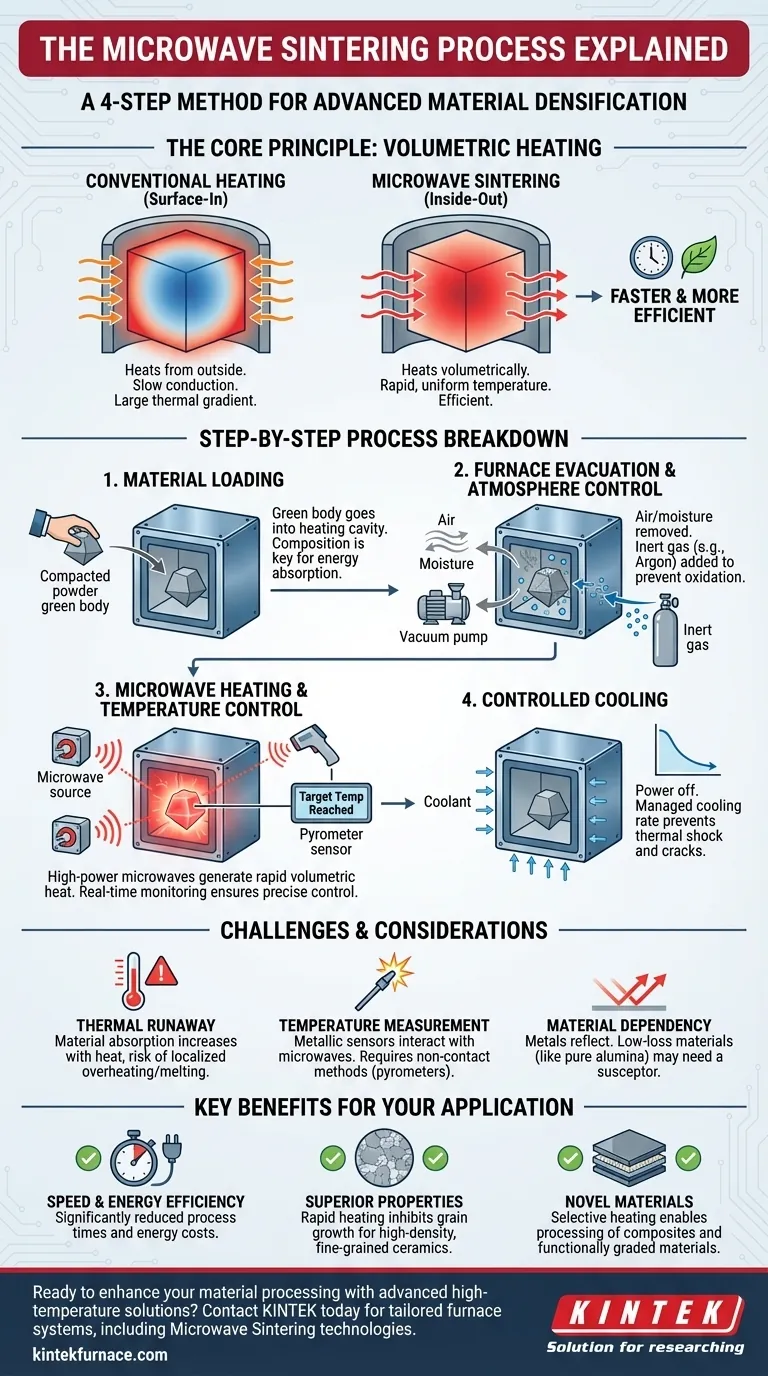
At its core, microwave sintering is a four-step process used to densify materials into a solid, coherent mass. It begins with loading the prepared material into the furnace, followed by evacuating the chamber to create a controlled atmosphere. The material is then rapidly heated to its sintering point using microwave energy, and finally, it undergoes a controlled cooling phase to ensure structural integrity.
Unlike a conventional oven that heats from the outside-in, microwave sintering heats the material directly from the inside-out. This fundamental difference in energy transfer is the key to its speed, efficiency, and ability to produce materials with superior properties.

The Principle: How Microwaves Heat Materials
To understand the process, you must first understand the unique heating mechanism. Microwave sintering does not rely on external heating elements and slow thermal conduction.
Direct Energy Coupling
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate certain materials. When they interact with polar molecules or ions within the material's structure, they cause them to oscillate and vibrate rapidly, generating heat volumetrically throughout the entire part.
Volumetric vs. Surface Heating
Conventional furnaces heat the surface of a material, which then slowly conducts heat toward the core. This creates a large thermal gradient. Microwave heating is volumetric, meaning the core can heat up as fast as or even faster than the surface, leading to much more uniform temperature distribution.
Faster, More Efficient Sintering
Because the heat is generated instantly and internally, the material reaches its sintering temperature in a fraction of the time required by conventional methods. This drastically reduces processing cycles and overall energy consumption.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Each of the four main stages serves a critical function in achieving the desired final material properties.
Step 1: Material Loading
The process starts with placing the material, typically a compacted powder "green body," into the heating cavity of the furnace. The material's composition and dielectric properties are critical, as they determine how effectively it will absorb microwave energy.
Step 2: Furnace Evacuation and Atmosphere Control
Once sealed, the furnace is evacuated to remove air and moisture. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation. The chamber is then often backfilled with a specific gas (like argon or nitrogen) to create an inert or controlled sintering atmosphere.
Step 3: Microwave Heating and Temperature Control
A microwave source, such as a magnetron, generates high-power microwaves that are guided into the cavity. The energy couples with the material, raising its temperature rapidly. Sophisticated sensors, like optical pyrometers, monitor the temperature in real-time to precisely control the heating rate and hold the material at the target sintering temperature.
Step 4: Controlled Cooling
After sintering is complete, the microwave power is turned off. The material is cooled at a carefully controlled rate. This step is crucial for preventing thermal shock, which can cause cracks and compromise the mechanical integrity of the final part, especially in brittle materials like ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universal solution and requires careful management.
Thermal Runaway
The primary challenge is thermal runaway. For many ceramics, their ability to absorb microwaves increases as they get hotter. If not properly controlled, this can create a feedback loop leading to localized overheating, melting, and damage to the part.
Temperature Measurement Difficulties
Standard metallic thermocouples cannot be used for direct measurement as they interact with the microwave field, creating sparks and inaccurate readings. This necessitates the use of non-contact methods like pyrometers or shielded thermocouples, which adds complexity.
Material Dependency
The process is highly material-dependent. Metals reflect microwaves and do not heat effectively. Materials with very low dielectric loss (like pure alumina at room temperature) are transparent to microwaves and may require a "susceptor"—a secondary material that heats in the microwave field and transfers its heat to the primary material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if microwave sintering aligns with your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency: Microwave sintering is an exceptional choice, often reducing process times from hours to minutes and cutting energy costs significantly.
- If your primary focus is creating fine-grained, high-density ceramics: The rapid heating rate inhibits grain growth, allowing you to achieve higher density and superior mechanical properties compared to conventional methods.
- If you are working with novel composites or functionally graded materials: The selective heating capabilities of microwaves can be a unique advantage, allowing you to process different phases at different rates.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can effectively leverage microwave sintering for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Step | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Material Loading | Place compacted powder green body into furnace cavity | Ensures proper microwave energy absorption |
| 2. Furnace Evacuation | Remove air and moisture, backfill with inert gas | Prevents oxidation and controls atmosphere |
| 3. Microwave Heating | Apply microwaves for rapid, volumetric heating | Reduces process time and energy use |
| 4. Controlled Cooling | Cool material at a managed rate | Prevents thermal shock and cracks |
Ready to enhance your material processing with advanced high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored furnace systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our microwave sintering and other furnace technologies can boost your efficiency and achieve superior results for ceramics, composites, and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance



















