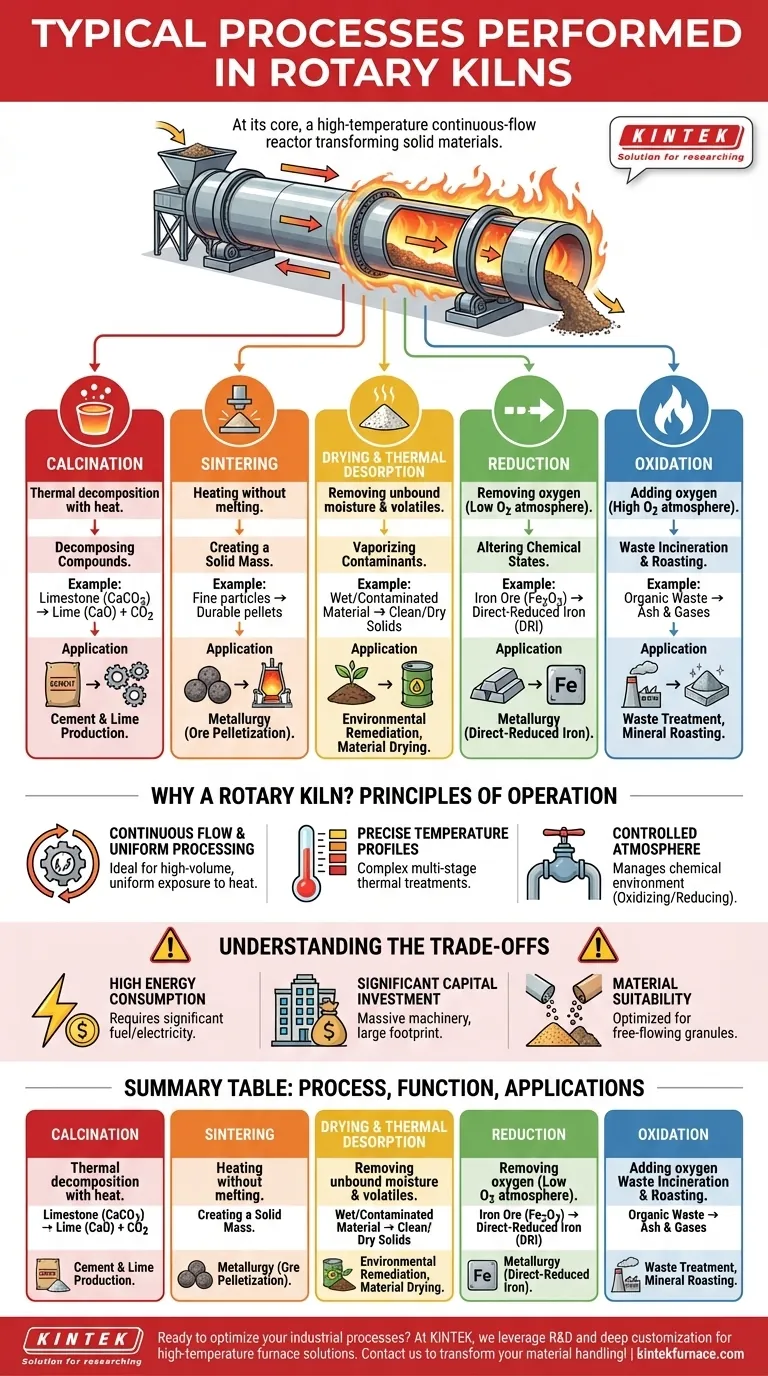
At its core, a rotary kiln is a high-temperature industrial furnace used to induce specific physical or chemical changes in solid materials. The most typical processes performed are calcination, sintering, drying, reduction, and oxidation, which are fundamental to industries like cement production, metallurgy, and waste treatment.
A rotary kiln is not simply a large oven; it is a dynamic, continuous-flow reactor. Its true purpose is to transform a material's fundamental properties by precisely controlling temperature, atmosphere, and residence time as it tumbles through the rotating cylinder.

The Core Functions: A Breakdown of Key Processes
A rotary kiln’s versatility comes from its ability to facilitate several distinct thermal processes, often in combination. Understanding these core functions is key to understanding the equipment's role.
Calcination: Decomposing Compounds with Heat
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process. It uses high heat to break down a compound, often driving off a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water.
The most common example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide, a critical step in making cement and other industrial chemicals.
Sintering: Creating a Solid Mass
Sintering is the process of forming a solid, coherent mass of material by heating it to a high temperature without melting it.
This process is used to increase the strength and density of a material. In metallurgy, for example, fine iron ore particles are sintered into durable pellets that can be fed into a blast furnace.
Drying and Thermal Desorption: Removing Volatiles
This is the simplest function, using heat to remove unbound moisture from a material. However, this process can be more advanced.
Thermal desorption is a similar process used for environmental remediation. It heats contaminated soils or sludges to a temperature high enough to vaporize volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other contaminants, separating them from the solid material for collection or destruction.
Reduction and Oxidation: Altering Chemical States
These are opposing chemical reactions that are controlled by the kiln's atmosphere.
Reduction is a process that removes oxygen, often used in metallurgy. For example, a rotary kiln can reduce iron ore (iron oxide) to produce direct-reduced iron (DRI). This requires a carefully controlled, low-oxygen atmosphere.
Oxidation is the opposite; it adds oxygen. This is commonly used in waste incineration, where organic compounds are burned (oxidized) to reduce their volume and destroy hazardous components. It is also used in mineral roasting to remove impurities like sulfur.
Why a Rotary Kiln? The Principles of Operation
The choice of a rotary kiln over other types of furnaces is driven by its unique operational advantages that are crucial for achieving consistent, large-scale material transformation.
Continuous Flow and Uniform Processing
The kiln is a slightly inclined, rotating cylinder. Material is fed into the higher end and slowly tumbles toward the lower end, ensuring that every particle is exposed to the heat uniformly. This continuous flow is ideal for high-volume industrial production.
Precise Temperature and Heat Profiles
Modern rotary kilns offer sophisticated control over the temperature profile along their length. This allows for complex processes where a material might first be dried at a low temperature, then calcined at a medium temperature, and finally sintered at a high temperature, all within the same unit.
Controlled Atmosphere
The kiln's internal atmosphere can be precisely managed to create the right chemical environment. An oxidizing atmosphere (rich in oxygen) is used for combustion and roasting, while a reducing atmosphere (poor in oxygen) is necessary for processes like iron ore reduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary kilns are not a universal solution. They involve significant trade-offs that must be considered.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures that can reach over 2,000°F (1,100°C) requires a tremendous amount of energy, making fuel costs a primary operational expense.
Significant Capital Investment and Footprint
Rotary kilns are massive, heavy pieces of machinery that require a large physical footprint and a substantial upfront capital investment. This makes them suitable for large-scale, continuous operations, not small-batch or experimental work.
Material Suitability
The design is optimized for free-flowing granular or pelletized solids. Materials that are very fine, sticky, or prone to clumping may require pre-processing (like pelletizing) before they can be effectively run through a kiln.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific process you employ in a rotary kiln is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is producing base commodities like cement or lime: You are leveraging calcination to drive a fundamental chemical decomposition at high, stable temperatures.
- If your primary focus is upgrading ores for metallurgy: You are using sintering to create physically robust pellets or reduction to chemically prepare the material for smelting.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation or waste treatment: You are using thermal desorption to vaporize contaminants or oxidation (incineration) to destroy hazardous organic matter.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's value lies in its power to reliably convert raw, bulk materials into precisely engineered products through controlled thermal and chemical transformation.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition to remove volatiles | Cement production, lime manufacturing |
| Sintering | Heating without melting to form solid mass | Metallurgy for ore pelletization |
| Drying/Thermal Desorption | Removing moisture or contaminants | Environmental remediation, material drying |
| Reduction | Removing oxygen in low-oxygen atmospheres | Iron ore reduction to direct-reduced iron |
| Oxidation | Adding oxygen for combustion or purification | Waste incineration, mineral roasting |
Ready to optimize your industrial processes with advanced rotary kiln solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can transform your material handling and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What supporting equipment is needed for a rotary kiln system? Essential Components for Efficient Thermal Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability
- What data is necessary to design a rotary kiln? Essential Factors for Efficient Thermal Processing
- What distinguishes direct from indirect rotary kilns? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Material



















