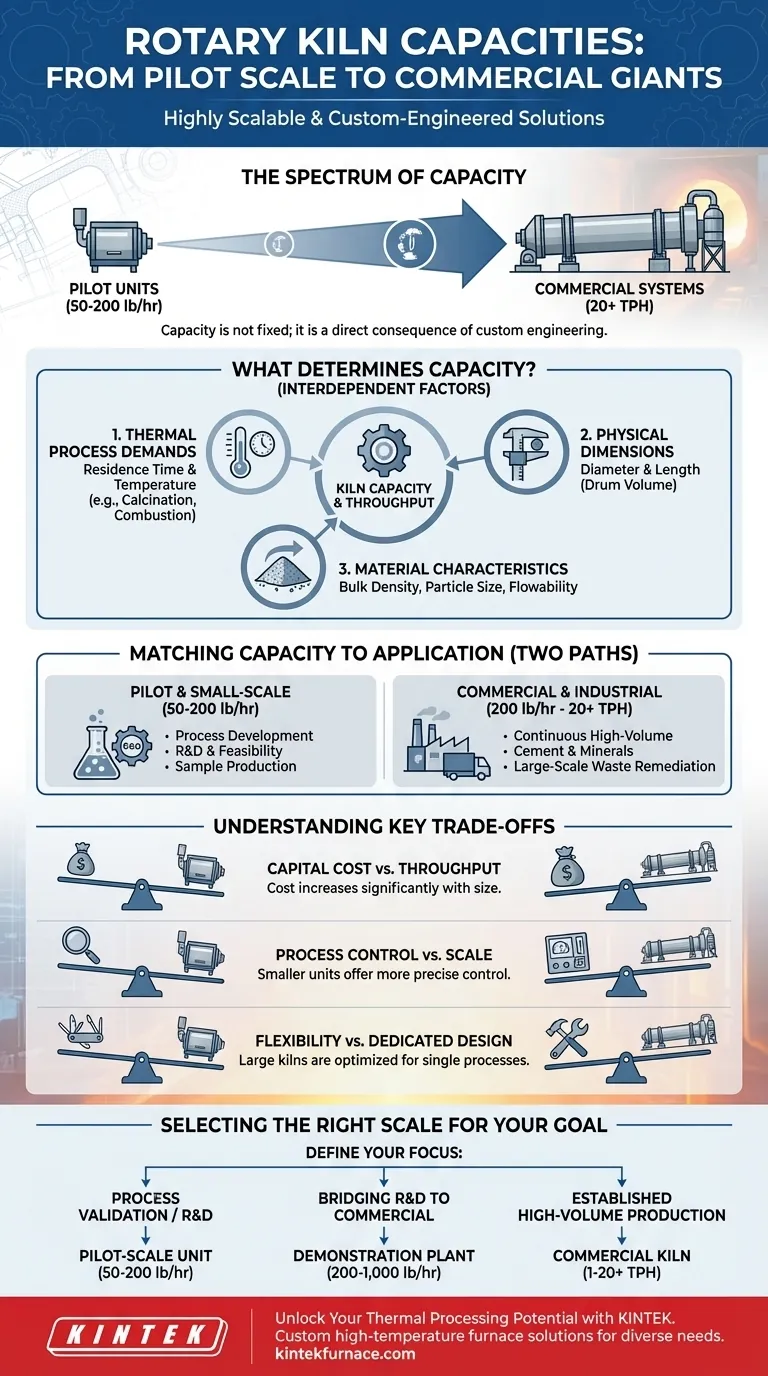
At their core, rotary kilns are highly scalable, with capacities ranging from small pilot units processing 50 to 200 pounds per hour (lb/hr) to massive commercial-scale systems that can handle over 20 tons per hour (TPH). This broad range exists because a rotary kiln is not an off-the-shelf product but a piece of custom-engineered equipment designed around a specific thermal process.
The capacity of a rotary kiln is not a fixed attribute but a direct consequence of its design. It is engineered to achieve a specific chemical reaction or phase change for a given material, and the required throughput is a key variable in that engineering process.

What Determines a Rotary Kiln's Capacity?
The final throughput of a rotary kiln is not an arbitrary number. It is the result of several interdependent factors, all centered on achieving the desired transformation of the material being processed.
The Demands of the Thermal Process
The primary function of a kiln is to act as a reaction vessel. The specific process—such as calcination, thermal desorption, or organic combustion—dictates the two most critical variables: residence time and temperature.
A process that requires a long residence time at a specific temperature will naturally have a lower throughput than one that can be completed quickly.
Physical Kiln Dimensions
Capacity is directly linked to the physical volume of the kiln drum. A larger diameter and length provide more volume, allowing more material to be processed at any given moment.
Engineers calculate these dimensions based on the required residence time and the desired production rate to ensure the material has sufficient time in the kiln to complete its transformation.
Material Characteristics
The properties of the feedstock itself are a major factor. Bulk density, particle size, moisture content, and flowability all influence how much material can be fed into the kiln and how it behaves inside the rotating drum. These characteristics must be accounted for in the design to prevent blockages and ensure efficient processing.
Matching Capacity to Application
The wide capacity range allows rotary kilns to serve entirely different industrial needs, from early-stage research to full-scale commodity production.
Pilot and Small-Scale Operations
Kilns in the 50 to 200 lb/hr range are typically used for process development, research and development (R&D), and feasibility testing. They allow companies to validate a process, test different materials, and produce sample quantities without the massive capital investment of a full-scale system.
Commercial and Industrial Production
Kilns processing from 200 lb/hr to over 20 TPH are the workhorses of heavy industry. These units are built for continuous, high-volume production in sectors like cement manufacturing, mineral processing, and large-scale waste remediation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a kiln based on capacity involves balancing performance with cost and flexibility. A larger kiln is not always the better choice.
Capital Cost vs. Throughput
The most obvious trade-off is cost. The capital expenditure for a large-capacity rotary kiln is substantial and increases significantly with size. This includes not just the kiln itself but also the foundational work, ancillary equipment, and complex installation.
Process Control vs. Scale
While all modern kilns feature advanced temperature control, maintaining a perfectly uniform temperature profile becomes more challenging as the drum diameter increases. Smaller pilot-scale units often provide more precise control, which can be critical for sensitive, high-value materials.
Dedicated Design vs. Flexibility
Large-scale commercial kilns are almost always designed and optimized for a single, specific feedstock and process. They are highly efficient for that task but lack the flexibility to run different materials or small test batches. A smaller pilot kiln offers far greater operational flexibility.
Selecting the Right Scale for Your Project
The correct kiln capacity is the one that aligns with your specific technical and business objectives.
- If your primary focus is process validation or R&D: A pilot-scale unit (50-200 lb/hr) offers the necessary control and flexibility at a manageable cost.
- If your primary focus is established, high-volume production: A large-scale commercial kiln (1-20+ TPH) engineered for your specific process is the only way to achieve the required throughput.
- If your primary focus is bridging R&D with full commercialization: A small commercial kiln (starting around 200-1,000 lb/hr) can serve as a demonstration plant to prove market viability before committing to a larger investment.
Ultimately, choosing the right capacity is about defining your goal first, then engineering the tool to meet it.
Summary Table:
| Capacity Range | Typical Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 50-200 lb/hr | Pilot-scale R&D, process validation, feasibility testing | High flexibility, precise control, lower capital cost |
| 200 lb/hr to 20+ TPH | Commercial production, cement, minerals, waste remediation | High throughput, dedicated design, higher capital investment |
Unlock Your Thermal Processing Potential with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're scaling from pilot to production or need tailored solutions for your specific materials and processes, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and results.
Contact us today to discuss how our rotary kilns and other furnace systems can drive your project forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















