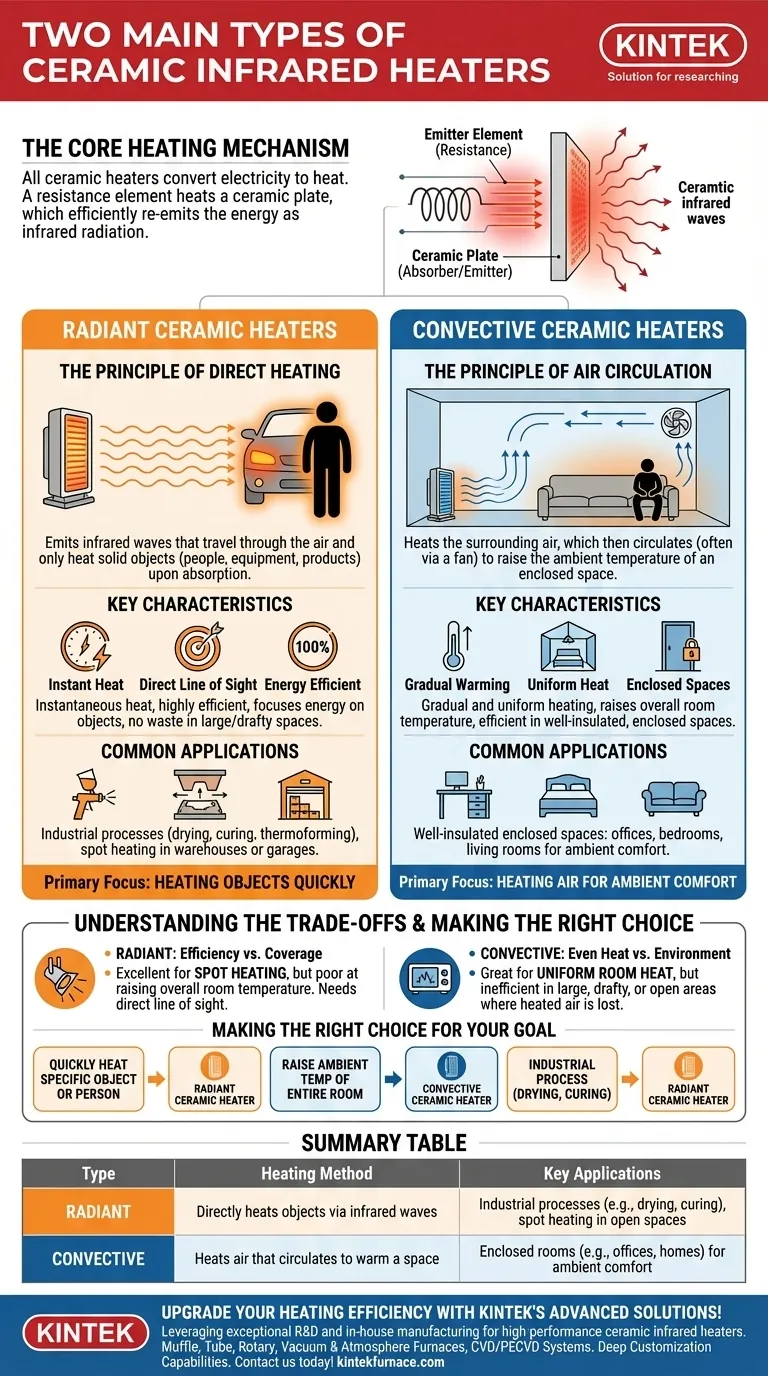
The two primary types of ceramic infrared heaters are convective and radiant. These types are defined not by their construction, but by their method of heat transfer. A convective heater warms the surrounding air, which then circulates to heat a space, while a radiant heater emits infrared waves that directly warm objects and people in their path, much like the sun.
The choice between convective and radiant ceramic heaters is not about which is "better," but which heating method best suits your application. Convective heaters warm the air in a space, while radiant heaters warm objects and people directly, making the right choice dependent on your specific goal.
The Core Heating Mechanism
All ceramic heaters share a fundamental design that allows them to efficiently convert electricity into heat. Understanding this is key to appreciating the differences between the two main types.
The Emitter Element
At the heart of the heater is a resistance element, typically a coil or ribbon made from a specialized metal alloy. When electricity passes through this element, it heats up rapidly due to electrical resistance.
The Role of Ceramic
This hot element is embedded within or mounted against a ceramic plate. The ceramic material is an excellent absorber and emitter of thermal energy. It absorbs the intense heat from the element and then re-emits it smoothly and evenly over a large surface area as infrared radiation.
Understanding Radiant Ceramic Heaters
Radiant heaters are the most common type used in industrial and targeted heating applications. Their function is based on the principle of direct energy transfer.
The Principle of Direct Heating
Radiant ceramic heaters emit infrared waves that travel through the air without significantly heating it. This energy only converts into heat when it is absorbed by a solid object, such as a person, a piece of equipment, or a product on a manufacturing line.
Key Characteristics
This method provides almost instantaneous heat to anything in its direct line of sight. It is highly efficient because no energy is wasted trying to heat the air in a large, drafty, or open space.
Common Applications
Because of their focused and efficient heat, radiant heaters are ideal for industrial processes like drying paints, curing coatings, thermoforming plastics, and providing spot heating for individual workstations in large warehouses or garages.
Understanding Convective Ceramic Heaters
Convective heaters are designed to raise the ambient temperature of an enclosed room. They are what most people think of when discussing portable space heaters.
The Principle of Air Circulation
In a convective heater, the hot ceramic plates are used to warm the air that comes into contact with them. The heater relies on natural convection (hot air rising) or, more commonly, a built-in fan to circulate the warmed air throughout the room.
Key Characteristics
This process gradually and evenly raises the temperature of the entire space. While the initial heating effect is not as immediate as with a radiant heater, it results in a more uniform and consistent room temperature over time.
Common Applications
Convective heaters are best suited for heating well-insulated, enclosed spaces like offices, bedrooms, and living rooms where the primary goal is overall comfort for the occupants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong type of heater for your environment will lead to inefficiency and poor performance.
Radiant: Efficiency vs. Coverage
Radiant heaters are exceptionally energy-efficient for spot heating. However, they are poor at raising the overall temperature of a room. If you move out of the heater's direct line of sight, you will no longer feel its warmth.
Convective: Even Heat vs. Environment
Convective heaters excel at creating a uniformly warm room, but they are only efficient in enclosed, well-insulated spaces. Using one in a large, drafty warehouse or with frequently opened doors is highly inefficient, as the heated air is constantly lost and must be replaced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct heater, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is heating a specific person or object quickly: A radiant ceramic heater is the most effective and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is raising the ambient temperature of an entire enclosed room: A convective ceramic heater will provide the most comfortable and uniform results.
- If your primary focus is an industrial process like drying or curing: A radiant ceramic heater is the industry standard for its direct and intense heat transfer.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heater depends on understanding whether you need to heat the objects in a space or the air itself.
Summary Table:
| Type | Heating Method | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Radiant | Directly heats objects via infrared waves | Industrial processes (e.g., drying, curing), spot heating in open spaces |
| Convective | Heats air that circulates to warm a space | Enclosed rooms (e.g., offices, homes) for ambient comfort |
Upgrade your heating efficiency with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industries with high-performance ceramic infrared heaters. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique heating requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes with tailored heating solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure



















