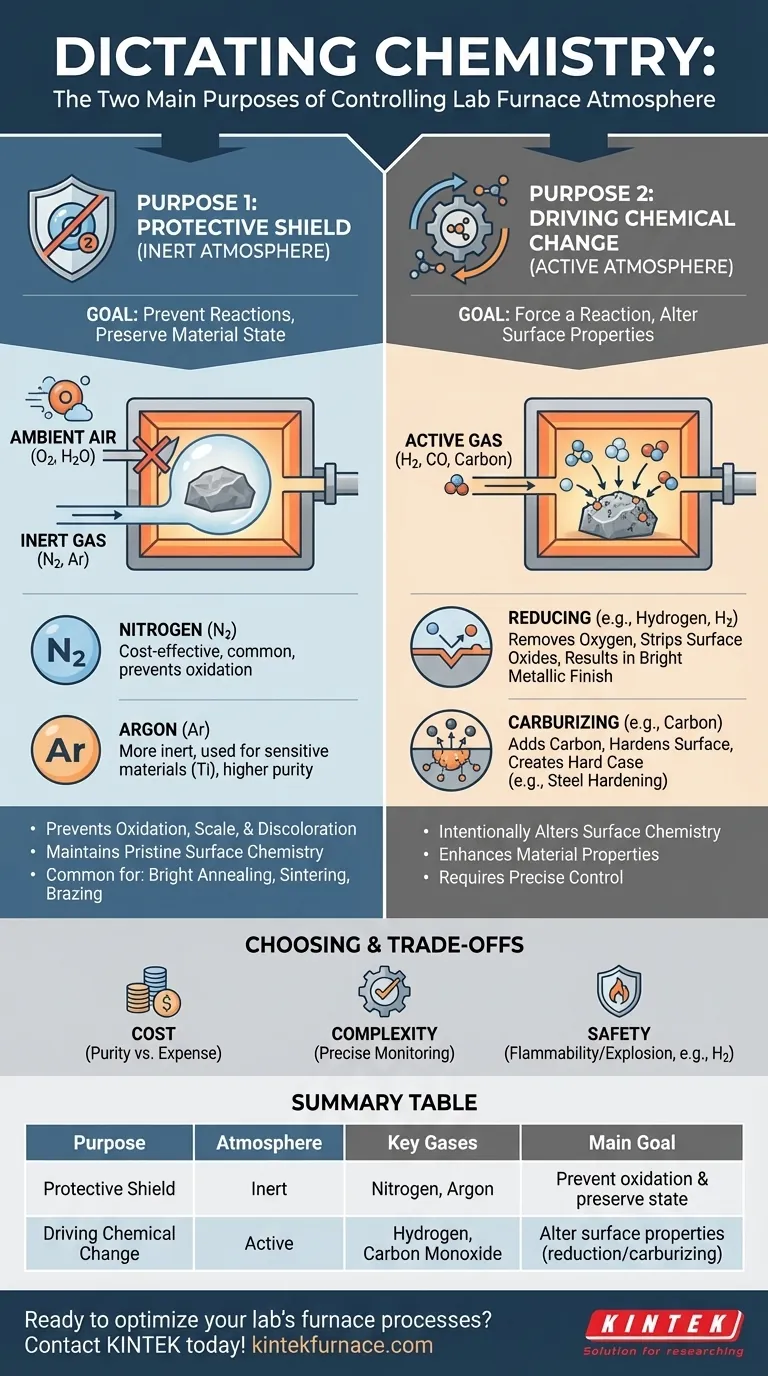
At its core, controlling a lab furnace atmosphere is about dictating chemistry. The two fundamental purposes are diametrically opposed: either you protect a material from any chemical change, or you intentionally force a specific chemical change to occur. This control allows you to either preserve a material's pristine state or actively engineer its surface properties for a desired outcome.
The choice is not merely about using a specific gas, but about making a strategic decision. You are either creating a protective shield to prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation, or you are introducing an active agent to intentionally cause a specific chemical transformation on the material's surface.

The First Purpose: Creating a Protective Shield (Inert Atmospheres)
The most common reason to control a furnace atmosphere is to prevent the material inside from reacting with its environment, particularly with oxygen. This is a protective, or inert, strategy.
What is an Inert Atmosphere?
An inert atmosphere is a gaseous environment that does not chemically react with the material being heated. Its primary function is to displace ambient air, specifically oxygen and water vapor, which are highly reactive at elevated temperatures.
Why Prevent Reactions?
For many materials, heating in air leads to oxidation, which can form a destructive scale, degrade material properties, or cause discoloration. An inert atmosphere acts as a protective shield, ensuring the material emerges from the furnace with the same surface chemistry it had when it went in.
Common Inert Gases
Nitrogen (N2) is the most widely used inert gas due to its relative abundance and low cost. It is effective for preventing oxidation in a vast range of heat-treatment processes.
Argon (Ar) is a more noble and thus more inert gas than nitrogen. It is used for highly sensitive materials that might still react with nitrogen at very high temperatures, such as certain titanium or refractory metals.
The Second Purpose: Driving Chemical Change (Active Atmospheres)
In direct contrast to a protective shield, an active atmosphere is specifically chosen to react with the material's surface. This is a transformative, or reactive, strategy.
What is an Active Atmosphere?
An active atmosphere contains gases that are intended to cause a specific chemical reaction, such as adding or removing elements from the material's surface. This process fundamentally alters the surface properties.
Example: Reducing Atmospheres
A reducing atmosphere, often rich in hydrogen (H2) or carbon monoxide (CO), is designed to remove oxygen. This is critical for processes like bright annealing, where any surface oxides are stripped away, resulting in a clean, bright metallic finish.
Example: Carburizing Atmospheres
A carburizing atmosphere is rich in carbon, typically from gases like propane or methane. This process is used to harden the surface of steel by diffusing carbon atoms into it, creating a "case" that is significantly harder than the core metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an atmosphere is not without practical considerations. The decision involves balancing cost, process complexity, and safety.
The Cost of Purity
While nitrogen is cost-effective, high-purity inert gases like argon can be significantly more expensive. The required purity level directly impacts operational costs.
The Complexity of Active Processes
Active atmospheres demand precise control. Incorrect gas composition, flow rates, or temperature profiles can lead to unintended reactions, ruining the workpiece. These processes require sophisticated monitoring and control systems.
Critical Safety Considerations
Many active gases, particularly hydrogen, are highly flammable and can be explosive. Using them necessitates stringent safety protocols, specialized furnace designs, and thorough operator training.
Choosing the Right Atmosphere for Your Goal
Your process goal dictates the correct atmospheric strategy. A clear understanding of your desired outcome will guide your choice between a protective or reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is preserving a material's existing state (e.g., bright annealing, sintering, brazing): Use a protective, inert atmosphere like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is enhancing a material's surface properties (e.g., case hardening, oxide removal): Use a carefully controlled active atmosphere containing gases like hydrogen or carbon sources.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose protection on a budget: Nitrogen is almost always the most cost-effective and versatile inert option.
Mastering your furnace atmosphere gives you direct control over the final properties and quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Atmosphere Type | Key Gases | Main Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective Shield | Inert | Nitrogen, Argon | Prevent oxidation and preserve material state |
| Driving Chemical Change | Active | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide | Alter surface properties via reactions like reduction or carburizing |
Ready to optimize your lab's furnace processes with tailored atmosphere control? Contact KINTEK today for expert solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior material outcomes efficiently and safely.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance



















