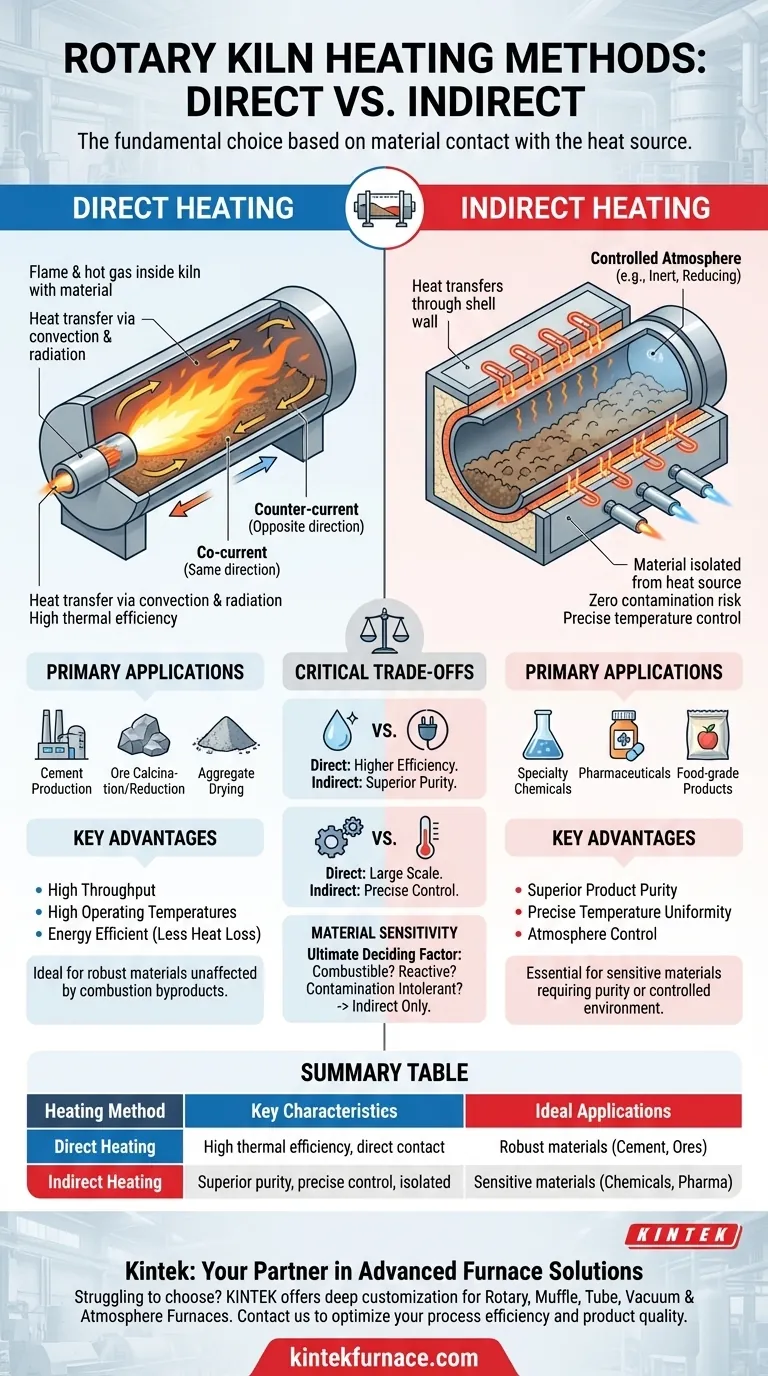
At its core, a rotary kiln's heating method is determined by a single critical factor: whether the material being processed can come into direct contact with the heat source. The two fundamental methods are direct heating, where a flame or hot gas is inside the kiln with the material, and indirect heating, where the kiln is heated from the outside and the heat transfers through the shell wall.
The choice between direct and indirect heating is not about which method is superior overall, but which is fundamentally suited to your material. This decision balances the need for thermal efficiency and high throughput against the requirement for product purity and precise atmospheric control.

Direct-Fired Kilns: Maximizing Throughput
Direct-fired kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry, designed for processing large volumes of robust materials at high temperatures.
How It Works
In a direct-fired system, a burner injects a flame and hot combustion gases directly into the kiln cylinder. This gas flows through the kiln, transferring heat directly to the material bed through convection and radiation.
The gas flow can be either co-current (flowing in the same direction as the material) or counter-current (flowing in the opposite direction), depending on the specific heat transfer profile required for the process.
Primary Applications
This method is ideal for materials that are not negatively affected by contact with combustion byproducts. Common applications include cement production, aggregate drying, and the calcination or reduction of mineral ores.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage of direct firing is thermal efficiency. Since the heat is generated inside the processing chamber, less energy is lost to the surrounding environment. This allows for very high operating temperatures and greater throughput compared to indirect designs.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Ensuring Precision and Purity
Indirect-fired kilns, often called calciners or retorts, are used when product purity and a controlled environment are non-negotiable.
How It Works
In this design, the rotating cylinder (retort) is enclosed within an insulated furnace or surrounded by heating elements. The heat source, which can be electric elements or external gas burners, heats the outside of the retort shell.
Heat then conducts through the metal shell to the material tumbling inside. The internal atmosphere is completely separate from the external heating environment.
Primary Applications
Indirect heating is necessary for processing sensitive materials that would be contaminated or would react with combustion gases. It's essential for producing specialty chemicals, certain food-grade products, and in processes that require a specific, controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing).
Key Advantages
The defining benefit is product purity. By isolating the material from the heat source, there is zero risk of contamination. This design also allows for much more precise temperature control and the ability to maintain a specific gas atmosphere inside the kiln.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing the right heating method involves a clear understanding of the compromises between efficiency, control, and final product quality.
Purity vs. Thermal Efficiency
Direct-fired kilns are significantly more energy-efficient, as heat is applied directly to the product. Indirect kilns inherently lose some heat from the external furnace to the surroundings, making them less thermally efficient.
Scale vs. Temperature Control
Direct-fired kilns can be built to enormous sizes, processing hundreds of tons per hour. However, precise, uniform temperature control across the material bed is more challenging. Indirect kilns offer superior temperature uniformity but are typically limited in diameter and length due to mechanical stresses on the externally heated retort.
Material Sensitivity
This is the ultimate deciding factor. If your material is combustible, will react with oxygen or CO2 in flue gas, or cannot tolerate even trace amounts of contamination, you have no choice but to use an indirect-fired kiln.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your process goal dictates the correct kiln design. The selection is a straightforward engineering decision once the material's properties are understood.
- If your primary focus is high-volume output and cost-efficiency for robust materials like cement or ores: A direct-fired kiln is the industry standard and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute product purity and precise control for sensitive materials like chemicals or pharmaceuticals: An indirect-fired kiln is the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific internal atmosphere, such as with inert nitrogen: You must use an indirect-fired design to isolate the process environment.
Selecting the correct heating method is a foundational decision that directly determines your product quality and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Characteristics | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Heating | High thermal efficiency, direct contact with heat source, suitable for robust materials | Cement production, mineral ore calcination, aggregate drying |
| Indirect Heating | Superior product purity, precise temperature control, isolated atmosphere | Specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food-grade products |
Struggling to choose the right heating method for your rotary kiln? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need high throughput for robust materials or precise control for sensitive processes, we can help optimize your operations. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















